Cannabis Deficiencies: How to Identify, Prevent and Fix Them
Growing cannabis can be a rewarding and enjoyable hobby, but it also comes with its own set of challenges and problems. One of the most common issues that cannabis growers face is the deficiencies of nutrients, which can affect the health, appearance, and yield of your plants. Nutrient deficiencies occur when your plants do not receive enough of the essential elements they need to grow and thrive. Some of the factors that can cause deficiencies of nutrients are poor soil quality, incorrect pH levels, overwatering or underwatering, pests or diseases, and environmental stress.
Fortunately, most deficiencies of nutrients can be identified and fixed with some simple adjustments and interventions. In this blog post, we will cover 13 of the most common deficiencies in cannabis, how to recognize them, and how to correct them. By learning how to spot and treat them, you can ensure that your marijuana plants grow strong and healthy, and produce high-quality buds.
The Importance Of Understanding What Are Cannabis Deficiencies
Cannabis is a fast-growing plant that needs lots of nutrients to grow well. A vital thing to know is that this plant is sensitive to several types of deficiencies. For example, this type causes difficult consequences if not done immediately treatment. Understanding the processes and how to treat them will ensure that your outdoor or indoor growth runs as smoothly as possible.
But what causes the deficiencies in nutrient availability? It can also be the soil pH level, temperature, and lighting. Besides preventing the plant from reaching its full potential.
To identify the deficiency and correct it, growers must first learn where to diagnose when seeing signs of inadequacy. By identifying a deficiency, you can treat your plants accordingly. The most common ones are iron, magnesium, and nitrogen deficiencies.
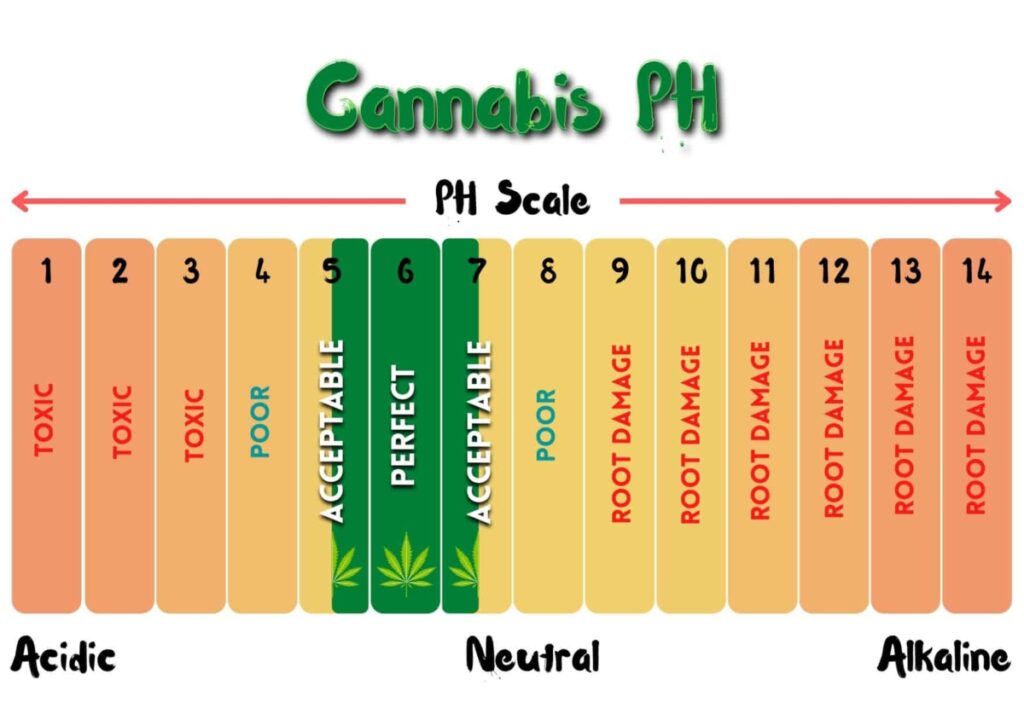
Understanding The Nutrients And pH Levels Of Cannabis
Providing a perfectly offset nutrient for your plants is not as straightforward as it sounds. Even if you have given all the must-have nourishment, sometimes you can find that nutrient lockout is at the root level.
For nutrient absorption to happen at the root level, marijuana plants need to be in the right pH range. The absorption of the nutrients is too acidic or alkaline makes it more difficult.
Another good idea and information are to know the pH of your water. The pH will vary from place to place because different areas have different levels of rain or runoff, and they may use different chemicals in treating the water. To be sure that you are using the right amount of product, test your local tap water first.
Maintaining an acidic ph in the soil of 6.0-7.0 (hydroponics of 5.5-6.5) is vital for the plant to absorb nutrients throughout its life cycle. An acidic environment also reduces your risk of root rot and other soil-related issues by lowering soil bacteria levels while increasing the availability of key nutrients.
An Overview Of Cannabis Plant Deficiencies, Macronutrients, and Micronutrients
It is very important to have complete knowledge of cannabis nutrient deficiencies, macronutrients, and micronutrients. Especially if you are planning to grow healthy cannabis plants in your garden for medicinal purposes.
Macronutrients:
Marijuana plants need many nutrients to grow healthy. Macronutrients are minerals must-haves in large quantities. Potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen are the foremost important ones. Rather than fats, carbs, and protein forming the cornerstone of our diet, cannabis needs these important minerals in large quantities to confirm growth.
Micronutrients:
Micronutrients are vital minerals and elements essential for plants’ healthy, and they play just as vital a role in plant growth. They include iron, zinc, sulfur, boron, and others. much like minerals and vitamins in the human diet, we don’t need large quantities of micronutrients to be healthy, but without them, we become ill quickly.
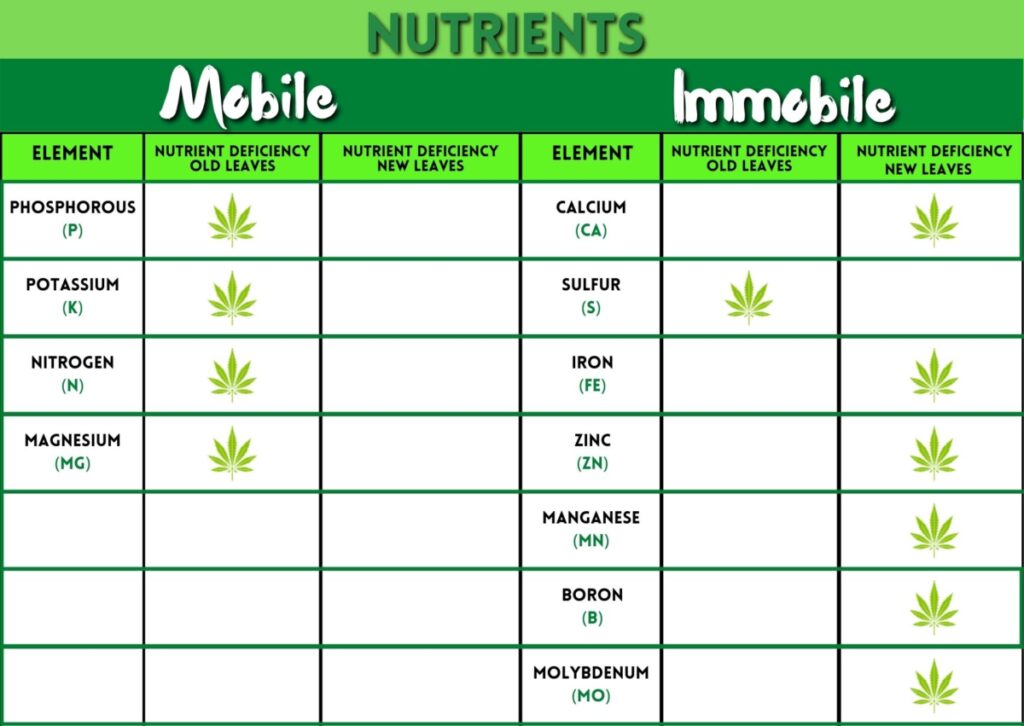
How To Prevent Cannabis Deficiencies: The Role Of Mobile And Immobile Nutrients
Over the past decade, an increasing number of studies focusing on the effects of cannabis deficiencies. Although cannabis is a complex plant with many potential elements to be studied, they relate many deficiencies to mobile and immobile nutrients.
Most commercial fertilizers are based on a single macroelement (N, P, K) or a single microelement (Fe, Mn, Zn). These elements are only available in the soil solution if the corresponding “mobile” nutrient is present. The mobile nutrients are easily leached from the soil and may be unavailable to plants for extended periods. The immobile nutrients are tied up in the soil colloids and are not available for plant uptake unless they are first released.
[plant nutrient deficiency chart]
Mobile Nutrients:
Dissolving mobile nutrients in water is necessary that can move around the plant’s structure. This includes nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium. Nutrient deficiencies in any of these can affect other aspects of growth within a cannabis plant, including yield size and flowering time. They absorb immobile nutrients into the leaves and buds, but they don’t move throughout the plant.
Immobile Nutrients:
A plant’s ability to acquire immobile nutrients varies according to its stage of growth. During germination and early seedling development, immobile nutrients such as boron, molybdenum, zinc, manganese, iron, sulfur, and calcium play a critical role in the formation of the roots, shoot apical meristem, and root hairs. Later during plant growth when water-soluble nutrients become more readily available, immobile nutrients become less important for overall plant health.
If your plant shows signs of deficiency of any nutrient, it will first appear in the newer growth phase. The plant won’t have enough nutrients to move around its system, so the new leaves suffer.
How To Recognize "Nutrient Burn" vs "Nutrient Deficiencies" in Your Cannabis Cultivation
This is a hot topic in the cannabis community. But what does it really mean, and how can you tell the difference?
When growing marijuana, growers want to keep their plants in the “green zone,” which is characterized by vibrant, healthy plants with minimal pest and disease problems. The “yellow zone” is characterized by stressed plants that are in need of some type of attention. Although growth in this area isn’t necessarily unhealthy, it could be if left untreated.
So while there are always exceptions, nutrient-burn is typically characterized by symptoms that just don’t look right. You may have heard of a “stretchy” plant or one that grows too tall too fast, a sign of light-related stress and lack of nutrients. Typically, however, nutrient-burn causes leaf tips to turn brown or purple and then dry up completely. This condition is called “bract necrosis.”
Step By Step Guide To Identify, Treat and Prevent Marijuana Plants Deficiencies

Marijuana plants, like all living organisms, need the right nutrients to survive and thrive. Some nutrients are ubiquitous, but others are not so common. Acquiring the correct cannabis nutrients is a lot easier when you have the right tools at hand.
Troubleshooting deficiencies of nutrients in cannabis require a step-by-step approach. The first thing you’ll want to do is make sure that you’re dealing with nutrient deficiencies and not something else. There are lots of reasons why plants would become sick or fail to thrive, but nutrient deficiency is one of the most common causes.
The following guide will walk you through the process of identifying and treating nutrient deficiencies in cannabis, using simple methods and inexpensive tools found around your home.
1. (N) Nitrogen Deficiency in Cannabis
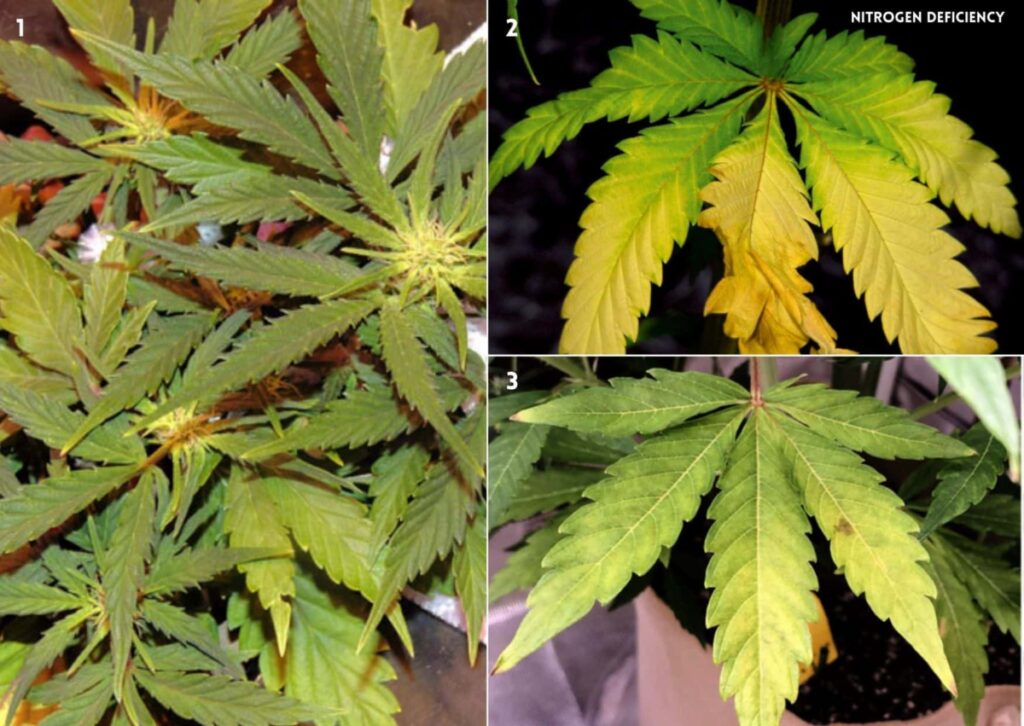

Nitrogen deficiency is a common problem for plants during the vegetative stage when cannabis needs a lot of nitrogen to grow new leaves and stems. Nitrogen is required for photosynthesis and chlorophyll production, which enables a plant to produce sugars. Besides sugar production, nitrogen also plays an important role in the formation of amino acids. Your plant’s roots use amino acids to help synthesize proteins.
Signs of Nitrogen (N) Deficiency
Some signs of N deficiency in cannabis are:
- Yellowing of the lower leaves, starting from the tips and edges and moving inward
- Drooping or wilting of the affected leaves
- Reduced growth rate and smaller leaves
- Pale green or yellow stems and branches
- Poor bud development and lower potency
If you notice any of these signs, you should act quickly to correct the deficiency to prevent further damage to your plants.
What is Nitrogen Toxicity?
N toxicity is a stress to the plant, especially during flowering. Excess Nitrogen can cause deficiencies in other nutrients, including phosphorous and potassium, which are needed for good yields and quality.
If you notice that your plant’s leaves are a dark green or purple color, this means that the Nitrogen levels in your plant container may be too high. To fix this problem, try decreasing the number of nutrients in your plant container, or flushing some of the excess water from your plant container so there is less fertilizer to absorb.
How to Prevent a Deficiency of Nitrogen
To prevent N deficiency, start with a good organic growing soil mix, and apply an all-purpose fertilizer weekly to supply your plants with a sufficient amount of Nitrogen, then stop giving it just before harvest time. Keep a pH of 6.0 to 6.5 in soil, and 5.5-6.0 in hydro.
You can add Mycorrhizae which are fungi that release enzymes to break down organic materials. They associate with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which convert non-organic materials into nitrogen gas, thus boosting the nitrogen levels of soil.
You can also increase the humidity in your grow room, as well as add a tad bit more water to its soil. Increasing airflow will also help prevent the issue, along with using a fan to blow air around the room.
How to Fix a Deficiency of Nitrogen
Treatment for this deficiency should be aimed at increasing the overall nitrogen levels.
Many standard nutrients have high levels of nitrogen. These are usually quick fixes for plants but can be harmful to them if they contain too much. Fish-based nutrients are often rich in nitrogen-containing amines. You can also try manure, alfalfa, or feather meal.
Check your nutrient’s PH. Take a PH reading using a PH test kit or electronic meter. Improve your compost by increasing nitrogen levels in it (Kitchen scraps are one way to do this). Consider adding a foliar feed spray, like compost tea.
When dealing with this problem during flowering, it is best to have an oscillating fan blowing gently around the room where your plants are located. This will help keep the plants cooler while they grow, which in turn will prevent them from having problems with their buds during flowering.
2. (P) Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis

ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.
Phosphorus is one of the three primary nutrients essential for growing cannabis, and deficiency acts as a common disorder that cannabis growers will encounter. It plays an important role in root growth, chlorophyll production, leaf formation, flowering development, seed production, fruit quality, and maturity time.
Phosphorus is a major component of DNA and RNA, and it has a hand in energy transfer and storage. Excessive phosphorus might be an insufficient source. Too much will make your plants grow slower, despite that, be sturdy. Since phosphorus is so important for general plant development, deficiencies early on can stunt growth.
Signs of Phosphorus (P) Deficiency
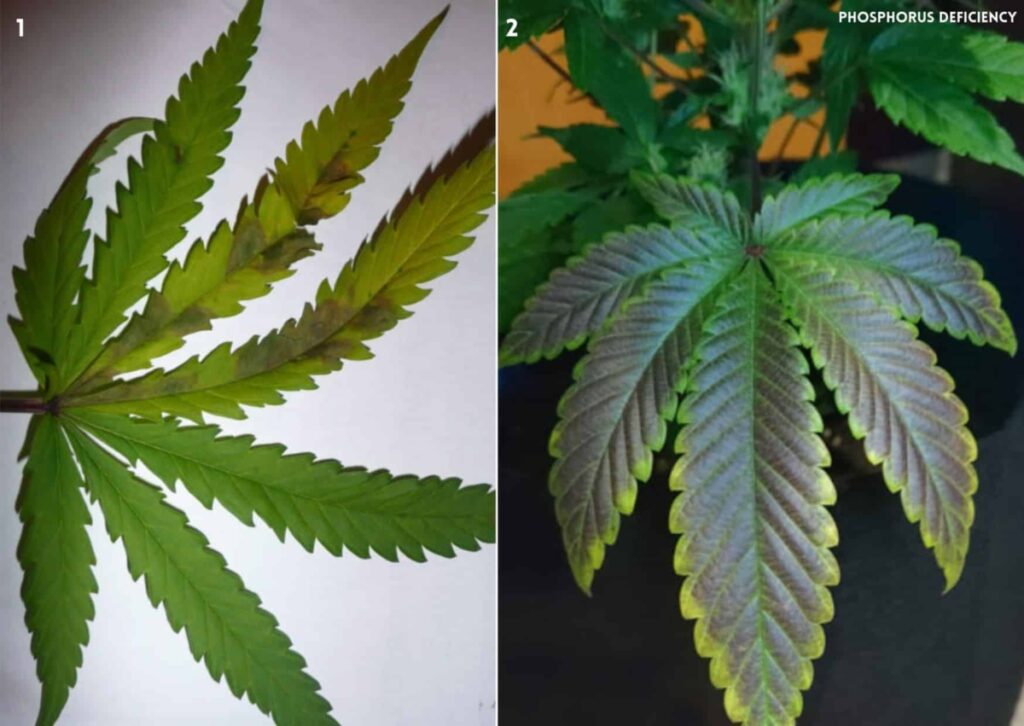
Phosphorus deficiencies can cause various symptoms, such as:
- Dark green or purple leaves with yellow or brown spots
- Reduced growth and bud development
- Drooping or curling of leaves
- Premature leaf fall
- Low resin production and potency
How to prevent Phosphorus (P) Deficiency
Phosphorus (P) deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies in growing cannabis. It is vital to the growth and development of all plants, especially during the germination and flowering stages.
Try to use a potting medium that is rich in phosphorus. Use an Air Pot for better growth because of aeration (and to prevent root rot) and add manure into the soil to improve it. Mycorrhizal fungi can help with overall soil health.
Aerobic microbes can convert insoluble phosphates to soluble forms, which enables your cannabis plants to easily absorb the nutrients they need to grow.
How to fix a Phosphorus (P) Deficiency
To fix a deficiency of phosphorus, you need to do the following steps:
- Flush your plants with clean water that has a pH of 6.0 to 7.0. This will remove any excess salts or minerals that may interfere with phosphorus uptake.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer that contains phosphorus, such as a bloom fertilizer or guano. Follow the instructions on the label and do not overfeed your plants.
- Adjust the pH of your water and nutrient solution to the optimal range of 6.0 to 7.0 ( for soil). Use a pH meter to measure and a pH adjuster to correct the pH if needed.
- Increase the temperature of your grow room by 5 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit. This will warm up the roots and improve their ability to absorb nutrients.
- Monitor your plants for signs of improvement or recovery. You should see new growth that is healthy and green within a week or two.
3. (K) Potassium Deficiency in Cannabis
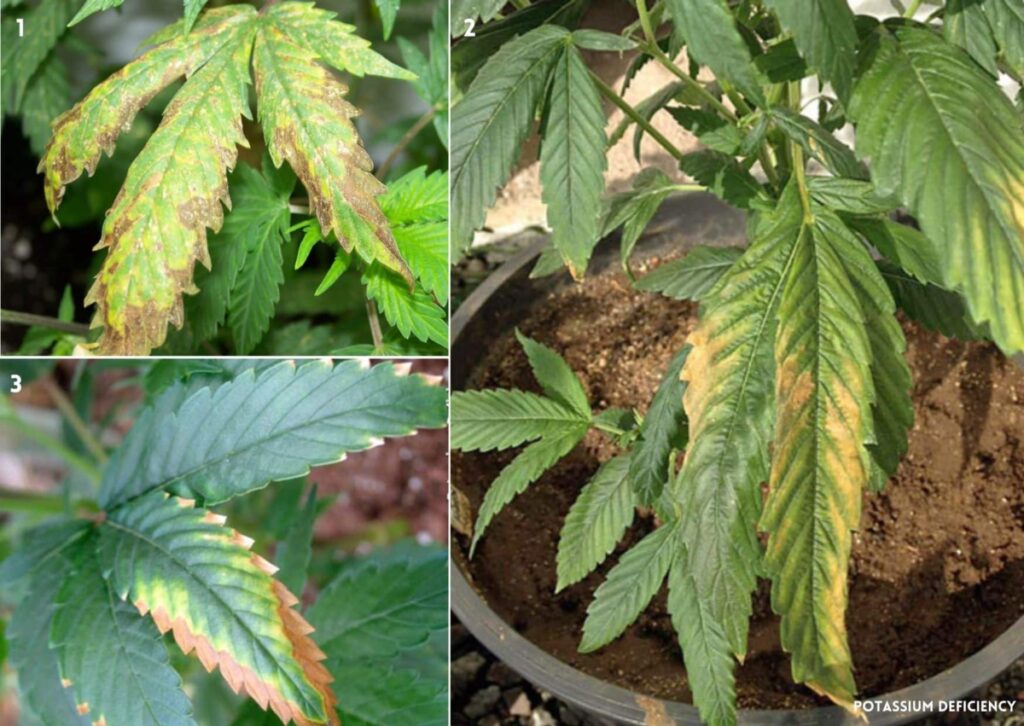

Potassium is an essential element for photosynthesis, which means it’s needed to help plants carry out the process by which they use sunlight to produce their food. It plays a part in regulating the uptake of carbon dioxide by leaf cells, yet it’s often overlooked.
A deficiency of potassium results from the way you water your plants or feed them nutrients. High levels of sodium can also cause it in the soil, as well as dry soil and drought conditions.
This nutrient plays a key role in photosynthesis, therefore all levels of growth, and especially root growth.
Signs of Potassium (K) Deficiency
Some signs of a deficiency of potassium in cannabis are :
- Yellowing of the leaf margins and tips, starting from the lower and older leaves and moving up to the newer ones.
- Browning or burning of the leaf edges and tips, sometimes accompanied by curling or wilting.
- Spots of dead tissue on the leaves, give them a scorched or rusty appearance.
- Reddish or purple stems, especially near the nodes.
- Smaller and weaker buds with less resin production.
How to prevent Potassium (K) Deficiency
To prevent a Deficiency of potassium, you should check the pH of your soil or medium, and make sure it is within the optimal range for potassium uptake. For soil, this is between 6.0 and 7.0, and for hydro or coco, this is between 5.5 and 6.5. You should also use a balanced fertilizer that contains enough potassium for your plant’s needs, and avoid overwatering or overfeeding your plants, as this can cause nutrient lockout or salt buildup. If you notice signs of a deficiency of potassium, you should flush your medium with pH-balanced water, and then apply a potassium-rich supplement or foliar spray to your plants.
How to Treat a Potassium (K) Deficiency
To treat nutrient deficiency of potassium, you need to check the pH of your water and soil or growing medium. The optimal pH range for cannabis is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics. If the pH is too high or too low, it can prevent the plant from absorbing potassium and other nutrients. You can adjust the pH using commercial products or natural remedies.
You also need to provide a balanced fertilizer that contains enough potassium for your plants’ needs. You can use organic sources of potassium such as wood ash, banana peels, kelp meal, or molasses, or synthetic ones such as potassium sulfate, potassium nitrate, or monopotassium phosphate. Follow the instructions on the label or consult an expert for the correct dosage and frequency.
If you have a severe deficiency of potassium, you may need to apply a foliar spray of diluted potassium solution directly to the leaves. This can provide a quick boost of potassium to the plant, but it is not a long-term solution. You still need to address the root cause of the deficiency and ensure proper feeding and watering practices.
4. (Mg) Magnesium Deficiency in Cannabis
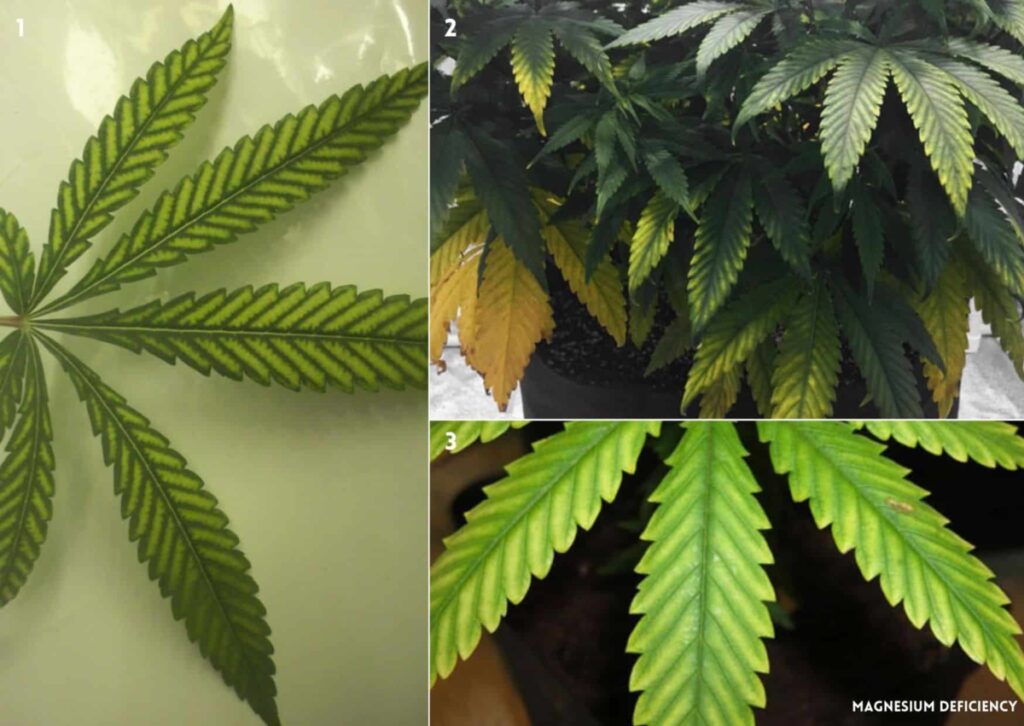

Magnesium deficiency is a common problem that affects the health and yield of plants. Magnesium is a mobile nutrient that is essential for photosynthesis, as it is the central atom in every molecule of chlorophyll.
Identifying Magnesium (Mg) Deficiency
A deficiency of magnesium can cause various problems, such as yellow leaves, curling of the edges, and reduced growth. To identify a deficiency of this element, you can look for these signs:
- The yellowing starts from the edges and moves inward, affecting the older leaves first.
- The veins of the leaves remain green, creating a contrast with the yellow tissue.
- The leaves may develop brown spots or necrosis in severe cases.
- The affected leaves may fall off prematurely.
How to Prevent Nutrient Deficiency of Magnesium
To prevent a deficiency of magnesium, you need to ensure that your plants have access to this nutrient through the soil or water. You can check the pH of your growing medium, as too low or too high a pH can block magnesium uptake. You can also avoid overwatering or low temperatures that can reduce magnesium absorption.
One of the easiest ways to supplement magnesium for your cannabis plants is to use Epsom salts, which are a natural source of magnesium sulfate. You can dissolve a teaspoon of Epsom salts in a gallon of water and water your plants as usual. You can repeat this process with lower doses until you see improvement in your plants’ health.
How to Treat a Deficiency of Magnesium
To fix A deficiency of magnesium, you need to check and adjust the pH of your soil or hydroponic solution, as magnesium may become unavailable if the pH is too low or too high. The ideal pH range for cannabis is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics. You also need to add a magnesium supplement to your nutrient solution or water. Some common sources of magnesium are garden lime, worm castings, dolomite lime, magnesium sulfate, and Epsom salts. Follow the instructions on the package and apply the supplement gradually until you see improvement in your plant’s condition.
5. Calcium (Ca) Deficiency in Cannabis
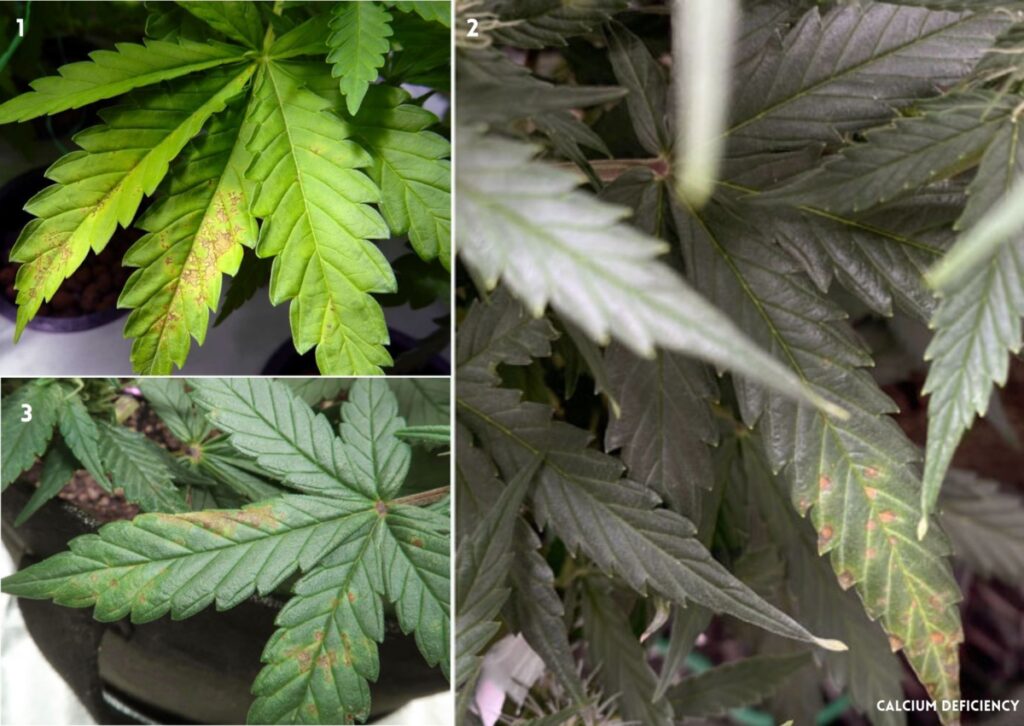

Ca deficiency in marijuana is a common problem that can affect the quality and yield of your crops. Calcium is an immobile nutrient, meaning that it cannot be moved from older leaves to new growth when there is a shortage. Therefore, calcium deficiency symptoms usually appear on the upper and outer parts of the plant, where new leaves and buds are forming.
Signs of Calcium (Ca) Deficiency
Some of the signs of Ca deficiency in cannabis are:
- Brown or bronze spots or splotches on the leaves, especially near the edges and tips
- Yellowing or purple coloration of the leaves around the spots
- Curling or drooping of the affected leaves
- Reduced growth and development of buds
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases
How to prevent Calcium (Ca) Deficiency
To prevent Calcium (Ca) Deficiency, add dolomitic lime to your growth medium. You can increase the amount of calcium in their diet by adding eggshells to the compost. Also, worm castings will provide a good amount of nutrients. Keep an ideal pH range between 6.0 and 7.0 (in soil).
How to Fix Cal-Mag Deficiency
To fix Cal-Mag Deficiency in cannabis, you should:
- Check and adjust the pH of your water and soil or hydroponic medium. The optimal pH range for cannabis is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics.
- Use a balanced fertilizer that contains calcium and other essential nutrients. Avoid over-fertilizing or using too much phosphorus, which can interfere with calcium uptake.
- Add a calcium supplement such as dolomite lime, gypsum, or calcium-magnesium (cal-mag) to your soil or nutrient solution. These products can help increase calcium availability and correct any deficiencies.
- Apply a foliar spray of calcium solution to the affected leaves. This can help boost the calcium levels in the plant and improve its health. Make sure to pH the solution to 5.8 and add a surfactant to help it stick to the leaves.
By following these steps, you should be able to prevent or fix Ca Deficiency in cannabis and ensure healthy and productive plants.
6. (B) Boron Deficiency in Cannabis
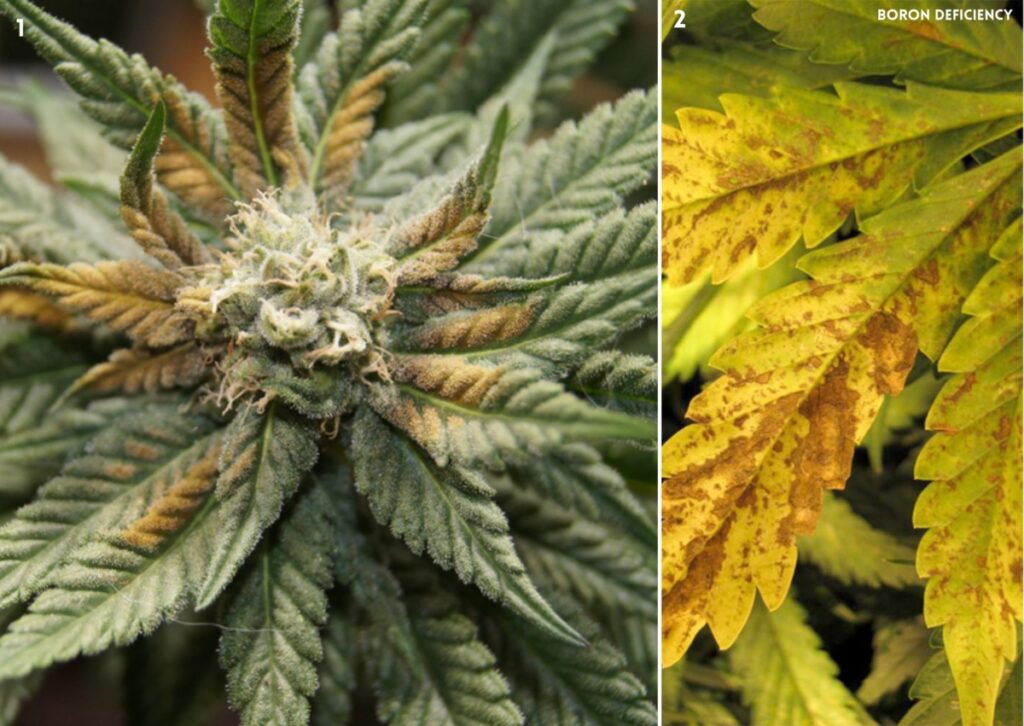

Boron is a mineral that cannabis plants need for healthy growth. It helps with calcium absorption in the roots of plants, so it usually appears together with calcium deficiencies. Besides improving nutrient absorption, boron also helps cannabis plants absorb more water from the soil and transpire more water vapor from their leaves If a plant is deficient in boron, its cell walls become weak and its cells cannot divide properly.
Signs of Boron (B) Deficiency
Signs of Boron deficiencies in cannabis are:
- New leaf growth was affected first, with edges appearing burnt and pale color
- Slow growth and thickened tips of leaves
- New shoots becoming burnt and twisted, with dark brown spots between the veins
- Leaves becoming thicker and brittle, and may wrinkle or curl
- Stems becoming rough or hollow, and roots showing unhealthy or slow growth
How to Prevent Boron Deficiency
We can prevent boron deficiencies by using well-draining, aerated soil, this will help to avoid root rot too. Adding into your compost generous amounts of bananas, apples, or chickpeas will add the boron that your plant needs. Avoid over-fertilizing your plants and keep humidity levels above 25%.
How to Fix Boron Deficiency
To fix boron deficiency in cannabis, you need to:
- Use nutrient packs that contain boron or add a boron supplement to your feeding regimen. Boron is usually present in most cannabis-friendly nutrients, but you may need to increase the dosage if your plants are deficient.
- Adjust the pH of your soil and water to the optimal range for boron absorption. Boron is best absorbed by cannabis roots in soil at a pH of 6.0 to 7.0, and in hydroponics at a pH of 5.5 to 6.5. If the pH is too high or too low, boron may become unavailable to your plants.
- Keep good moisture levels in your growing medium and maintain a moderate humidity level in your growing room. Boron deficiency can be triggered by underwatering or very dry air, as boron needs moisture to move within the plant. Avoid overwatering or soggy soil, as this can cause other nutrient problems.
- Watch your plants for recovery and monitor their symptoms. After applying these fixes, you should see new growth that is healthy and green, without any signs of boron deficiency. If the problem persists or worsens, you may need to flush your system with clean water and start over with fresh nutrients.
7. Copper (Cu) Deficiency in Cannabis
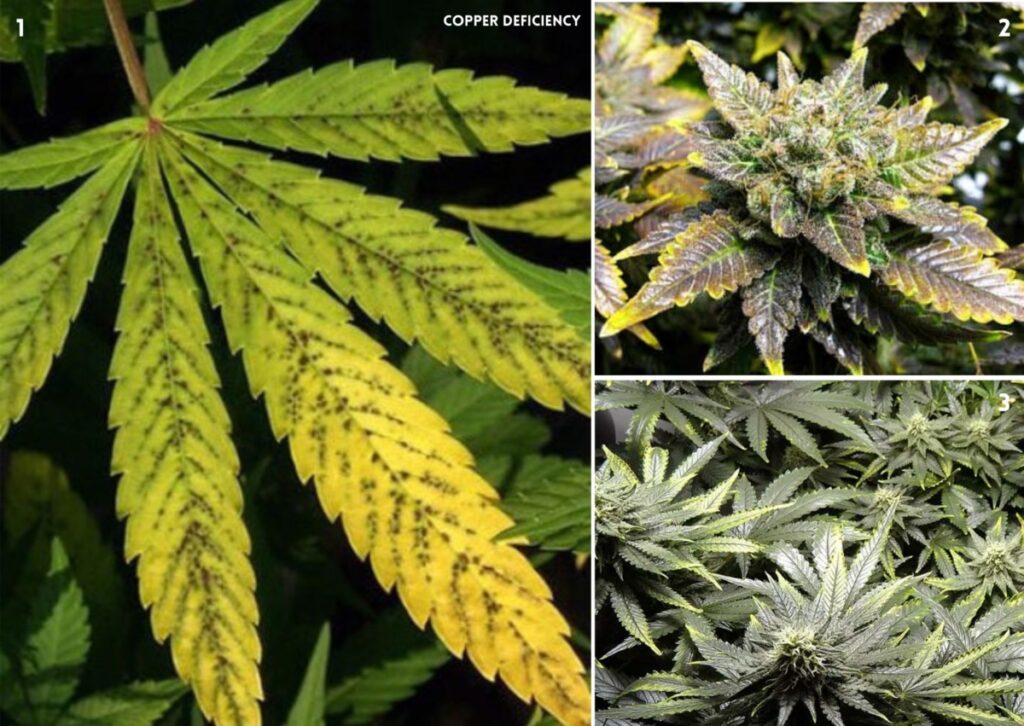

Copper is an essential element in plant growth. It plays a role in manufacturing chlorophyll, which is key to photosynthesis. It helps regulate several enzymes that are important for cell division and growth, assists in the processing of nitrogen, and is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates. Copper also helps form the structure of plant cell walls and acts as an antioxidant.
Signs of a Deficiency of Copper
Signs of Cu deficiency in cannabis include:
- Slow wilting, twisting, and curling of new growth
- Bright yellow or white tips and edges of leaves
- dark green, blue, or purple coloration of leaves
- shiny or metallic appearance of leaves
- Dead spots on leaf tips and margins
- Reduced bud development and ripening
How to prevent a deficiency of Chopper
To prevent a deficiency of chopper in cannabis plants, it is important to use a balanced fertilizer that contains adequate amounts of the chopper and other micronutrients. Alternatively, the chopper can be applied as a foliar spray or a soil amendment. However, care should be taken to avoid over-application of the chopper, as it can cause toxicity and nutrient imbalances in cannabis plants
How to Fix a Deficiency of Copper
To Fix a Cu deficiency, you need to check the pH of your soil or water and adjust it if necessary. The optimal pH range for cannabis is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics. You can also add a copper-containing fertilizer or supplement to your plants, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Be careful not to overdo it, as too much copper can be toxic to your plants.
8. (Fe) Iron Deficiency in Cannabis
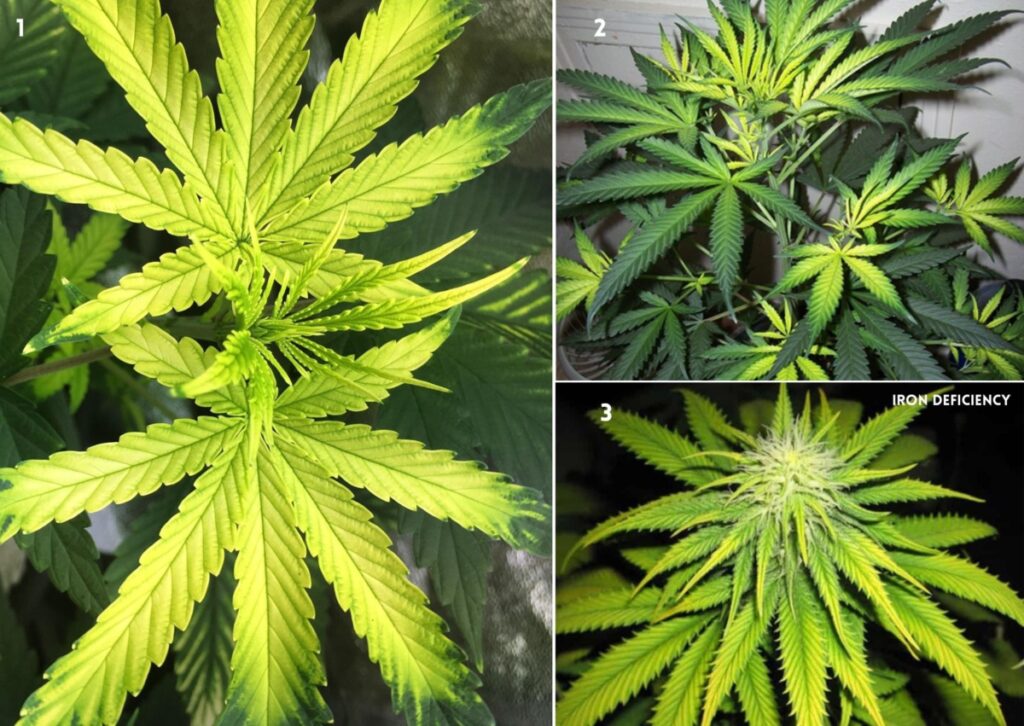

Several factors can lead to Fe deficiency. The first is pH, which is necessary for the uptake of iron. If the pH is too high or too low, this can interfere with absorption and therefore cause a deficiency. Other minerals such as zinc, manganese, and copper can also affect how much iron your body absorbs. Iron is an essential component in the formation of chlorophyll, and it is vital to the formation of enzymes and pigments.
Signs of a Deficiency of Iron
Some signs of a deficiency of Iron in cannabis are:
- Yellowing of the new leaves, while the veins remain green.
- Slow growth and stunted development of the shoots.
- Pale green or white color of the leaves is due to a lack of chlorophyll.
- Necrosis spots and leaf drop in severe cases.
How to Prevent a Deficiency of Iron
To prevent Fe deficiency, it is important to maintain the pH of the growing medium within the optimal range for cannabis, which is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil and between 5.5 and 6.5 for hydroponics. Iron becomes less available to plants when the pH is too high or too low. It is also advisable to use a high-quality nutrient solution that contains chelated iron, which is more easily absorbed by plants.
How to Fix a Cannabis Deficiency of Iron
To fix Fe deficiency, you can apply a foliar spray of iron chelate or iron sulfate to the affected leaves. This will provide a quick boost of iron to the plants and help them recover faster. You can also add some iron chelate or iron sulfate to your nutrient solution or water, but make sure to adjust the pH accordingly. Iron deficiency can be corrected within a few days if treated promptly and properly.
9. (Mn) Manganese Deficiency in Cannabis
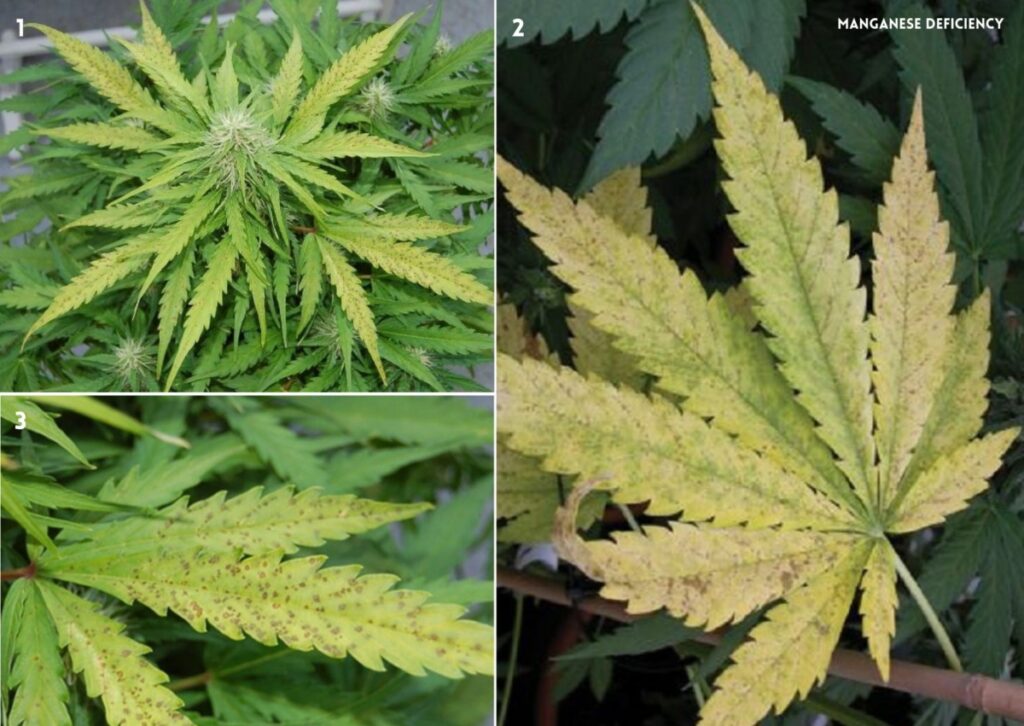

Manganese is an essential element that helps with several important functions of the cell. It allows nitrogen to be used by the plant, stimulates respiration, which is how oxygen gets into the plant, and it aids in photosynthesis. Manganese also helps roots grow properly and protects them from harmful microbes.
Signs of Manganese (Mn) Deficiency
A deficiency of Manganese can cause various symptoms in cannabis plants, such as:
- Yellowing or browning of the leaves, especially between the veins
- Necrotic spots or patches on the leaves
- Reduced growth and yield
- Curling or wilting of the leaves
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases
How to Prevent a Deficiency of Manganese
To prevent a Deficiency of Manganese, it is essential to maintain the optimal pH of the growing medium. For soil, the pH should be between 6.0 and 7.0, and for hydroponics 5.5 and 6.5. A pH above 6.5 can prevent the plants from absorbing manganese. It is also advisable to avoid excessive iron supplementation, as iron can lock out manganese and make it unavailable to the roots.
How to Fix a Cannabis Deficiency of Manganese
To fix a deficiency of Manganese, the first step is to flush the soil with pure water at 6.0 pH to remove any excess nutrients and iron that may be interfering with manganese uptake. Then, apply a light nutrient solution with a balanced ratio of micronutrients, including manganese. Alternatively, you can use a foliar spray with a manganese chelate product to provide a quick boost of manganese to the affected leaves. However, foliar spraying should not be done during flowering or under intense light, as it can cause damage to the buds or burn the leaves.
10. Molybdenum (Mb) Deficiency in Cannabis
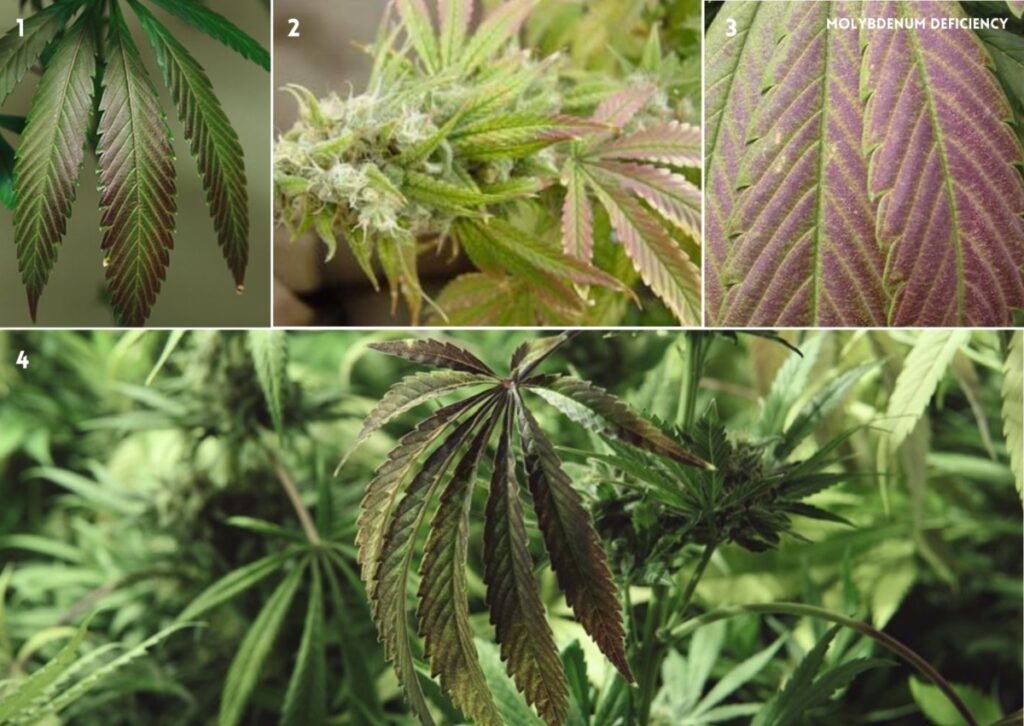

Molybdenum is a trace element that plays a vital role in cannabis. It helps convert nitrate into ammonium, which is essential for protein synthesis and nitrogen metabolism. Mb deficiency is very rare in cannabis, but it can occur when the pH of the growing medium is too low or when there is an excess of sulfur or phosphorus.
Signs of a Deficiency of Molybdenum
Some signs of a deficiency of molybdenum in cannabis are:
- Yellowing of older leaves, starting from the edges and moving inward
- Pink, red, or orange discoloration of leaf margins or tips
- Curling or twisting of leaves
- Reduced growth and flowering
How to Prevent a Deficiency of Molybdenum
To prevent Mb deficiency in cannabis, you should follow these steps:
- Maintain a balanced pH in your growing medium. Molybdenum is more available at higher pH levels, so aim for a range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics.
- Use a fertilizer that contains molybdenum or supplement your plants with a foliar spray of molybdenum solution. You can find molybdenum in some commercial fertilizers or make your own solution by dissolving sodium molybdate or ammonium molybdate in water.
- Avoid over-fertilizing your plants with nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur, as these nutrients can interfere with molybdenum uptake.
- Monitor your plants for signs of Mb deficiency and treat them promptly if they occur. You can reverse the symptoms by adjusting the pH and applying molybdenum foliar spray.
How to Fix a Deficiency of Molybdenum
To fix an Mb deficiency, you need to check and adjust the pH of your growing medium and water. Molybdenum is best absorbed by cannabis roots in a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics. You also need to provide a balanced fertilizer that contains molybdenum and other micronutrients. You can apply it as a soil amendment or a foliar spray. Damaged leaves may not recover, but new growth should show signs of improvement.
11. (Si) Silicon Deficiency in Cannabis
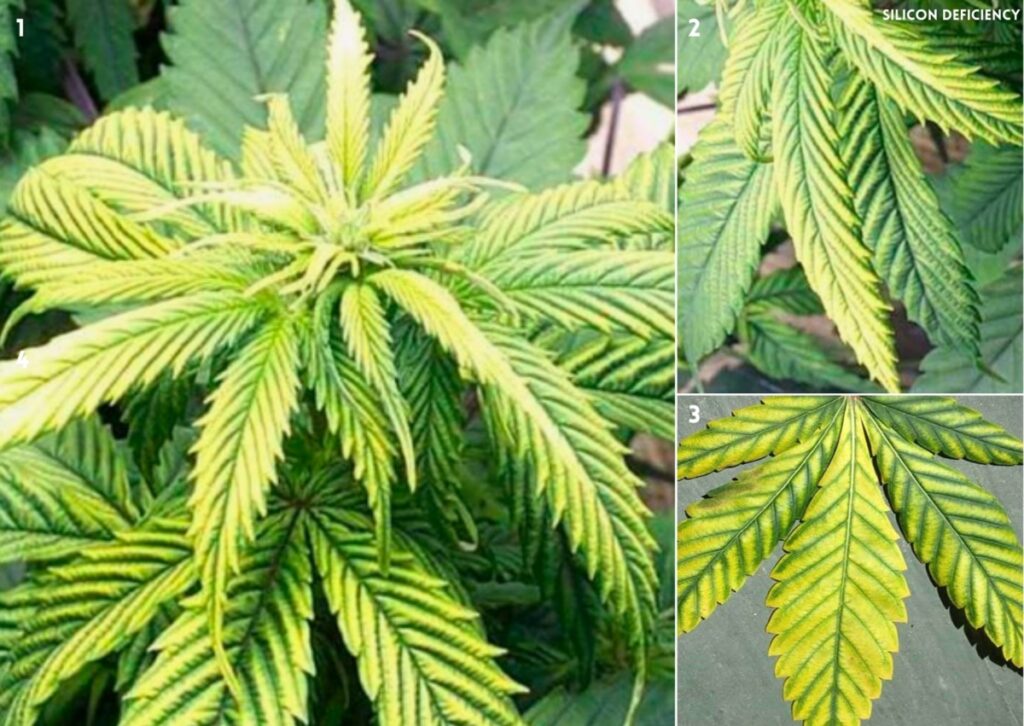

Silicon is an essential nutrient for dynamic plant growth. It helps cell walls to be more sturdy, which allows plants to carry out photosynthesis. If there is not enough silicon available, the plants cannot perform photosynthesis. Thus, reducing flower production. Silicon also makes plants more resistant to fungal and bacterial diseases and insect infestations.
Signs of a Deficiency of Silicon
some signs of silicon deficiency in cannabis are:
- Lightening or yellowing of older leaves at the base of the plant
- Wilting or drooping of leaves due to reduced water uptake
- Stunted growth and reduced yields
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases
How to Prevent a Deficiency of Silicon
To prevent silicon deficiency, you need to ensure that your plants have access to enough silicon in their growing medium and water. Some sources of silicon include diatomaceous earth, silica planting medium, silicate salts, and liquid silicon. You also need to monitor the pH level of your water and soil, as extreme pH values can limit the uptake of silicon by the plants.
How to Fix a Deficiency of Silicon
To fix silicon deficiency, you need to check and adjust the pH of your water and growing medium, as incorrect pH can cause a nutrient lock-out. The ideal pH for cannabis is around 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics. You can also add silicon supplements to your nutrient solution or apply them as foliar sprays. Silicon supplements are usually available as potassium silicate or calcium silicate. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and avoid over-fertilizing your plants.
12. Sulfur (S) Deficiency in Cannabis
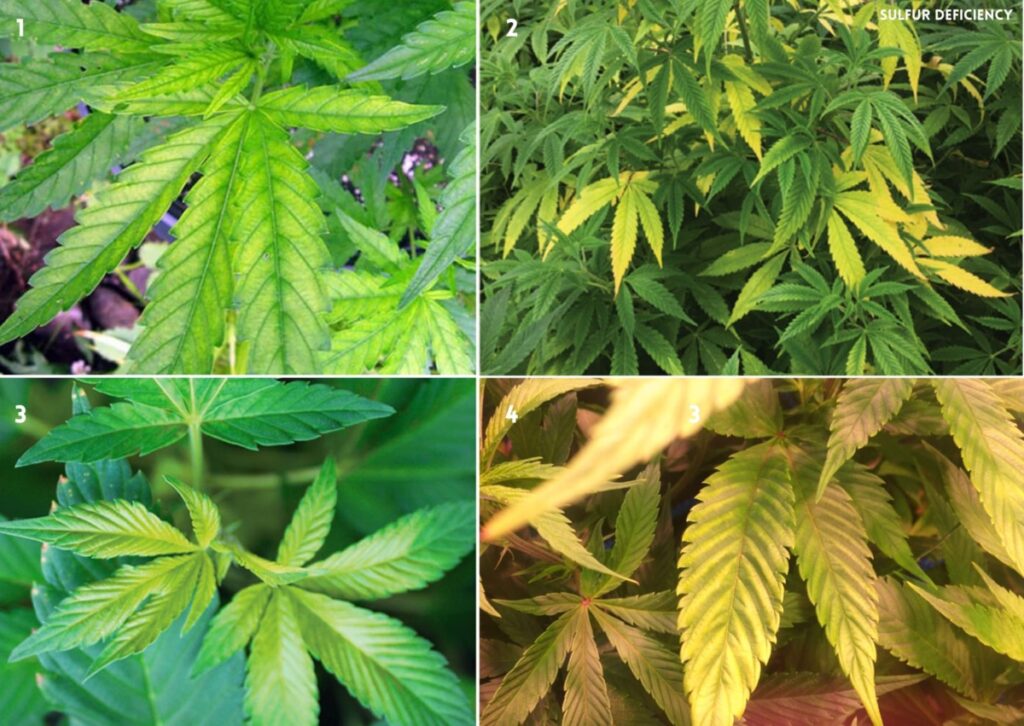

Sulfur (S) deficiency is very rare in cannabis because most fertilizers have adequate amounts of them. It contributes to the formation of vital enzymes and proteins. Hence, the synthesis of oils and terpenes. It also plays an essential role in photosynthesis for plant respiration.
Signs of a Deficiency of Sulfur
Some signs of S deficiency in cannabis are:
- Young leaves turn lime green to yellow, starting from the back of the leaf and moving forward.
- Leaf veins also turn yellow, and leaf tips may appear burnt or hook downward.
- Growth is stunted and stalks become woody and purple.
- Buds do not develop properly and may lose potency.
How to prevent a Deficiency of Sulfur
To prevent an S deficiency, you should:
- Monitor and adjust the pH of your soil or water as necessary. Sulfur is best absorbed in a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics.
- Do not overfeed or overwater your plants, as this can cause nutrient lockout and reduce the availability of sulfur.
- Ensure you use a fertilizer that contains sulfur or sulfates, such as calcium sulfate or potassium sulfate. You can also supplement your plants with Epsom salts, which are a source of magnesium and sulfur. Use one or two teaspoons of Epsom salts per gallon of water and apply it to your plants once or twice a month.
How to treat a Deficiency of Sulfur
To fix Sulfur (S) deficiency, you need to check and adjust the pH of your water and soil or hydroponic medium. The optimal pH range for cannabis is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics. You also need to provide a balanced fertilizer that contains sulfur, such as Epsom salt or gypsum. Sulfur moves slowly through the plant, so it may take some time to see improvement after correcting the deficiency.
13. (Zn) Zinc Deficiency in Cannabis
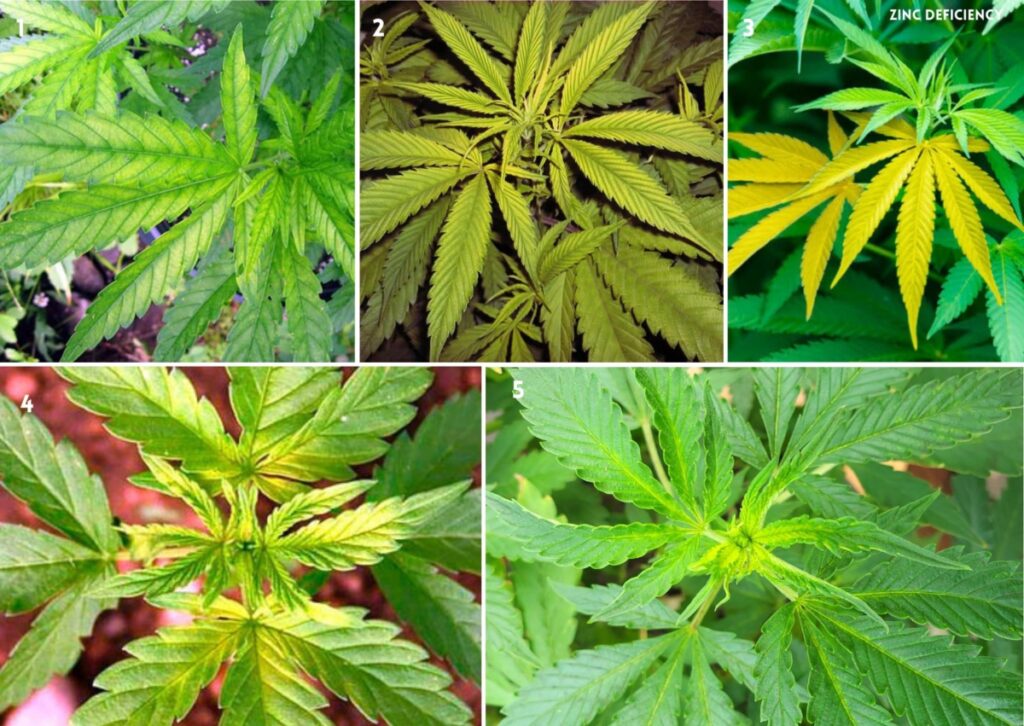

Zinc is a mineral that is necessary for trace amounts. It comprises a mixture of cell membranes, proteins, and growth hormones. Zinc also aids in the production of protein and sugar, the production of chlorophyll, and the growth of healthy stems.
Signs of a Deficiency of Zinc
Some signs of a deficiency of Zinc in cannabis are:
- Yellowing between the veins of the younger leaves
- Discoloration and necrosis of the leaf tips
- Wrinkled, distorted, or banded appearance of the leaves
- Stunted vertical growth and reduced internodal spacing
- Reduced flower development or quality
How to prevent a Deficiency of Zinc
To prevent a deficiency of Zinc, you should:
- Check and adjust the pH of your water and soil or hydroponic medium. Zinc is best absorbed by cannabis roots in a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics.
- Use a complete fertilizer, mineral supplement, or Cal-Mag product that contains zinc and other trace elements.
- Avoid overwatering or overfeeding your plants, as this can cause nutrient lock-out or salt buildup that can interfere with zinc uptake.
- Flush your plants with clean, pH-balanced water if you suspect Zn deficiency due to nutrient imbalance or excess. This will remove any harmful salts and restore the proper nutrient availability.
- Ensure your plants have adequate root space and aeration. Compacted soil or root-bound pots can restrict root growth and increase the risk of a deficiency of Zinc.
How to Treat a Deficiency of Zinc
To fix a deficiency of Zinc, you need to address the root cause, which is usually related to pH or nutrient imbalance.
One of the most common causes of a deficiency of Zinc is a high pH level in the soil or growing medium, which prevents the plant from absorbing zinc and other nutrients. To correct this, you need to flush your plants with water that contains a mix of about half the nutrients your plants need, such as manganese, zinc, and iron. Zinc is absorbed better in an acidic root environment, so to correct a deficiency of zinc, your pH should be more on the acidic side. If you use hydroponics or coco coir, aim for a pH between 5.5 and 6.5, and in the soil a pH between 6.0–7.0.
Another possible cause is nutrient lock-out due to overfeeding or using heavily filtered or reverse osmosis (RO) water that lacks zinc and other minerals. To avoid this, you should use cannabis-friendly nutrients that contain zinc and other micronutrients, and follow the recommended dosage and schedule. You should also avoid overwatering your plants, as this can cause root problems and affect nutrient uptake.
After applying these solutions, you should monitor your plants for recovery. The damaged leaves may not recover completely, but new growth should be healthy and green. Zn deficiency can be prevented by maintaining a proper pH level, using quality nutrients and water, and taking good care of your roots.




















