Calcium Deficiency in Cannabis Plants: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Calcium is an essential nutrient for marijuana plants. It plays a vital role in cell wall structure, cell division, root and flower growth, and enzyme activity. Calcium also helps the plant cope with heat stress and resist diseases.
However, too much or too little calcium can cause problems for your marijuana plants. In this blog post, we will discuss the symptoms of calcium deficiency and toxicity, what causes them, and how to prevent and fix them.
What Are the Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency in Cannabis Plants?
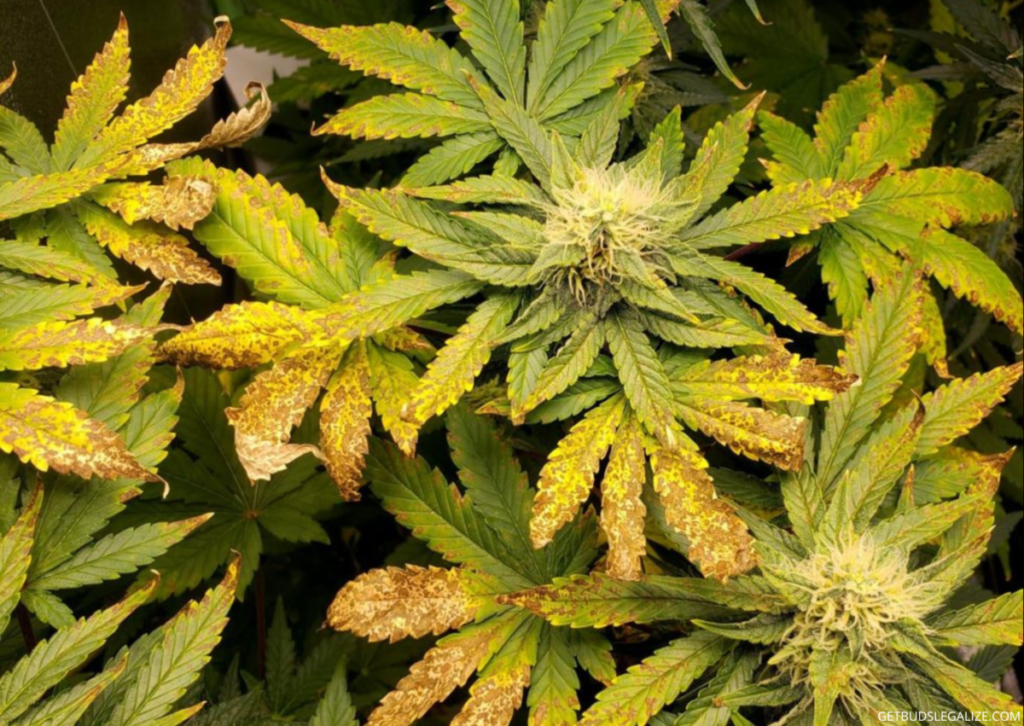
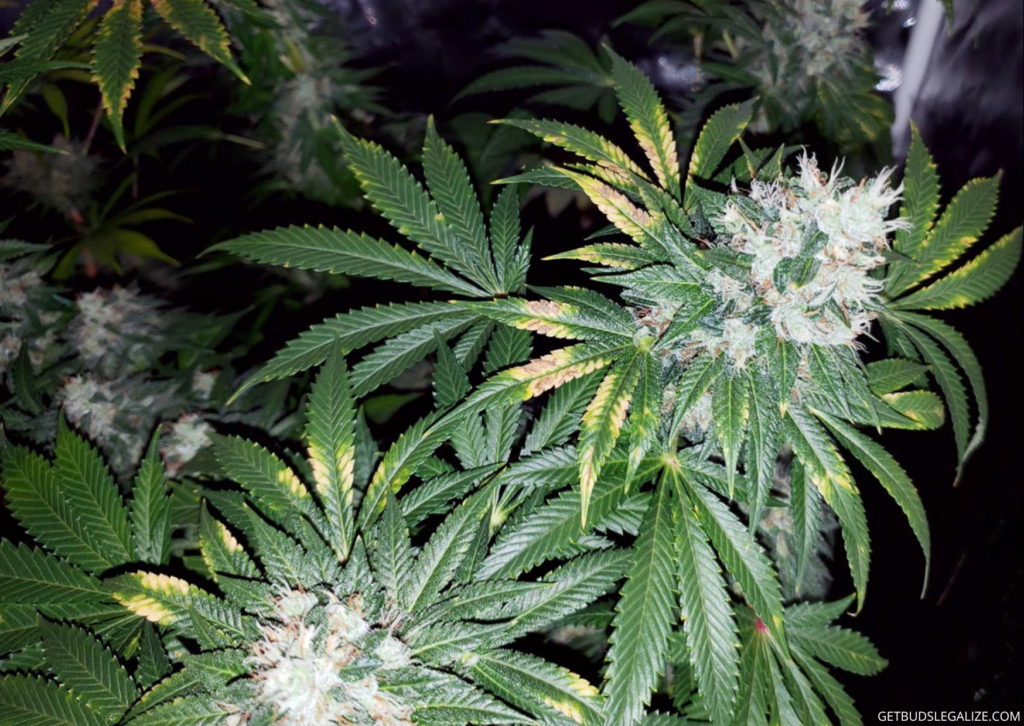


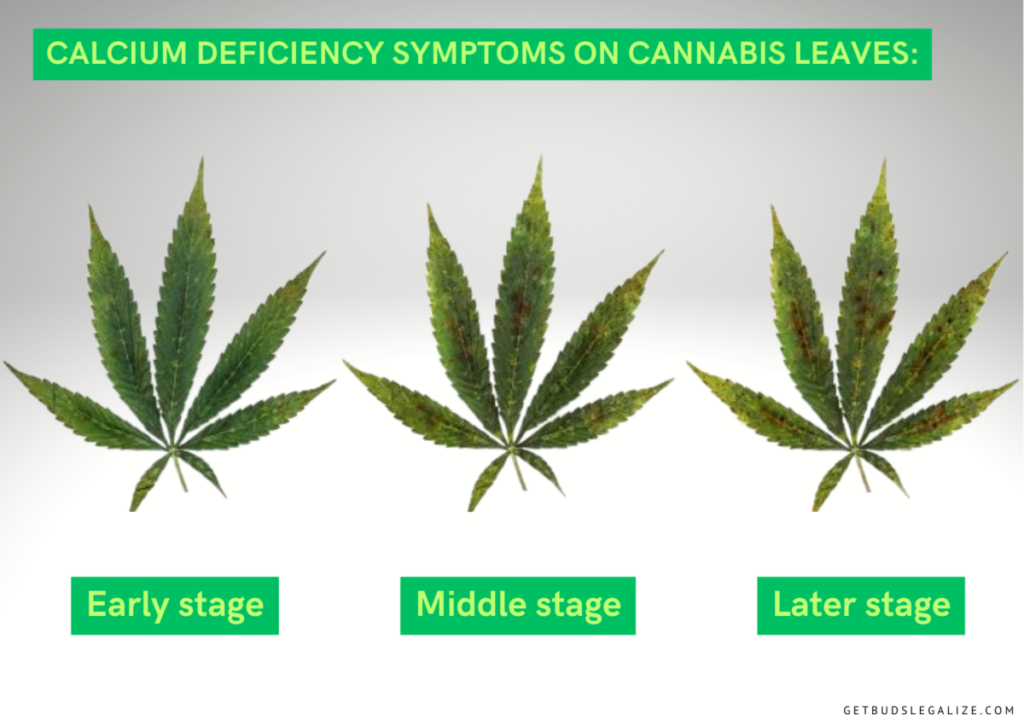
Calcium deficiency usually affects the new growth of cannabis first. The symptoms include:
- Curling or crinkling leaf tips: The tips of the cannabis leaves may curl downwards or upwards, indicating a lack of calcium in the new growth.
- Rot development across new leaves and buds: The new leaves and buds may develop brown or black spots of rot, which can spread and affect the quality and quantity of the harvest.
- Delayed growth: The plant may grow slower than normal, as calcium is needed for cell division and expansion.
- Brown or yellow chlorotic spots on the edges or throughout the leaves: The leaves may show signs of chlorosis, which means they lose their green color and turn yellow or brown. This can reduce the photosynthesis and the energy production of the plant.
- The roots turn brown: The roots may also suffer from calcium deficiency, and become brown, weak, and prone to infections.
A deficiency of calcium can also cause blossom end rot in some cannabis strains, which is a condition where the bottom of the buds turns brown and rot.
What Causes Calcium Deficiency in Cannabis?
There are several factors that can cause or contribute to calcium deficiency in cannabis plants. Some of the most common ones are:
- Using filtered or ro water (reverse osmosis) may lack the proper amount of calcium and other minerals.
- Growing in acidic growing mediums (below 6.2 pH), can lock out calcium and prevent it from being absorbed by the roots.
- Growing in hydroponic or coco coir-based systems without adding supplements of calcium, as these mediums do not naturally contain enough calcium for cannabis plants.
- Providing excess potassium, which can compete with calcium for uptake and cause a deficiency.
How to Fix Calcium Deficiency in Plants
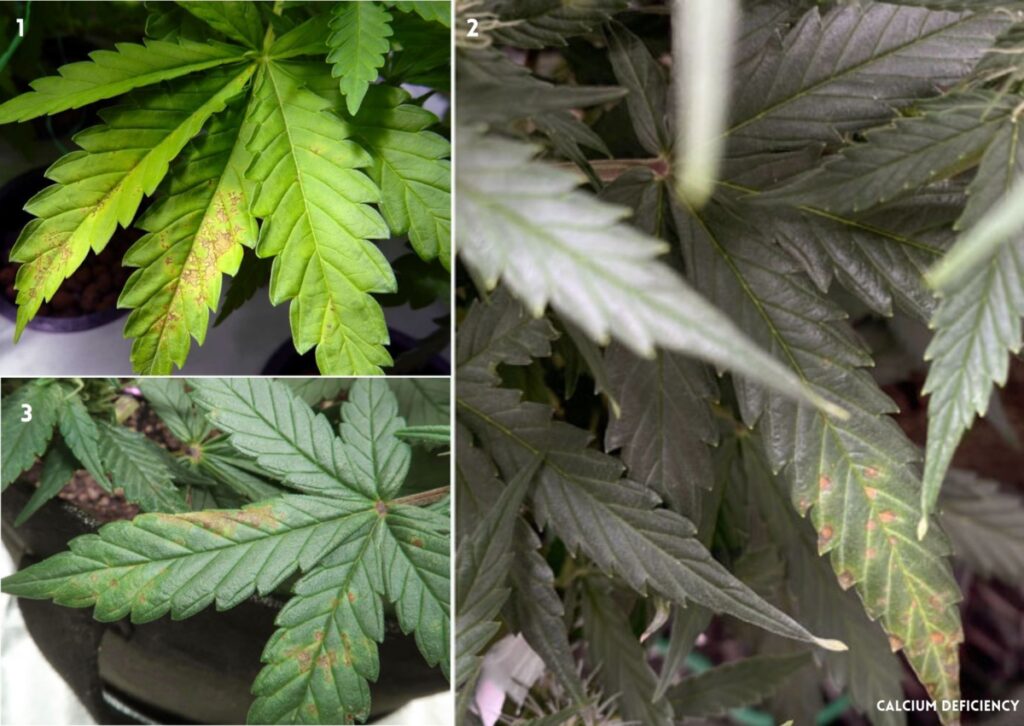

If you notice signs of calcium deficiencies in your plants, you should act quickly to fix them before it causes irreversible damage. Some steps to fix it are:
- Flush your soil or medium with plain water to remove any excess salts or nutrients that may be interfering with calcium uptake.
- Adjust the pH levels of your soil or water to the optimal range of 6.0-7.0 for soil, and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics.
- Apply a foliar spray of a calcium-rich solution to your plants. You can use commercial products such as Cal-Mag or homemade solutions such as diluted milk (1 part milk to 10 parts water), and calcium nitrate (1 teaspoon per gallon of water). You should spray your plants once a week until you see improvement in their health and appear rance.
- Add more calcium to your nutrient solution or soil. You can use products such as Cal-Mag, dolomite lime, bone meal, etc. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and apply them sparingly to avoid overdoing it.
However, be careful not to overdo with nutrients, as too much calcium can cause other nutrient imbalances or lockouts.
How to Prevent Calcium Deficiency?
The best way to prevent a calcium deficiency in cannabis is to provide them with optimal growing conditions and a balanced nutrient solution. Some tips are:
- Test and adjust the pH of your soil or water regularly. Aim for a pH between 6.0 and 7.0, while for hydroponic growers, this means keeping the pH between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Avoid overwatering or underwatering your plants, as this can affect their ability to absorb nutrients.
- Choose a high-quality fertilizer that contains calcium and other essential minerals. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and do not overfeed your plants.
- Add organic amendments to your growing medium such as dolomite lime, bone meal, or eggshells to your soil to increase the calcium content.
- Monitor your plants for signs of calcium deficiency. If you notice any symptoms, flush your plants with plain water and apply a calcium supplement as soon as possible.
What Are Some Sources of Calcium for Cannabis Plants?
There are many sources of calcium for your plants, both organic and synthetic. Some examples are:
Dolomite lime: This is a natural mineral that consists of calcium and magnesium carbonate. It can be used to amend the soil before planting or during the flowering stage to increase the pH and supply calcium. Dolomite lime also helps to buffer the soil and prevent a nutrient lockout. It is recommended to use about 1 tablespoon per gallon of soil and mix it well.
Gypsum: This is a natural mineral that consists of calcium sulfate. It can be used to enrich the soil or water with calcium without altering the pH. Gypsum also helps to improve the soil structure and drainage. It is recommended to use about 2 teaspoons per gallon of water and apply it every two weeks.
Eggshells: This is a natural source of calcium carbonate that can be obtained from kitchen waste. They can be crushed and mixed with the soil or compost. Eggshells also provide other micronutrients such as zinc and iron. It is recommended to rinse and dry the eggshells before crushing them and use about 1/4 cup per gallon of soil.
Bone meal: This is a natural source of calcium phosphate that can be obtained from animal bones. It can be mixed with the soil or compost. Bone meal also provides phosphorus, which is important for flowering and root development. It is recommended to use about 1/2 cup per cubic foot of soil and mix it well.
Milk: This is a natural source of calcium that can be obtained from dairy products. It can be diluted with water and sprayed on the foliage. Milk also provides sugars, proteins, and enzymes that can benefit the plant’s health and growth. It is recommended to use a 1:10 ratio of milk to water and spray it once a week.
Calcium nitrate: This is an artificial source of calcium nitrate that can be purchased from gardening stores. It can be dissolved in water and sprayed on the foliage or added to the nutrient solution. Calcium nitrate also provides nitrogen, which is important for vegetative growth and chlorophyll production. It is recommended to use about 1/4 teaspoon per gallon of water and apply it every two weeks.
Calcium chloride: This is an artificial source of calcium chloride that can be purchased from gardening stores. It can be dissolved in water and sprayed on the foliage or added to the nutrient solution. Calcium chloride also helps to lower the pH and increase the solubility of other nutrients. It is recommended to use about 1/8 teaspoon per gallon of water and apply it every two weeks.
Calcium supplements: These are commercial products that contain different forms of calcium that can be purchased from gardening stores. They can be sprayed on the foliage or added to the nutrient solution. Those products are designed to address the specific needs and conditions of cannabis plants. They usually come with instructions on how much and how often to use them.
Cannabis Calcium Toxicity vs Calcium Deficiency: How to Recognize the Differences?

The toxicity of calcium is rare, but it can happen if you overfeed your plants with calcium-rich fertilizers or supplements. It can also occur if the pH of your growing medium is too high, which prevents the plant from absorbing other nutrients. The symptoms of calcium toxicity include:
- Reduced growth and yield
- Leaf burn or scorching
- Red and Orange spots on leaves
- Leaves will drop slightly
- Iron deficiency symptoms (interveinal chlorosis)
- Magnesium deficiency symptoms (purple or reddish coloration of leaves)
- Potassium deficiency symptoms (small leaves with twisted tips)
How to Fix A Calcium Excess in Cannabis Plants
Here are some tips on how to fix a calcium excess in cannabis plants depending on the medium you are using.
- In soil: The best way to fix a calcium excess is to flush the soil with pH-balanced water that contains a balanced nutrient solution. This will wash away the excess calcium and other salts from the soil and restore the optimal pH level. You may also stop feeding your plants for 1 week to let them recover from the stress.
- In coco: The best way to fix a calcium excess is to flush the coco with pH-balanced water that contains half of the normal dose of nutrients. This will lower the concentration of calcium and other elements in the coco and prevent further lockout. You should also use filtered or distilled water for watering and feeding your plants, and adjust the cal-mag dosage according to your water quality and plant needs.
- In hydroponic: The best way to fix a calcium excess in hydro is to drain the reservoir and refill it with fresh pH-balanced water that contains a lower dose of nutrients. This will dilute the excess calcium and other salts in the water and allow your plants to absorb them more efficiently. You should also monitor the EC or ppm level of your nutrient solution regularly and adjust it according to your plant stage and strain.
What Are Some Common Mistakes That Cannabis Growers Make When Dealing with Calcium Deficiency?
Some common mistakes that cannabis growers make when dealing with a deficiency of calcium are:
- Misdiagnosing a calcium deficiency by mistaking it for another nutrient deficiency or disease
- Applying too much or too little calcium to their plants
- Applying calcium at the wrong time or frequency
- Applying calcium without adjusting their pH level
- Applying calcium without monitoring their water quality and salinity levels
- Applying calcium without checking its fertilizer composition and dosage
Act Fast and Save Your Crop!
Calcium deficiency in cannabis can be prevented by using good-quality soil or water, following a proper feeding schedule, and maintaining a suitable environment for your plants. Calcium is a crucial nutrient for growing weed that should not be overlooked. By recognizing and fixing nutrient deficiencies in time, you can ensure that your plants grow healthy and produce high-quality buds.
FAQs about Calcium Deficiency in Cannabis
If you are growing marijuana in a hydroponic setup, you may need to pay extra attention to your calcium levels. Cannabis requires more calcium than most other crops, especially during the flowering stage. A deficiency of Calcium can cause bud rot, leaf curl, and reduced potency.
To fix it, you can:
- Check your nutrient solution pH and adjust it to the optimal range for cannabis (usually between 5.5 and 6.5)
- Use a hydroponic nutrient formula that contains calcium and other micronutrients
- Monitor your electrical conductivity (EC) and avoid overfeeding your plants
- Change your nutrient solution regularly to prevent nutrient lockout or buildup
- Add a calcium supplement such as Cal-Mag or Botanicare Cal-Max to your nutrient solution
The best way to add calcium to the soil of your weed plants depends on your soil type and condition. If you have acidic soil, you can use lime to raise the pH and add calcium at the same time. If you have alkaline soil, you can use gypsum to add calcium without affecting the pH. You can also use organic sources of calcium such as eggshells, bone meal, or oyster shells.
To add calcium to the soil of your plants, you can:
- Test your soil pH and calcium levels with a soil test kit or send a sample to a lab
- Choose a suitable calcium amendment based on your soil type and condition
- Apply the amendment according to the label instructions or recommendations
- Mix the amendment well with the topsoil or incorporate it into the planting hole
- Water your plants well after applying the amendment
Calcium deficiency is a common problem in cannabis growth, especially in hydroponic or neutral-medium indoor grows. Calcium is an important nutrient that helps provide structure to the plant and helps it withstand stress like heat. A deficiency of calcium can inhibit nutrient uptake at the roots, impede flower growth, and cause brown or bronze spots on the leaves.
To fix it, you need to adjust the pH of your water and your growing medium to the optimal range for cannabis plants. Soil should have a pH of 6.0-7.0, while hydroponics should have a pH of 5.5-6.5. You can use a pH meter or pH test strips to measure the pH and add pH up or down solutions to adjust it accordingly.
You must also supplement your plants with a calcium-rich fertilizer or additive, such as cal-mag, dolomite lime, gypsum, or eggshells. Follow the instructions on the product label and apply it to your plants according to their stage of growth and nutrient needs. You can also foliar spray your plants with a diluted solution of calcium nitrate or calcium chloride to provide a quick boost of calcium to the leaves.
It may take a few weeks for your plants to recover, so be patient and monitor their progress. Avoid overfeeding your plants with nitrogen or potassium, as these nutrients can compete with calcium for absorption. Also, make sure your plants have adequate ventilation and air circulation to prevent heat stress and mold.
Cal-mag deficiency is a term that refers to a combined deficiency of calcium and magnesium in cannabis plants. These two nutrients are often deficient together because they have similar functions and interactions in the plant. The symptoms include:
- Brown or bronze spots on the leaves, especially on new growth and near the edges
- Yellowing or curling of the leaves
- Stunted growth and reduced yields
- Weak stems and branches
- Poor bud development and quality
Cal-mag deficiency can be caused by low pH, soft or filtered water, high temperatures, overwatering, or overfeeding with nitrogen or potassium.
A deficiency of Calcium magnesium in veg can affect the health and productivity of your cannabis plants in the flowering stage. To fix it, you need to follow the same steps as for fixing a deficiency of calcium during flowering:
- Adjust the pH of your water and your growing medium to the optimal range for cannabis plants
- Add to your plants with a cal-mag supplement
- Foliar spray your plants with a calcium-rich solution
- Avoid overfeeding your plants with nitrogen or potassium
- Provide adequate ventilation and air circulation
By fixing it, you can ensure that your plants have enough calcium and magnesium to support their growth and development in the flowering stage.
To fix a deficiency of calcium, you can use a calcium-rich fertilizer or supplement, such as dolomite lime, gypsum, bone meal, or eggshells. Apply the calcium source according to the instructions on the label or the recommendations of a soil test. You can also adjust the pH of your soil to around 6.5, which is optimal for cannabis plants and calcium absorption.
Cannabis leaf Septoria is a fungal disease that can affect cannabis plants. It causes yellow spots with brown margins on the leaves, similar to calcium deficiency. However, there are some differences that can help you distinguish between them:
- Septoria spots are more irregular in shape and size than calcium deficiency spots.
- Septoria spots tend to appear on older leaves first, while calcium deficiency spots tend to appear on newer leaves first.
- Septoria spots may have tiny black dots (spores) in them, while calcium deficiency spots do not.
- Septoria spots may spread to other parts of the plant, while calcium deficiency spots usually remain on the leaves.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.




















