Chemical compound THCA found in raw cannabis were proven to be effective
THC is not the most dominant chemical in marijuana, despite common belief. There is hardly any THC in marijuana flowers. Hence, THC is generally found as an additional chemical compound THC found in the raw cannabis plant instead.
Would you ever try raw cannabis for food? Here you will recognize if you have, cannabis can not get you high in its raw form. This is because THC-A is not psychoactive and has a clear tendency to be transformed into THC.
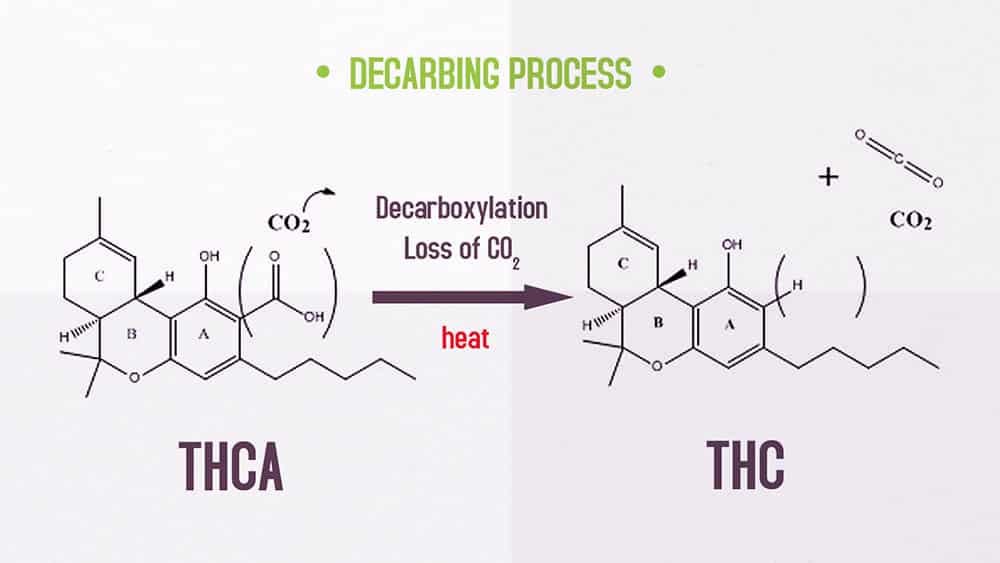
THCA is THC if, through a process called decarboxylation, heat is applied, for example by smoking or vaporizing cannabis.
Cannabinoid acids and cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds in cannabis that are responsible for their effects. Cannabinoid extraction happens in relatively small, glass-like cells called trichomes. These trichomes are highly concentrated on the flowers or buds of female cannabis plants.
Today, patients and doctors know a lot about certain cannabinoids like THC and CBD. But THC and CBD are just two of the more than 113 cannabinoids identified in cannabis.
What many people don’t know is that when a cannabis plant produces cannabinoids, it synthesizes them in their acidic form.
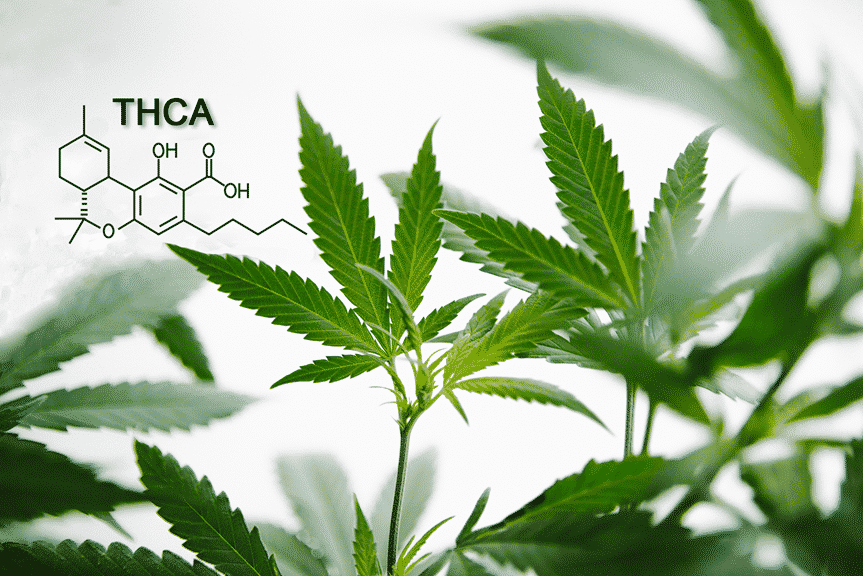

THC-A in contrast with THC chemical compound
THC-A is the most common cannabinoid found in fresh flowers of weed. THCA is the acidic form of THC.
Besides THC-A, cannabis acid (CBDA), cannabinolic acid (CBNA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabic acid (CBCA) and cannabinodiolicacid (CBNDA) are also other compounds contained inside fresh cannabis.
The decarboxylation process eliminates the carboxyl unit from these acids, which converts them to their altered state. THCA becomes THC, CBDA becomes CBD, etc. by decarboxylation.
The chemical composition of the THCA is very similar to the non-acidic THC.
THCA, however, contains a non-THC carboxylic acid group. While this might seem like a minor shift, the effect of THCA and THC on your body is important.
For reference, the high marijuana experience of THC chemical compound is generally associated with, while the impact of THCA is not. THCA does not function on the brain’s CB1 receivers.
THCA is also generated by processes that occur in the plant, while THC is produced from natural conditions to which the plant is exposed (i.e. daylight and heat).
THCA is currently, during its developing phases, the prevalent cannabinoid in cannabis. THC is produced mainly after harvesting the plant throughout the curing and treatment stages.
What involves during the chemical compound reaction
Especially if it were not for THCA, THC would not exist. THCA serves as a backbone for the development of THC and is converted to THC by a method called decarboxylation when exposed to high temperatures. The existence of the THCA chemical compounds in raw cannabis creates an issue for testing laboratories when assessing the cannabinoid substance of various strains. This is due to certain techniques that rely on heat during the test, as well as discrepancies in the weights of the organic molecules of THC and THCA.
The devices used to conduct this analytical test require heat and have been discovered to alter up to 70% of the THCA in the samples, creating significant differences between the results of the laboratory.
Processes that seemed complicated but possible
Decarboxylation involves the removal of the carboxylic acid group found on THCA. Decarboxylation starts to occur at 194°F and speeds up as the temperature increases. The optimal temperature for decarboxylation is between 284-320°F. At lower temperatures, decarboxylation can take hours while decarboxylation at optimal temperatures can occur in a few minutes.
Decarboxylation is usually achieved when cannabis is smoked, vaporized, or baked into edibles. Decarboxylation is a time-dependent process, meaning that more THCA is converted to THC when exposed to high temperatures for longer periods. This particular reaction is interesting, as THCA and THC degradation to CBNA and CBN can occur at lower temperatures than decarboxylation. THCA does not undergo decarboxylation in the body when eaten, which explains the absence of psychoactive effects when consuming raw cannabis.
What are the benefits of THCA?
The effect of the THCA chemical compound is psychotropic and thus varies from the effect of THC. THC functions by binding to the cannabinoid receptors in the brain and elsewhere in the body.
Nevertheless, it is less clear how THCA affects the body. Studies show that THCA does not have any effects on or has substantially weaker effects on cannabinoid receptors than THC.
However, THCA is more attractive than THC as a drug due to a lack of psychoactive effects. Unfortunately, there has been no work on THCA’s medical applications.
THCA had the following advantages in the few studies that existed:
Anti-inflammatory
The anti-inflammatory properties of THCA make it unique from other cannabinoids. For example, researchers have examined the effects of THC and THCA on levels of a chemical that regulates immune cell function, known as tumor necrosis factor-alpha. They determined that THC increases the level of TNF in the body, whereas THCA chemical compound lowers its production.
This may contribute to the anti-inflammatory properties of THCA, as TNF plays a role in inflammation and fever. It also suggests that THCA may be useful in treating pain, muscle spasms, menstrual cramping, and immune system disorders.
Anti-emetic
Marijuana is commonly used to treat nausea and vomiting, due to its anti-emetic properties. Interestingly, THCA has been found to have anti-emetic effects that are distinct from other cannabinoids like THC.
In one study, researchers found that THCA significantly reduced nausea and vomiting in animal models, although these effects were not achieved through activation of the CB1 receptor.
Anti-cancer
Much like other cannabinoids, THCA chemical compound has shown potentially beneficial effects in cancer. THCA has been shown to slow tumor growth in a variety of tumor cell types. These effects, however, were not found to be as significant as other cannabinoids like CBD.
Neuroprotective
THCA may also have neuroprotective effects, meaning that it can help protect cells of the brain and nervous system from damage. A study using brain cell cultures exposed to a toxic chemical known as MPP found that THCA protected the brain cells from toxicity.
THCA was able to increase the number of living cells after exposure to MPP by 123%. CBD was also tested in the study and showed similar levels of protection. The neuroprotective properties of THCA suggest that it may be useful for treating neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
The Bottomline
THCA is one of several cannabinoids that can boost the health of patients. And while THCA may be a successor, THCA appears to deliver many of its advantages.
Most notably, THCA is a non-high cannabinoid that is essential to patients that require medicinal marijuana but not affected by THC.
















