Exploring The Colorful World of Cannabis Flavonoids
Cannabis, with its complex chemistry, offers a treasure trove of compounds that contribute to its diverse effects and potential health benefits. Among these are flavonoids, a class of plant compounds known for their various physiological effects and contributions to flavor and color in many fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
What Are Flavonoids in Cannabis?
Flavonoids are a diverse group of phytonutrients (plant chemicals) found in fruits, vegetables, grains, tea, wine, and many other plant-based foods. They are responsible for the vivid colors of many fruits and flowers, ranging from red to blue to yellow. Flavonoids are renowned for their antioxidant properties, which means they help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation by scavenging harmful free radicals.
There are several subclasses of flavonoids, including flavonols (e.g., quercetin, kaempferol), flavones (e.g., apigenin, luteolin), flavanones (e.g., hesperidin, naringenin), flavan-3-ols (e.g., catechins, epicatechins), anthocyanidins (e.g., cyanidin, pelargonidin), and isoflavones (e.g., genistein, daidzein). Each subclass has its unique properties and potential health benefits.
What Role Do Flavonoids Play In Cannabis Plants?
Flavonoids play several important roles in marijuana plants, contributing to their overall health, protection, and functionality. Here are some key roles that flavonoids play in cannabis:

1. UV Protection:
Flavonoids act as natural sunscreen for marijuana plants. They absorb ultraviolet (UV) radiation, protecting the plant’s delicate tissues from damage caused by excessive exposure to sunlight. This is particularly important for outdoor-grown marijuana plants, which are exposed to varying levels of UV radiation depending on environmental factors.
2. Antioxidant Defense:
Cannabis flavonoids possess antioxidant properties, meaning they can neutralize harmful free radicals in the plant’s cells. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage to cellular structures. By scavenging free radicals, flavonoids help protect marijuana plants from oxidative damage and maintain their overall health and vitality.
3. Pigmentation:
Flavonoids contribute to the pigmentation of flowers and leaves. They are responsible for producing the various colors observed in marijuana plants, including purple, blue, red, and orange hues. The specific combination and concentration of flavonoids present in a cannabis strain determine its unique color profile, which can be influenced by factors such as genetics, environmental conditions, and nutrient availability.
4. Anti-Microbial Defense:
Flavonoids have been shown to exhibit antimicrobial properties, helping marijuana plants defend against bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens. By inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms, flavonoids contribute to the plant’s immune response and resistance to diseases and infections.
5. Pollination Attraction:
Some flavonoids may play a role in attracting pollinators to cannabis flowers. By emitting specific scents and colors that appeal to bees, butterflies, and other pollinating insects, flavonoids help facilitate the pollination process, which is essential for the reproduction and genetic diversity of marijuana plants.
Overall, flavonoids are integral components of the complex chemical profile of cannabis plants. Alongside cannabinoids and terpenes, they contribute to the plant’s therapeutic properties, sensory characteristics, and overall resilience in natural environments.
As our understanding of cannabis chemistry continues to evolve, further research into the specific roles and effects of flavonoids in cannabis plants may uncover additional insights into their potential benefits for human health and wellness.

What Potential Health Benefits Do Cannabis Flavonoids Offer?
Flavonoids, while less studied compared to cannabinoids like THC and CBD have shown promising benefits. Here are some potential benefits associated with their use:
1. Anti-inflammatory properties:
Flavonoids in cannabis, such as cannaflavins A and B, have demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds may help reduce inflammation, which is implicated in various chronic diseases like arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Antioxidant activity:
Flavonoids are antioxidants that neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. They may protect against chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disease by preventing oxidative damage to cells.
3. Neuroprotective effects:
Some flavonoids, such as apigenin, have shown neuroprotective properties in preclinical studies. These compounds may help protect brain cells from damage caused by oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer‘s and Parkinson’s.
4. Anti-cancer potential:
Certain flavonoids found in cannabis, such as apigenin and quercetin, have been studied for their potential anti-cancer effects. These compounds may inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells, induce apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells, and prevent angiogenesis (forming new blood vessels that feed tumors).
5. Cardiovascular support:
Flavonoids like quercetin have been associated with cardiovascular benefits, including improved blood flow, reduced blood pressure, and protection against heart disease. These effects may be attributed to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
6. Anti-allergic properties:
Some flavonoids, such as cannflavin A, have been found to exhibit anti-allergic effects by inhibiting the release of histamines and other inflammatory mediators. This could potentially benefit individuals with allergies or allergic conditions.
It’s important to note that much of the research on flavonoids is still in its early stages, and more studies are needed to fully understand their potential health benefits and mechanisms of action.
Additionally, the effects of flavonoids may vary depending on factors such as the specific compounds present, their concentrations, and how they interact with other components of the cannabis plant.
Flavonoids and Endocannabinoid System

Some research suggests that certain flavonoids found in cannabis may interact with the ECS, which is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, memory, appetite, and pain sensation.
For instance, flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol have been found to have a mild affinity for cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB2 receptors, which are primarily located in immune cells and tissues associated with inflammation. By interacting with these receptors, flavonoids may modulate immune responses and inflammation.
Moreover, flavonoids can also influence the activity of enzymes involved in the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids, such as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). By regulating the levels of endocannabinoids like anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), flavonoids may indirectly affect ECS signaling and function.
However, it’s important to note that research on flavonoids and their interaction with the ECS is still in its early stages, and much more investigation is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications.
Additionally, the effects of flavonoids can vary depending on factors such as their concentration, the presence of other cannabis compounds (like cannabinoids and terpenes), and individual differences in metabolism and physiology.
List Of Flavonoids In Cannabis And Their Potential Benefits
Cannabis contains a variety of flavonoids, although research on them is still ongoing. Some of the flavonoids identified in cannabis include:
1. Cannflavins:
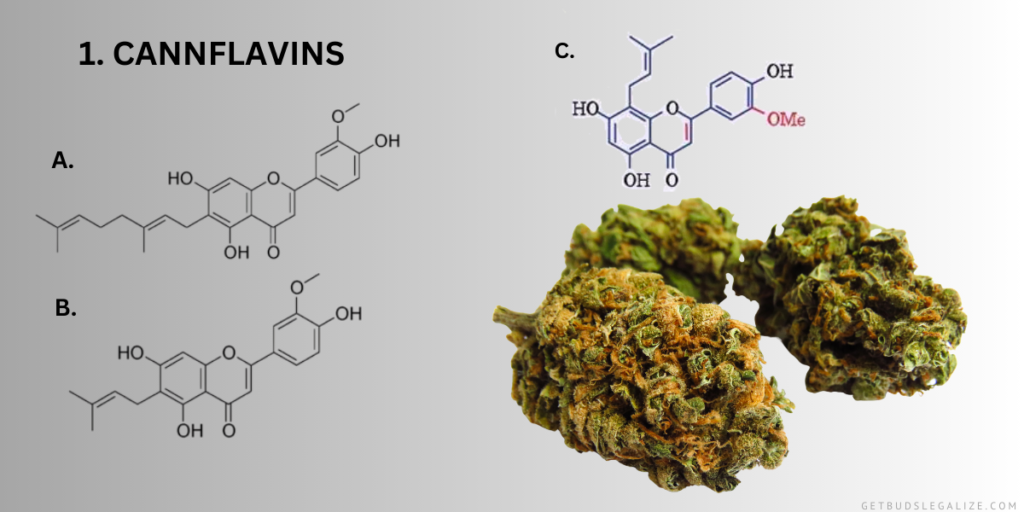
Among the unique flavonoids found in cannabis are the cannflavins, namely Cannflavin A, Cannflavin B, and Cannflavin C. These compounds have garnered attention for their potential anti-inflammatory properties. Cannflavin A, in particular, has shown promise in preclinical studies for its potent anti-inflammatory effects, surpassing those of aspirin in some research.
2. Apigenin:
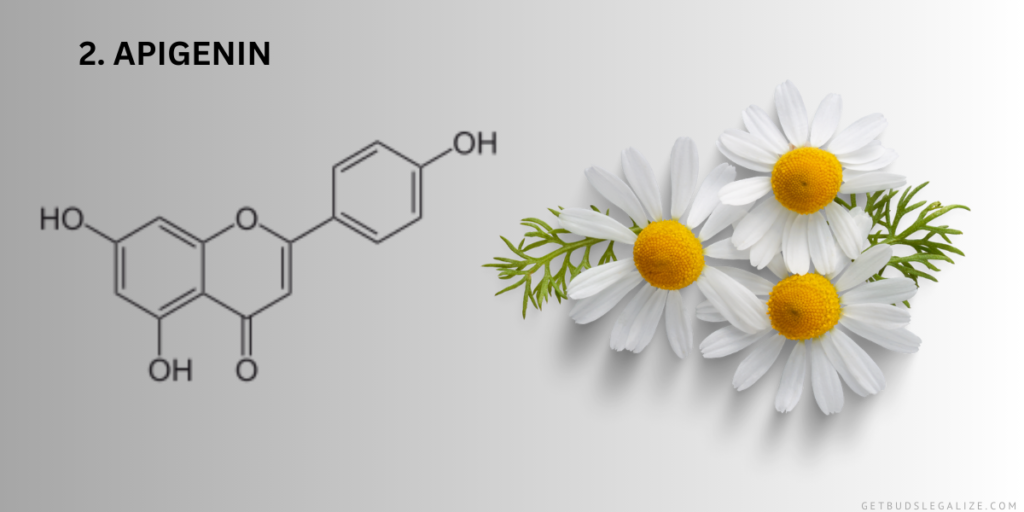
Another noteworthy flavonoid present in cannabis is apigenin. This compound is widely known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies suggest that apigenin may contribute to the overall therapeutic effects of cannabis, potentially enhancing its medicinal value.
3. Luteolin:
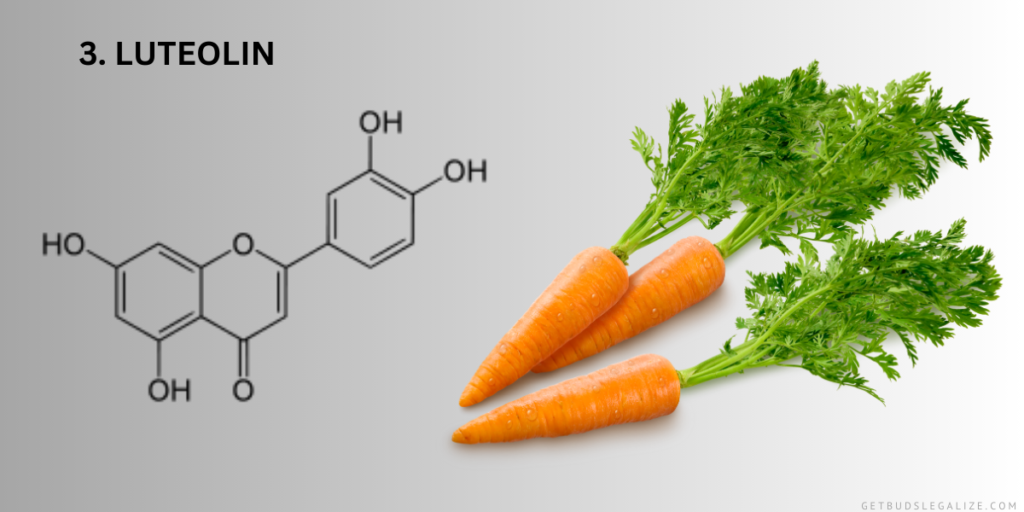
Luteolin is a flavone commonly found in various plants, including cannabis. Studies suggest that luteolin may exert neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects. Its presence in cannabis adds to the diverse array of compounds that contribute to the plant’s medicinal properties.
4. Kaempferol:

Kaempferol is another flavonoid identified in cannabis, celebrated for its potential health benefits. Research indicates that kaempferol may possess anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties, making it a compound of interest in the realm of medicinal cannabis.
5. Quercetin:
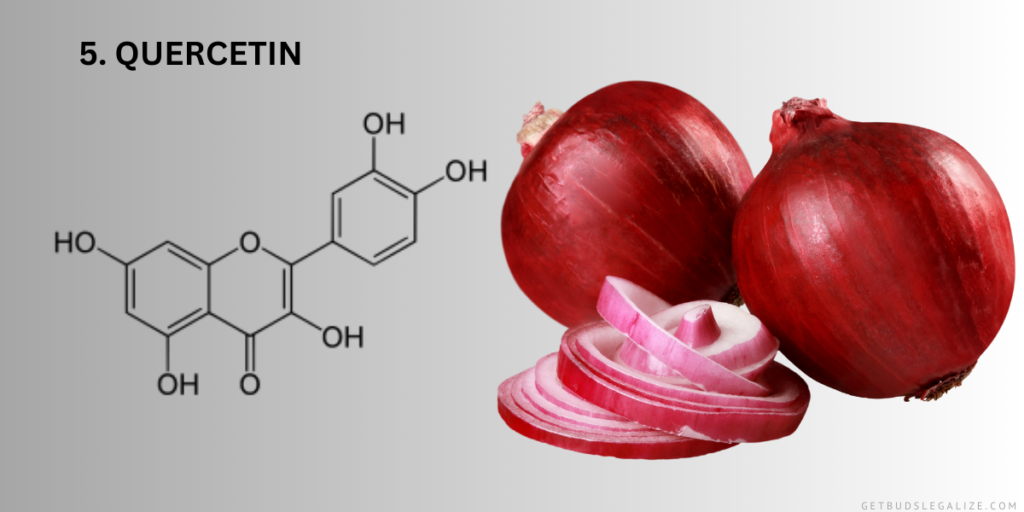
Quercetin is a flavonoid abundant in various fruits and vegetables, including cannabis. Known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, quercetin has been investigated for its potential role in supporting cardiovascular health and reducing inflammation-related conditions.
6. Orientin:
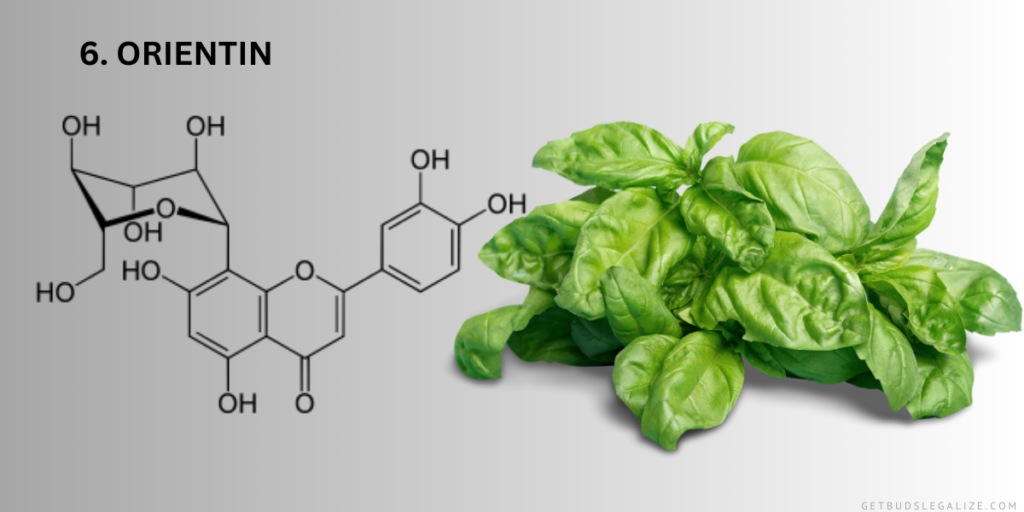

Orientin, while less studied compared to some other flavonoids, is also present in cannabis. It belongs to the flavone class of flavonoids and has demonstrated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in preliminary research. Further exploration is warranted to uncover its full therapeutic potential.
7. Vitexin and Isovitexin:
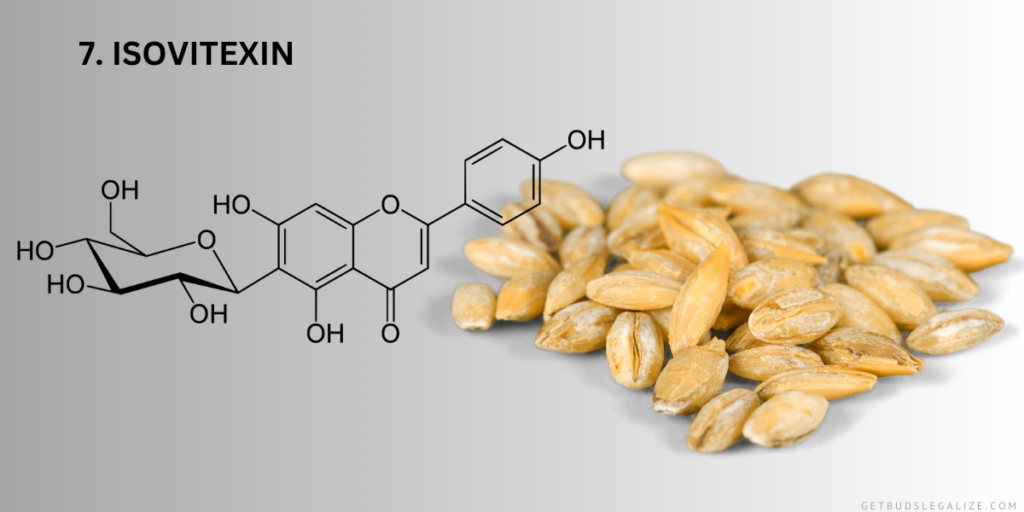
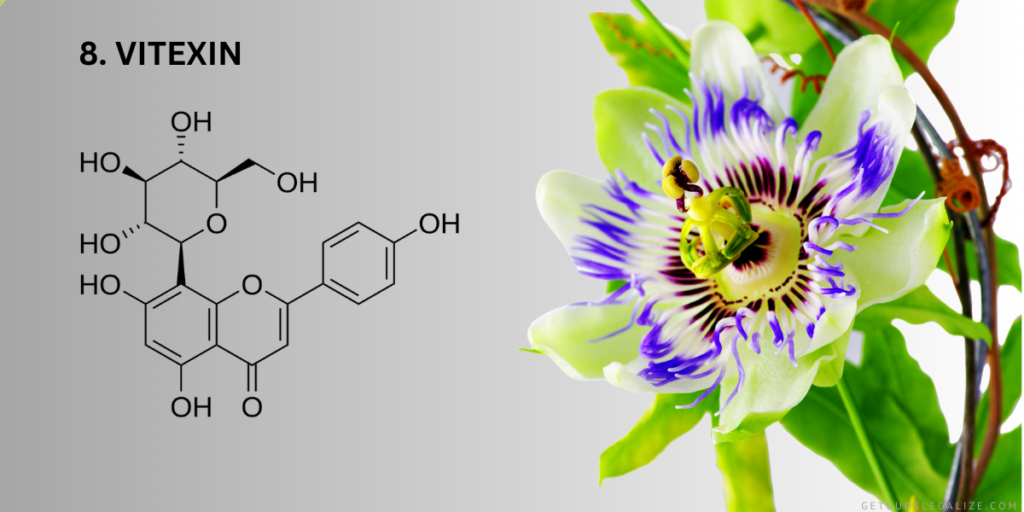
Vitexin and its derivative, isovitexin, are flavonoids found in cannabis with potential health-promoting properties. These compounds have been investigated for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. While research on vitexin and isovitexin in cannabis is still emerging, their presence underscores the complexity of the plant’s chemical composition.
Flavonoids vs Terpenes: What Are The Differences?

Flavonoids and terpenes are both classes of compounds found in plants, including cannabis, but they have distinct structures, functions, and roles in plant physiology and human health.
1. Structure:
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids are a diverse group of polyphenolic compounds characterized by a common structure consisting of two aromatic rings (A and B rings) connected by a three-carbon bridge. They often have hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to the rings, which contribute to their antioxidant properties.
- Terpenes: Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds characterized by repeating units of a five-carbon molecule called isoprene. Depending on the number of isoprene units, terpenes can be classified as monoterpenes (two isoprene units), sesquiterpenes (three isoprene units), diterpenes (four isoprene units), and so on.
2. Function:
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids serve various functions in plants, including UV filtration, pigmentation (coloration), pollination attraction, and defense against pathogens and herbivores. They also possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties, which may benefit human health.
- Terpenes: Terpenes play a crucial role in plant defense mechanisms, acting as repellents against herbivores and pathogens or attracting beneficial organisms like pollinators. In addition to their aromatic qualities, terpenes contribute to the flavor and aroma of plants. In cannabis, terpenes are believed to modulate the effects of cannabinoids and offer therapeutic benefits through the entourage effect.
3. Occurrence:
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids are widespread in the plant kingdom and can be found in fruits, vegetables, grains, herbs, spices, and beverages like tea and wine. In cannabis, flavonoids contribute to the plant’s overall chemical profile but are typically present in lower concentrations compared to terpenes and cannabinoids.
- Terpenes: Terpenes are ubiquitous and are found in a wide variety of plants, including cannabis, conifers, citrus fruits, and herbs. They are particularly abundant in the resinous glands (trichomes) of cannabis flowers, where they contribute to the plant’s aroma and flavor profile.
4. Health Benefits:
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids have been studied for their potential health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, neuroprotective, and cardiovascular protective effects. They may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health and wellness.
- Terpenes: Cannabis terpenes exhibit various pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic, sedative, and antimicrobial effects. When combined with cannabinoids, terpenes may enhance the therapeutic potential of cannabis by influencing its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
In summary, while flavonoids and terpenes are important secondary metabolites found in plants, they differ in structure, function, occurrence, and health benefits. Together with cannabinoids, these compounds contribute to the complex chemical profile of cannabis and its potential effects on human health and well-being.
Future Directions
As legalization and research surrounding cannabis continue to expand, we’ll likely uncover even more about the therapeutic potential of flavonoids. Further studies are needed to fully understand how these compounds interact with other cannabinoids and terpenes in the entourage effect, as well as their specific mechanisms of action in the body.
Conclusion
Cannabis flavonoids represent a fascinating area of research with promising therapeutic potential. While cannabinoids like THC and CBD often steal the spotlight, flavonoids play a crucial role in the plant’s medicinal properties. By delving deeper into these colorful compounds, we may unlock new avenues for treating a wide range of health conditions.
FAQs about Flavonoids and Cannabis
Some common flavonoids found in cannabis include quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin, and cannflavin A and B. Each of these compounds may have unique effects and potential health benefits.
Flavonoids have been studied for their potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. They may also play a role in supporting cardiovascular health and immune function.
The flavonoids found in cannabis are typically consumed alongside other cannabinoids and terpenes when using cannabis products. This can include smoking or vaporizing dried flowers, consuming edibles or tinctures, or using topical products.
Flavonoids themselves are not psychoactive compounds. However, they may interact with other cannabinoids, such as THC, to modulate their effects. The overall psychoactive experience of cannabis is influenced by the combination of various compounds present.
While flavonoids are generally considered safe when consumed in food, supplements, or herbal preparations, more research is needed to fully understand their effects when consumed in high concentrations or combination with other cannabis compounds.
Researchers are exploring the potential therapeutic applications of isolated flavonoids. Cannflavin A and B, for example, have shown promise as anti-inflammatory agents and may be developed into pharmaceutical drugs in the future.
Yes, different cannabis strains can have varying concentrations of flavonoids, along with other cannabinoids and terpenes. Factors such as genetics, growing conditions, and processing methods can all influence the flavonoid profile of a particular strain.
The legal status of cannabis and its compounds, including flavonoids, varies by region. In areas where cannabis is legal for medical or recreational use, products containing flavonoids may be available from licensed dispensaries. However, regulations regarding extraction, manufacturing, and distribution may apply.
Increasing flavonoids in cannabis involve several factors, including genetics, growing conditions, and post-harvest handling. Here are some tips to increase flavonoid levels in cannabis plants:
1. Genetics Selection: Choose cannabis strains known for their high flavonoid content. Some strains naturally produce higher levels of flavonoids than others. Look for strains with colorful buds, as the pigments responsible for these colors often indicate higher flavonoid concentrations.
2. Lighting: Providing the right type and intensity of light during the flowering stage can enhance flavonoid production. Some growers believe that exposing plants to ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly UVB, can stimulate flavonoid synthesis as a defense mechanism. However, it’s essential to be cautious with UV light as excessive exposure can damage the plant.
3. Temperature and Humidity: Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels throughout the plant’s life cycle can help maximize flavonoid production. Fluctuations in temperature and humidity stress the plant, triggering it to produce more flavonoids as a protective response. However, extreme conditions can harm the plant, so providing stable and appropriate environmental conditions is crucial.
4. Nutrients and Supplements: Providing the right nutrients and supplements can support flavonoid biosynthesis. Certain nutrients, such as magnesium, phosphorus, and sulfur, are essential for flavonoid production. Additionally, some growers use organic supplements or additives specifically formulated to enhance terpene and flavonoid production.
5. Harvesting and Curing: Proper harvesting and curing techniques are crucial for preserving and even enhancing flavonoid levels. Harvesting at the right time, when the trichomes are at their peak maturity, ensures maximum flavonoid content. Additionally, curing the buds slowly and properly, with controlled temperature and humidity, allows flavonoids to develop and mature, leading to a more flavorful and aromatic final product.
6. Avoiding Stress: Minimize stress during the plant’s growth cycle. Stress from factors like nutrient deficiencies, pests, diseases, or environmental extremes can reduce flavonoid production. Maintaining optimal growing conditions and promptly addressing any issues that arise can help prevent stress and promote healthy flavonoid development.
7. Selective Pruning: Some growers believe that selective pruning techniques, such as defoliation or removing certain growth tips, can redirect the plant’s energy towards flavonoid production in the remaining buds.
8. Genetic Manipulation (Advanced): In more advanced settings, genetic manipulation techniques such as breeding or genetic engineering can be used to develop cannabis strains with enhanced flavonoid profiles. However, this approach requires specialized knowledge and resources.
Remember that while these techniques can potentially increase flavonoid levels in cannabis, the plant’s genetics play a significant role in determining its flavonoid content. Additionally, regulations and laws regarding MEDICAL cannabis cultivation vary by location, so always ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants





















