What To Know About Endocannabinoids And The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system is a complex network of cell signaling that plays an active role in regulating several functions in the human body. It comprises endocannabinoids, enzymes, and cannabinoid receptors.
The endocannabinoid system was discovered only in the early 1990s when a chemist isolated the first endocannabinoid in the human brain. Since then, researchers have been studying this system and its functions.
Endocannabinoids are similar to the cannabinoids produced by the cannabis sativa (C. sativa) plant. However, the human body naturally synthesizes endocannabinoids. The prefix “endo” means “within,” referring to substances produced within the body.
What Is The Endocannabinoid System And What Is Its Role?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system present in the body that helps regulate and balance essential bodily functions. According to research, the ECS may be a potential therapeutic target in various physiological conditions, including:
- Energy balance
- Control of nausea and vomiting
- Memory and learning
- Appetite stimulation
- Blood pressure
- Pain
- Immune response
- Embryonic development
In addition, it may also be a target for pathological conditions like:
- Traumatic brain injury
- Huntington’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
It is essential to conduct further research to gain a better understanding of the system. However, researchers have identified three main components that are involved in it:
1. Endocannabinoids:
These are naturally occurring neurotransmitters that are lipid-based. Neurons in the body use these chemical messengers to send signals to each other. Endocannabinoids assist in various bodily functions and are produced as required, making it challenging to determine typical levels.
Two of the primary endocannabinoids identified include – 2-archidonoyl glyerol (2-AG) and Anandamide (AEA or arachidonoyl ethanolamide). Experts believe that there are additional endocannabinoids in the body, but their roles and functions are not conclusively known yet.
2. Endocannabinoid Receptors:
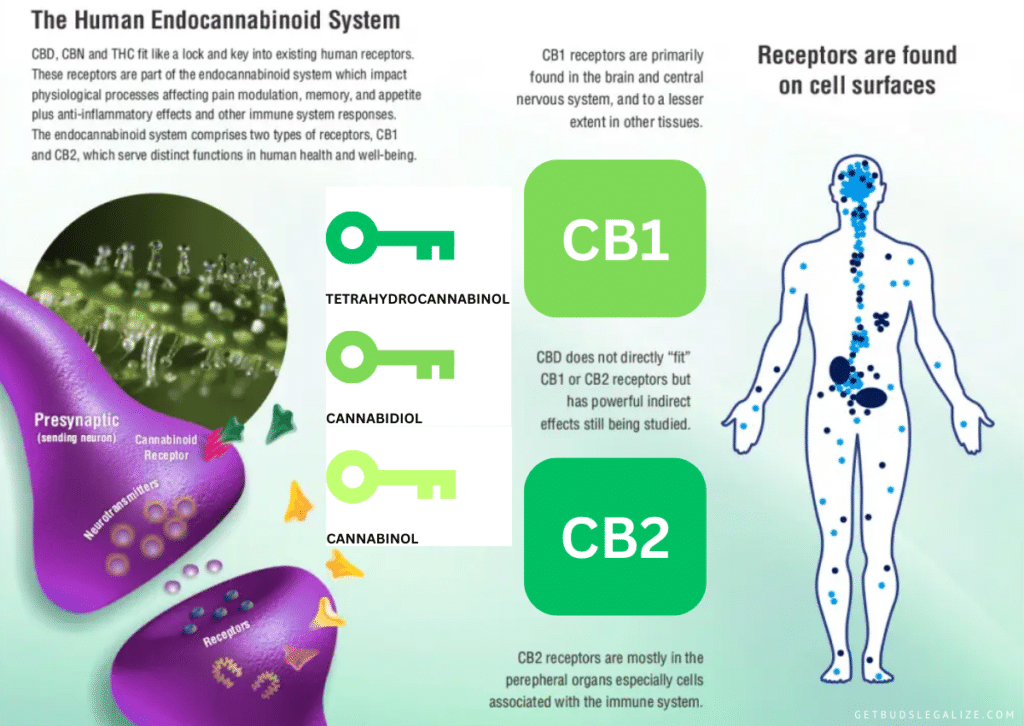
Cannabinoid receptors are present on the surface of cells throughout the body. The receptors bind to endocannabinoids, which signals the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) to initiate a response.
There are two primary cannabinoid receptors present in the body – CB1 and CB2. CB1 is mainly found in the central nervous system (CNS), which comprises the brain and spinal cord. CB2 is predominantly present in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and immune cells.
Experts believe that a third cannabinoid receptor exists, but research is inconclusive. Depending on the location of the receptor in the body, endocannabinoids may attach to either type of receptor, causing different responses.
For example, endocannabinoids may target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to alleviate pain or bind to a CB2 receptor in an immune cell, signaling that the body is undergoing inflammation.
3. Enzymes:
Enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids after they have carried out the response. Two main enzymes break down endocannabinoids – monoacylglycerol acid lipase and fatty acid amide hydrolase. Monoacylglycerol acid lipase breaks down 2-AG, while fatty acid amide hydrolase breaks down AEA.
How Does The Body Produce And Release Endocannabinoids?
The human body naturally produces endocannabinoids, which are present in various organs and tissues such as the brain, muscle, and circulating cells. When endocannabinoids bind with cannabinoid receptors, they become active. These receptors are located throughout the body, and research is ongoing to understand the exact physiological mechanism that triggers their binding to the endocannabinoid.
Experts believe that when a system in the body is out of balance, the receptors bind to the cannabinoids to help restore balance. The endocannabinoid system is precise and regulates different processes in a targeted way.
For example, if body temperature is out of the normal range, the ECS will regulate it without altering other processes. Once balance is restored, enzymes break down the cannabinoids to prevent overcorrection of the problem.
What Is The Function Of Endocannabinoids And The ECS?
The endocannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system have a vast range of functions, which researchers still do not fully understand. However, the ECS plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis, which refers to the maintenance of stability and optimal conditions within the body to promote proper functioning.
For instance, the endocannabinoid system helps the body to return to the optimal range and maintain homeostasis if the body falls out of the normal range.
According to research, the ECS regulates the function of various bodily activities, including:
- Pain sensation
- Inflammation and other immune responses
- Appetite and digestion
- Sleep
- Mood
- Metabolism
- Reproduction system function
- Learning and memory
What Are The Therapeutic Uses Of Cannabinoids?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) contains several potential therapeutic targets, according to research. While the body naturally produces endocannabinoids, there are also many cannabinoids found in the Cannabis sativa plant that have medical relevance.
Two of the most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). They can bind to cannabinoid receptors and produce similar effects to endocannabinoids. THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects that people associate with cannabis, while CBD does not produce these effects.
Ongoing studies are investigating the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids. For instance, a 2016 study on rats examined the effect of CBD on joint inflammation. The study found that applying a topical gel containing CBD reduced pain and joint swelling in rats without any side effects.
Additional research suggests that cannabinoids may help treat various conditions like sleep disturbances, pain in adults, nausea, and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, and abnormal muscle tightness caused by multiple sclerosis.
Further research is needed to determine the medical and health benefits of inhibiting or stimulating the endocannabinoid system.
For Summarize
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is not yet fully understood, but research suggests that it plays a critical role in maintaining balance and proper function in the body.
The ECS comprises endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes that work together to help regulate various bodily processes such as temperature, sleep, and mood.
The ECS has the potential to be used as a therapeutic target for treating various health conditions.
FAQs about The Endocannabinoid System
Endocannabinoids are molecules that are produced by our bodies. They are similar to cannabinoids, which are compounds found in the cannabis plant, such as THC and CBD. Endocannabinoids act as messengers that bind to cannabinoid receptors on the surface of cells.
Enzymes are molecules that catalyze chemical reactions in the body. Their role is to create and decompose endocannabinoids. For example, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is an enzyme that degrades anandamide, one of the most important endocannabinoids. Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is an enzyme that degrades 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), another major endocannabinoid.
The ECS is involved in regulating a variety of physiological and cognitive processes, such as:
- Learning and memory
- Emotion and mood
- Pain and inflammation
- Appetite and metabolism
- Sleep and circadian rhythms
- Reproduction and fertility
- Immune function and response
The ECS works by maintaining a state of balance or homeostasis in the body. It does this by modulating the activity of other neurotransmitters, hormones, and immune cells. The ECS can also respond to external stimuli, such as stress, injury, or infection, by producing more or less endocannabinoids to restore equilibrium.
Cannabis contains over 100 different cannabinoids, which can interact with the ECS in various ways.
THC is the most psychoactive cannabinoid, which means it can alter perception, mood, and cognition. THC mimics the effects of endocannabinoids by binding to CB1 receptors, which can result in euphoria, relaxation, pain relief, increased appetite, impaired memory, and altered sensory perception.
CBD is the most abundant non-psychoactive cannabinoid in medical marijuana. This means that it does not cause intoxication or impairment. CBD can modify the activity of CB1 receptors by acting as an allosteric modulator. This means that it can change the shape and function of the receptor without directly binding to it.
CBD can also interact with other receptors and enzymes in the body, such as serotonin receptors, TRPV1 channels, and FAAH inhibitors. CBD can have several positive effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, anti-epileptic, neuroprotective, and analgesic effects.
Endocannabinoid deficiency is a hypothetical condition that occurs when the body does not produce enough endocannabinoids or when the endocannabinoid system is impaired or dysregulated.
This can lead to various symptoms and disorders, such as chronic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine, irritable bowel syndrome, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Endocannabinoid deficiency can be caused by genetic factors, environmental factors, lifestyle factors, or disease states.
Some researchers suggest that supplementing with cannabinoids from cannabis or other sources may help restore endocannabinoid balance and alleviate symptoms.
The endocannabinoid system is a network of receptors and molecules that modulate various physiological processes, such as pain, inflammation, appetite, and memory.
The endocannabinoid system discovery is attributed to Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, who isolated the first endocannabinoid, anandamide, in 1992. He also identified tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), two compounds from the cannabis plant that interact with the endocannabinoid system.

















