Cannabis Magnesium Deficiency (Mg): Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Magnesium is an essential nutrient for plants, as it plays a key role in photosynthesis, enzyme production, and chlorophyll formation. Without enough magnesium, cannabis plants will show signs of stress and poor health, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and reduced yields.
In this blog post, we will explain how to identify, prevent, and treat magnesium deficiency in plants of cannabis. We will also cover the most common causes and risk factors for this condition, and the best treatment options available.
Who's Most at Risk?
Marijuana plants grown in coco coir are more prone to magnesium deficiency than those grown in soil or other mediums. This is because coco coir has a high cation exchange capacity, which means that it can hold onto certain nutrient ions (such as calcium and magnesium) and make them unavailable to the plant roots. Coco coir also tends to have a low pH, which further reduces the absorption of magnesium by the plant.
Using coco coir as a growing medium requires careful attention to the pH and nutrient levels of the irrigation water. If the pH is too low (below 5.5), the plant roots will not be able to take up enough magnesium, even if it is present in the water. If the water does not contain enough magnesium (or calcium), the coco coir will deplete it quickly and cause a deficiency.
What Causes a Magnesium Deficiency in Cannabis?
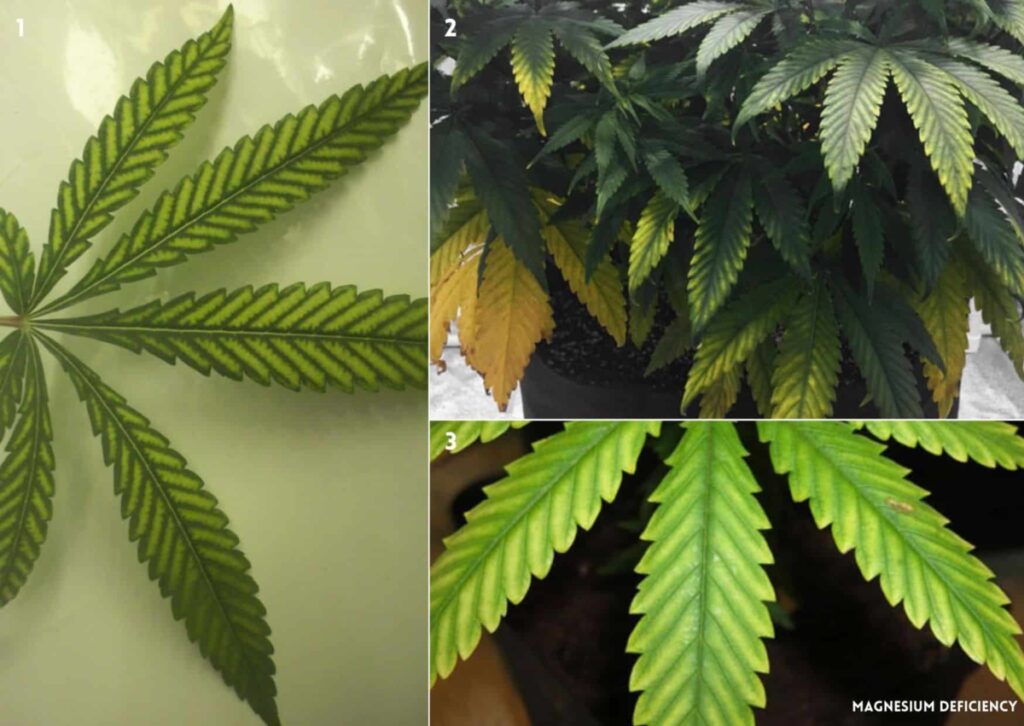

Some of the main causes of a deficiency of magnesium are:
PH Too Low For Cannabis: Magnesium is best absorbed by cannabis roots when the pH of the growing medium is between 6.0 and 7.0. If the pH drops below this range, magnesium becomes less available and the plant cannot take it up efficiently. This can happen in soil, coco coir, or hydroponic systems if the pH is not monitored and adjusted regularly.
Constant Moisture In The Soil: Magnesium is a mobile nutrient, which means that it can move from older leaves to newer leaves when needed. However, if the soil is constantly wet, magnesium can leach out of the soil and be lost. This can happen if you overwater your plants, have poor drainage, or use unfiltered tap water that contains chlorine or other chemicals.
Low Root Temperatures Can Make It Magnesium Deficient: Another factor that can affect the absorption of magnesium in cannabis is the temperature of the root zone. If the roots are exposed to low temperatures (below 18°C or 65°F), they become less active and less able to absorb nutrients. This can happen in outdoor grows during cold nights or in indoor grows with inadequate insulation or ventilation.
Mineral Excess During Flowering: During the flowering phase, marijuana plants need more phosphorus and potassium than nitrogen and magnesium. If you use a fertilizer that has a high ratio of phosphorus and potassium to nitrogen and magnesium, you may cause a nutrient imbalance that blocks the absorption of magnesium. This can happen if you use bloom boosters, bat guano, or other high-PK fertilizers without adjusting the dosage or supplementing with magnesium.
Poor soil quality: Magnesium is naturally present in most soils, but it can be depleted over time by erosion, crop rotation, or intensive cultivation. If you use poor-quality soil that lacks organic matter, minerals, or beneficial microbes, your weed plants may not get enough magnesium from the soil. You can improve your soil quality by adding compost, worm castings, or other organic amendments that contain magnesium and other nutrients.
What Are the First Signs of Magnesium Deficiency in Cannabis?
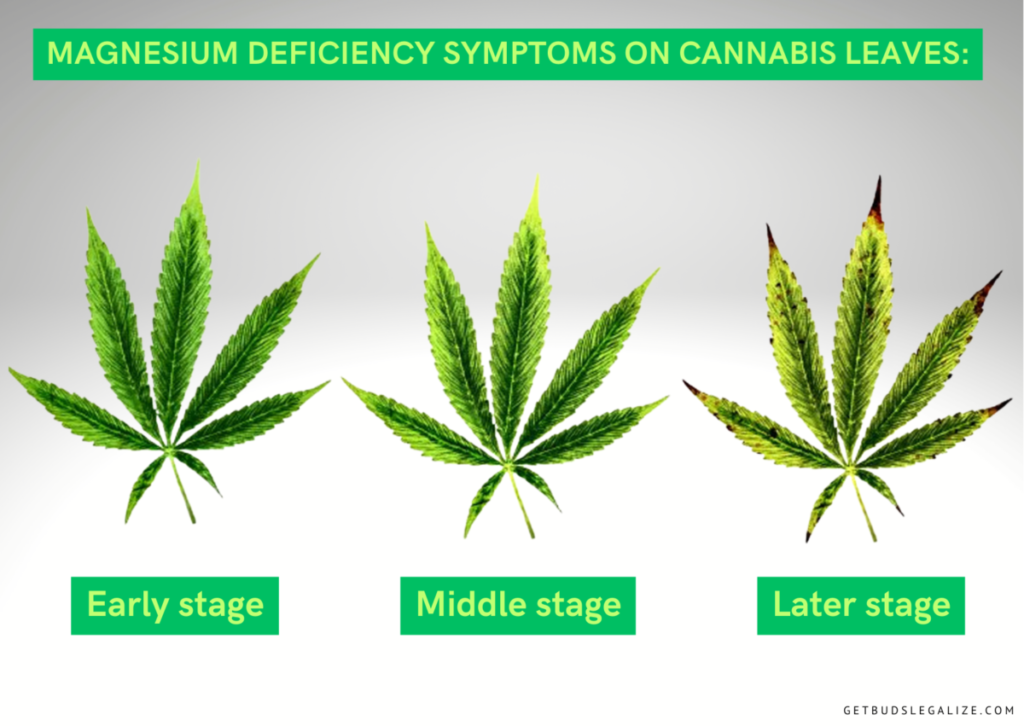
Some of the first symptoms you can spot are:
- Yellowing of the lower leaves, starting from the edges and moving towards the center, while the veins remain green.
- Brown spots or necrosis on the affected leaves.
- Curling or wilting of the leaves.
- Purple or red stems and petioles coloration.
- Pale green or yellow new growth.
Magnesium deficiency can be confused with other nutrient deficiencies, such as iron or nitrogen. However, cannabis iron deficiency usually affects the newer leaves first and causes interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between the veins). Nitrogen deficiency in cannabis affects the lower leaves first but also causes uniform yellowing of the entire leaf.
How to Fix Magnesium Deficiency in Plants?
To fix cannabis magnesium deficiency, you need to address the underlying cause and supplement your plants with a magnesium source. Some possible solutions are:
1. Adjust the pH: Check and correct the pH of your soil and water to ensure it is within the optimal range for your plants.
2. Flush the soil: If you have over-fertilized your plants or suspect a nutrient lockout, flush the soil with plain water at the correct pH for 15-20 minutes to remove any excess salts or nutrients that may be interfering with magnesium uptake. Then, resume your normal watering schedule with water containing nutrients and cal-mag supplements at the correct pH.
3. Add magnesium supplements: You can use products such as Epsom salt, dolomite lime, or Cal-Mag Supplement to provide extra magnesium to your plants. Follow the instructions on the label and apply them as a foliar spray or a soil drench.
4. Improve the soil quality: You can add organic amendments such as compost, worm castings, or bat guano to enrich your soil with magnesium and other nutrients.
5. Water properly: Make sure you water your plants deeply and evenly, and allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
How Long Does It Take for Cannabis to Recover from Magnesium Deficiency?
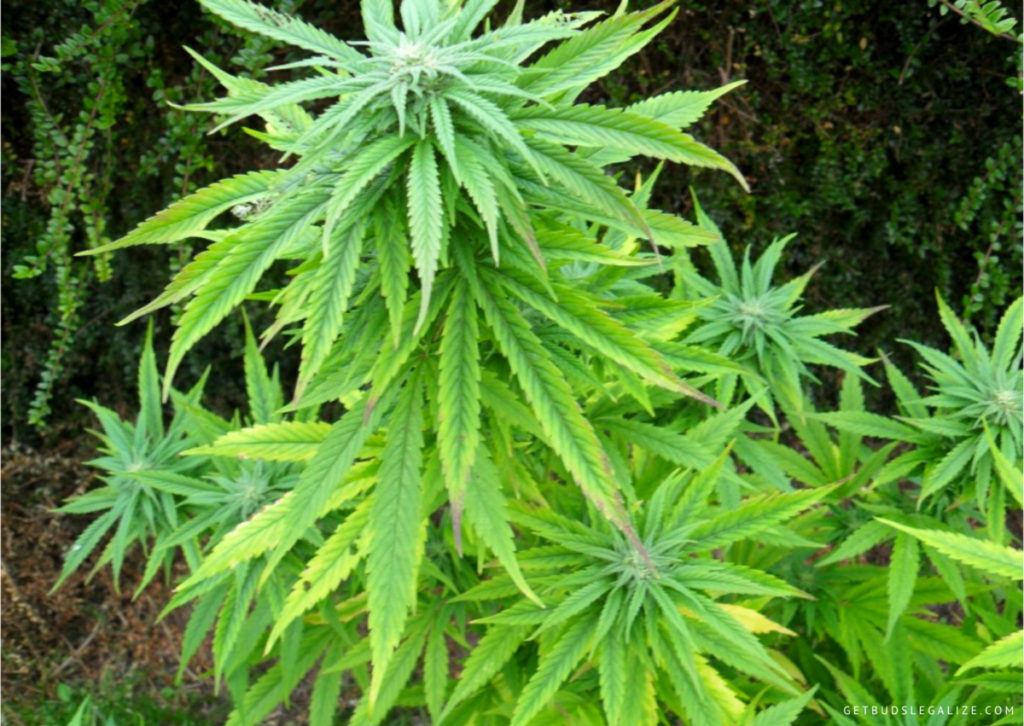
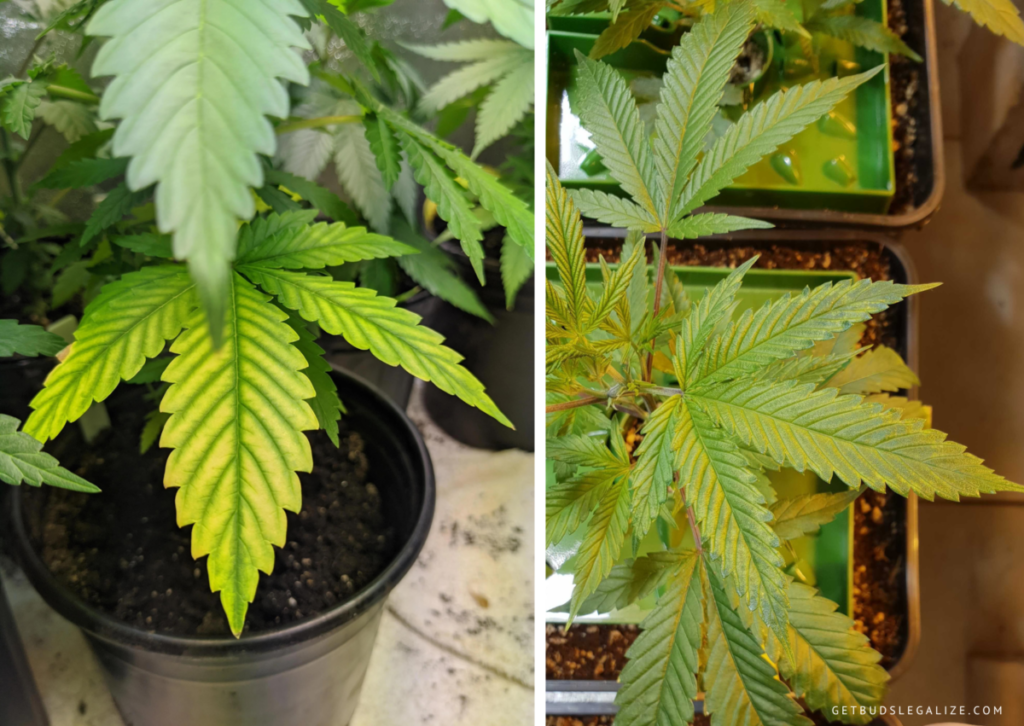


The recovery time depends on several factors, such as the severity of the deficiency, the stage of growth, and the type of growing medium.
Generally, plants of cannabis can recover from mild to moderate magnesium deficiency within a week or two after correcting the problem. However, severe magnesium deficiency may take longer to recover, and some of the damaged leaves may not recover at all.
How to Prevent a Magnesium Deficiency
To prevent a cannabis magnesium deficiency, you should:
1. Check and adjust the pH of your water and soil or growing medium: Magnesium is best absorbed by cannabis plants in a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics. If the pH is too high or too low, magnesium may become unavailable to the plants, even if it is present in the medium.
2. Avoid over-fertilizing your plants: Excessive amounts of nitrogen, potassium, or calcium can interfere with magnesium uptake and cause a deficiency. Use a balanced fertilizer that contains all the macro and micronutrients that cannabis plants need, and follow the recommended dosage and frequency.
3. Ensure your plants have good drainage and aeration in their root zone: Poor drainage can lead to waterlogged conditions that prevent oxygen from reaching the roots, which can impair nutrient absorption and cause root rot. Aeration helps to improve oxygen levels and prevent compaction of the medium, which can also affect nutrient availability. You can improve drainage and aeration by using perlite, vermiculite, or coco coir in your soil mix, or by using air pots or fabric pots for your containers.
4. Add a magnesium supplement to your nutrient solution or soil: If you suspect that your plants are suffering from a magnesium deficiency, you can give them a boost by adding a magnesium-rich supplement to your watering or feeding regimen. You can use Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate), which is cheap and widely available, or a commercial product that contains magnesium chelate, which is more easily absorbed by plants. Follow the instructions on the label and apply the supplement until you see signs of improvement in your plants.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.
Tips for Avoiding Magnesium Deficiencies in Cannabis
There are some simple ways to prevent and treat magnesium deficiency in cannabis.
- Use a balanced cannabis nutrient that contains adequate amounts of magnesium and other micronutrients. Avoid over-fertilizing or using too much nitrogen, as this can interfere with magnesium uptake.
- Adjust the pH levels of your soil or water to ensure optimal nutrient availability. Magnesium is best absorbed by cannabis plants when the pH is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil and 5.5 and 6.5 for hydroponics.
- Add organic amendments such as dolomite lime, Epsom salt, or compost to your soil to boost magnesium levels and improve soil structure. These amendments can also help buffer pH fluctuations and prevent a nutrient lockout.
Prevent a deficiency of magnesium from recurring by maintaining a regular feeding schedule, testing your soil or water quality, and avoiding environmental stressors such as extreme temperatures, pests, or diseases.
What are the Differences Between Magnesium & Calcium Deficiencies?
Magnesium and calcium are both important nutrients for cannabis plants, but they have different roles and symptoms of deficiency. Magnesium is a mobile nutrient that helps with chlorophyll production and photosynthesis. Calcium is an immobile nutrient that helps with cell integrity and nutrient transport. Here are some differences between magnesium and calcium deficiencies in cannabis:
- Magnesium deficiency usually affects the older and lower leaves first, while calcium deficiency affects the newer and upper leaves first.
- Magnesium deficiency causes yellowing between the veins and browning of the leaf tips, while a deficiency of calcium causes brown or bronze spots or splotches on the leaves.
- Magnesium deficiency can be caused by low pH, soft or filtered water, or excess potassium or calcium, while a deficiency of calcium can be caused by low pH, high humidity, or excess nitrogen or phosphorus.
- Magnesium deficiency can be corrected by adding Epsom salts or a magnesium supplement to the water or soil, while a deficiency of calcium can be corrected by adding lime, gypsum, or a calcium supplement to the water or soil.
To prevent magnesium and calcium deficiencies in cannabis, it is important to maintain a balanced pH level, use quality water and nutrients, and avoid overwatering or underwatering your plants. You should also monitor your plants regularly for any signs of nutrient problems and act quickly if you notice any symptoms.
Is a Magnesium Deficiency Really That Bad?
A cannabis magnesium deficiency can be easily identified and fixed if detected early. However, if left untreated, it can severely affect the health and performance of cannabis plants. Therefore, it is essential to provide adequate magnesium to cannabis plants throughout their life cycle, especially during the flowering stage when they need it the most.
Cannabis Magnesium Deficiency - FAQs
To fix a magnesium deficiency, you need to check the pH of your soil or water and adjust it if necessary. You also need to supplement your plants with a magnesium-rich fertilizer, such as Epsom salt or Cal-Mag. Magnesium deficiency can be prevented by using a balanced nutrient solution and avoiding overwatering or overfeeding your plants
Magnesium is a mobile nutrient that is essential for photosynthesis and phosphorus metabolism. Some of the symptoms of magnesium deficiency are:
- Yellowing between the veins of the older leaves, while the veins remain green.
- The purple coloration on the stems and petioles.
- Curling and dying of the most affected leaves.
- Reduced growth.
There are several possible reasons why your cannabis roots are not absorbing magnesium. Some of them are:
- Low pH: Magnesium is best absorbed by cannabis roots when the pH is between 6.0 and 7.0. If the pH is too low, magnesium becomes less available to the plant.
- High calcium or potassium levels: Magnesium competes with calcium and potassium for uptake by the roots. If there is too much calcium or potassium in the soil or water, magnesium may be locked out.
- Overwatering: Overwatering can cause root rot, which damages the root system and reduces its ability to absorb nutrients, including magnesium.
Magnesium is an essential nutrient for cannabis. It plays a key role in photosynthesis, chlorophyll production, and enzyme activation. Without enough magnesium, cannabis plants may show signs of deficiency, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and reduced yields. Magnesium also helps cannabis plants cope with stress and improve their flavor and aroma.
The Cal-mag deficiency symptoms are:
- Spots on new or upper leaves, usually yellow or brown in color
- Yellowing between the veins of the leaves
- Deformed or curled leaves
- Stunted growth and slow flower development
- Weak stems and hollow stems
To fix a deficiency of it, it is important to check the pH level of the soil or water, as low pH can prevent the absorption of these minerals. Adding a cal-mag supplement or fertilizer can also help restore the balance and prevent further damage.
To fix a deficiency of Cal-Mag, you need to identify the cause and correct it as soon as possible. Some possible causes are:
- Low pH: A pH level that is too low can prevent plants from absorbing calcium and magnesium from the water or the soil. You can use a pH meter or test strips to check the pH of your growing medium and adjust it accordingly. The optimal pH range for most plants is between 5.5 and 6.5.
- High EC: EC stands for electrical conductivity, which measures the amount of dissolved salts in the water or the soil. A high EC can indicate an excess of nutrients, which can create a nutrient imbalance and lock out calcium and magnesium. You can use an EC meter to check the EC of your growing medium and flush it with plain water if it is too high. The optimal EC range for most plants is between 1.0 and 2.0 mS/cm.
- Insufficient watering: Underwatering can cause plants to wilt and stress, which can affect their nutrient uptake and metabolism. You should water your plants regularly and deeply, making sure that the water drains well and does not accumulate in the bottom of the pots or trays. You can use a moisture meter or your finger to check the moisture level of your growing medium and water accordingly.
- Inadequate lighting: Low light levels can reduce photosynthesis and transpiration, which are processes that help plants move nutrients from the roots to the leaves. You should provide your plants with enough light for their specific needs, using artificial lights if necessary. You can use a light meter or a timer to measure the light intensity and duration of your plants and adjust accordingly.
- Low temperature: Cold temperatures can slow down plant growth and metabolism, which can affect their nutrient uptake and utilization. You should keep your plants in a warm and stable environment, avoiding sudden changes or fluctuations in temperature. You can use a thermometer or a thermostat to monitor the temperature of your growing area and provide heating or cooling if necessary.
To supplement your plants with Cal-Mag, you can use a commercial Cal-Mag product or make your own by mixing Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) and calcium nitrate in water. You should follow the instructions on the label or consult an expert for the correct dosage and frequency of application. You should also avoid using products that contain phosphorus, iron, or sulfur, as they can interfere with calcium and magnesium absorption.
















