How to Fix Cannabis Boron Deficiency (B): Symptoms and Solution
Boron is a micronutrient that is essential for the healthy growth and development of cannabis plants. It plays a key role in cell wall formation, cell division, sugar transport, and hormone regulation. A cannabis boron deficiency can affect the yield and quality of your buds, as well as make your plants more susceptible to diseases and pests.
What Causes Boron Deficiency in Cannabis Plants?
To prevent or correct boron problems, it is important to understand the possible causes, usually related to the growing environment:
• Soil pH: The optimal pH range for cannabis in soil is 6.0-7.0, and for hydroponics or coco coir is 5.5-6.5. Boron is more available at a lower pH, so if the pH is too high, the plants may not be able to absorb enough boron. Conversely, if the pH is too low, the plants may absorb too much boron and suffer from toxicity.
• Soil moisture: Cannabis needs adequate water to transport nutrients to its roots and leaves, including boron. However, overwatering or underwatering can also affect boron availability and uptake. Overwatering can leach boron out of the soil or cause root rot while underwatering can dry out the soil and reduce nutrient mobility.
• Soil structure: Cannabis prefers well-drained, airy soils that allow their roots to breathe and expand. Heavy, compacted soils can restrict root growth and water drainage, leading to a deficiency of boron or excess. Adding organic matter or perlite can improve soil structure and aeration.
• Soil temperature: Cannabis roots thrive at temperatures between 15-30°C, with some growers claiming that 24°C is the ideal point. If the soil temperature is too low or too high, the roots may become stressed and unable to absorb nutrients properly, including boron.
• Calcium levels: Calcium and boron have a synergistic relationship in cannabis, meaning they work together to support plant functions such as cell wall formation and carbohydrate transport. However, too much calcium can interfere with boron absorption and cause a deficiency. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid using tap water or supplements that contain excess calcium.
• Humidity levels: Cannabis needs moderate humidity levels to maintain its transpiration and photosynthesis processes. However, very low humidity (below 25%) can reduce moisture availability and nutrient uptake, including boron. Using a humidifier or misting the plants can help increase humidity levels.
By paying attention to these factors, cannabis growers can ensure that their plants receive adequate boron and avoid nutrient deficiency or excess symptoms.
How to Identify a Deficiency of Boron?
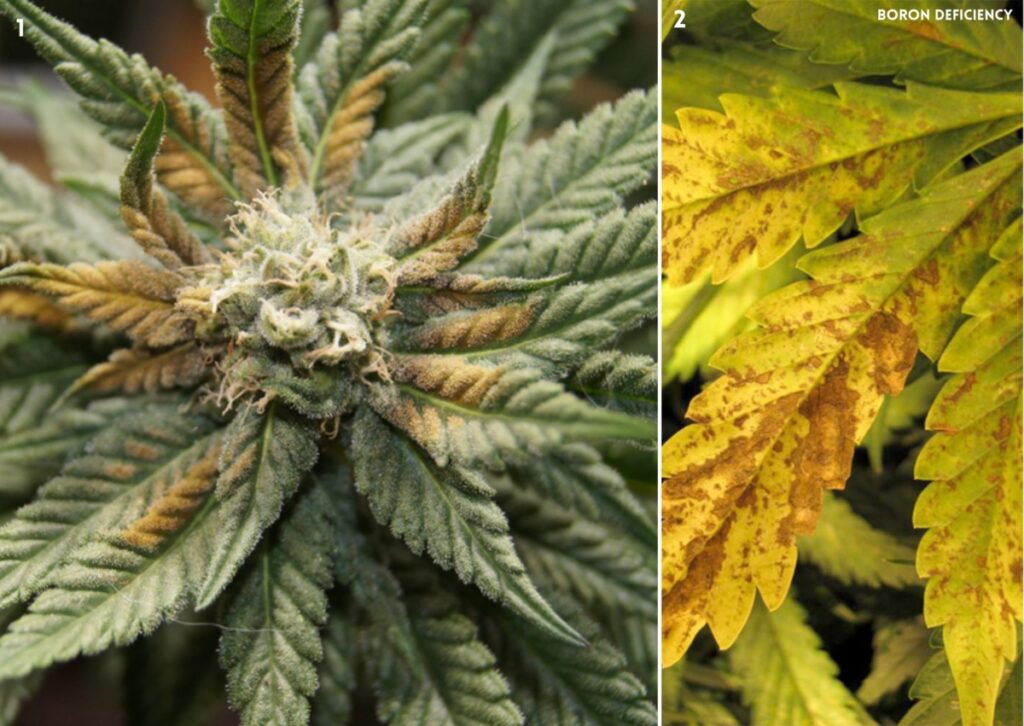

Boron is a vital micronutrient for plant health and growth, but it is often deficient in the soil. A deficiency of boron can cause serious problems for your plants, such as:
- Loss of turgor: Plants will lose vigor and vitality, wither and fall. This can be especially evident in cannabis, which is known for its lush and vibrant appearance.
- Reduced fertility: Plants will produce less pollen and have lower chances of pollination. The calyxes, which are the protective structures around the flowers, will develop small, brown, necrotic spots. The bracts, which are modified leaves that surround the flowers, will also show signs of damage.
- Impaired growth: Plants will have stunted and distorted growth at all stages, from vegetative to reproductive. The flowers, both male and female, will be poorly developed and may not form at all.
- Death of meristems: The meristems are the regions of the plant where new cells are formed and differentiated. They are essential for plant growth and development. A deficiency of boron can kill the meristems, leading to irreversible damage and loss of productivity.
What Are the Symptoms of Boron Deficiency in Plants?
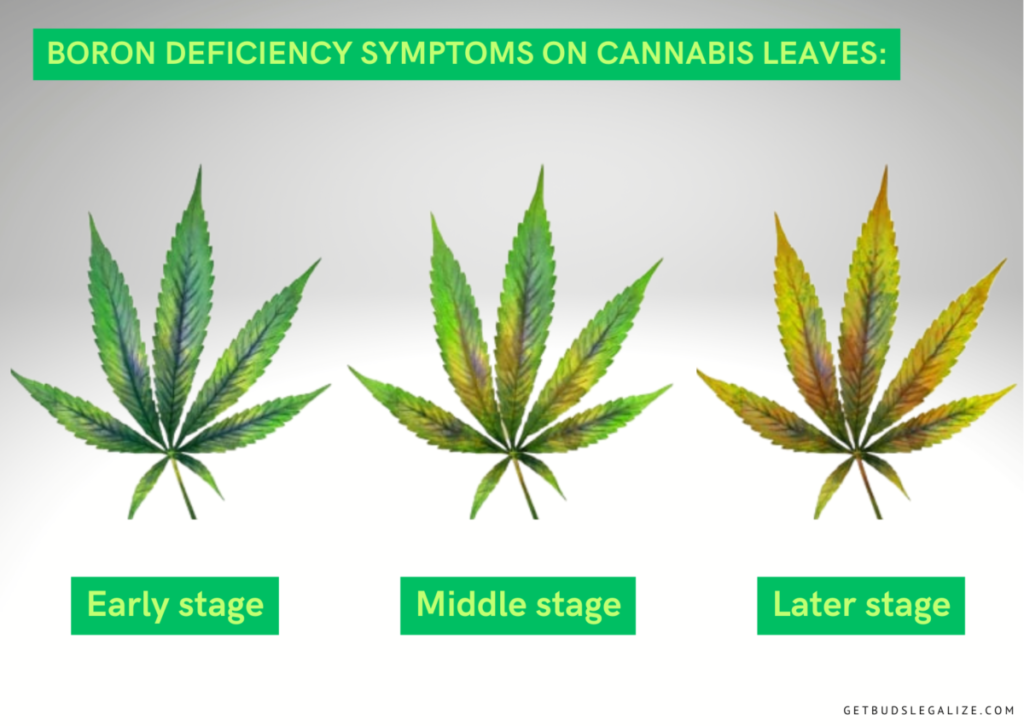
The deficiency of boron is a common problem that affects the plants of cannabis in different ways. Without enough boron, cannabis can exhibit various symptoms, such as:
- Distorted and stunted new growth: The new leaves and shoots may look twisted, curled, or burned. They may also have a bright green color. The new growth may die and fall off, resulting in a topped plant. The lateral branches may also be weak and discolored.
- Reduced vertical growth: The main stem and the branches may become thick and short, with a clustered appearance. The apical meristem may stop growing and producing new leaves.
- Droopy and wilted plant: The deficiency of boron affects the cell strength and structure of the plant, making it unable to support its own weight. The plant may droop and collapse over time.
- Soft and purple stems: The deficiency of boron interferes with the metabolic processes of the plant, causing a loss of vigor and vitality. The stems may become soft and purple, indicating a lack of nutrients and oxygen.
- Poor root development: The deficiency of boron impairs the root growth and function of the plant, leading to reduced uptake of water and nutrients. The main roots may die off and the secondary roots may be swollen and infected.
- Brown spots and necrosis on the leaves: The deficiency of boron causes damage to the leaf tissue, resulting in brown spots surrounded by dry areas. The spots may expand and cover the whole leaf, causing it to crumble and die.
How to Prevent Cannabis Boron Deficiency
The first step to prevent a cannabis boron deficiency is to ensure that your soil is healthy and well-balanced. Good soil should have:
- High-quality base: You can either purchase a premium soil mix from a reputable source or make your own super soil by combining organic matter, minerals, and amendments.
- Rich microbial life: You can boost the beneficial bacteria and fungi in your soil by using organic fertilizers (see below) or by adding products like Rhizobacter and Easy Roots Mycorrhiza Mix. These products contain ingredients that stimulate the growth of microorganisms that help your plants absorb nutrients, fight pests, and regulate pH.
- Suitable temperature range: The ideal soil temperature for marijuana plants is between 15–30°C. If the soil is too cold or too hot, it can affect the availability and uptake of boron and other nutrients.
- Proper watering schedule; You should avoid overwatering or underwatering your plants, as both can cause stress and nutrient lockout. Check the moisture level of your soil regularly and water only when the top few centimeters are dry.
- Correct pH level. The optimal pH range for growing cannabis in soil is between 6–7. Boron is most readily absorbed by the roots at a pH of around 6.5. You should monitor the pH of your soil, water, and nutrient solution frequently and adjust it if necessary.
The second step to prevent a deficiency of boron is to use high-quality fertilizers and supplements that provide your plants with all the nutrients they need, including boron. We recommend using organic nutrients and supplements such as worm castings, fish and bone meals, wood ash, guano, bokashi extracts, molasses, and more. These products have several advantages over synthetic fertilizers:
- They are slow-release and less likely to cause a nutrient burn or salt buildup in your soil.
- They enhance the overall health and vitality of your soil by feeding beneficial microorganisms.
- They contain trace elements and organic compounds that improve the flavor and aroma of your buds.
By following these two steps, you can prevent a deficiency of boron in your cannabis garden and ensure that your plants grow strong and healthy.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.
How to Treat Boron Deficiency in Plants
To treat a deficiency of boron, you should follow these steps:
- Confirm that your plants have boron deficiency by looking for the symptoms. Some common signs are twisted or curled new leaves, dying shoot tips, hollow or cracked stems, and poor fruit or flower formation. Different crops may have different symptoms, so check the specific signs for your plants.
- Find out what is causing boron deficiency in your plants. Some possible causes are low soil boron levels, high soil pH, low organic matter, excessive leaching, or overuse of nitrogen or potassium fertilizers. You can test your soil for boron content and pH using a soil test kit or send a sample to a laboratory for analysis.
- Apply boron fertilizer to your plants according to the recommendations for your crop and soil type. You can use organic sources of boron such as compost, manure, seaweed, or bone meal, or synthetic sources such as borax, boric acid, or sodium borate. You can apply boron as a soil amendment or as a foliar spray. Be careful not to apply too much boron, as it can be toxic to plants at high levels.
- Monitor your plants for improvement and adjust your boron application as needed. You should see some recovery within a few weeks after applying boron fertilizer. If not, you may need to apply more boron or address other factors that may be affecting your plants’ growth and health.
What is Cannabis Boron Toxicity?

The toxicity of boron is a condition that occurs when plants receive too much boron, a micronutrient that is essential for cell wall formation, carbohydrate metabolism, and flower development. Boron-toxicity can cause severe damage to the leaves, stems, and roots of your plants of weed, resulting in reduced growth, yield, and quality.
What Are the Symptoms of an Excess of Boron in Cannabis Plants?
The main sign of toxicity of boron is the appearance of necrotic lesions or nutrient burns on the leaves, which cannot be reversed. The leaves also age prematurely and fall off. The whole plant is impacted by toxicity, especially the roots, which may show stunted or damaged growth. In some cases, localized chlorosis may occur, but this is rare.
It can be difficult to distinguish the toxicity from the deficiency of boron, as both can cause leaf problems. However, a key difference is that the toxicity of boron causes black edges around the affected areas on the leaves, while the deficiency causes dry spots.
What Causes the Toxicity of Boron?
- Overapplication of boron-containing fertilizers or supplements
- High pH levels in the soil or growing medium reduce the availability of other nutrients and increase boron uptake
- Low humidity or drought stress reduces transpiration and increases boron concentration in plant tissues
- Poor drainage or waterlogging that impairs root function and causes a nutrient imbalance
How to Fix It?
- Flushing the soil or growing medium with plain water to leach out excess boron
- Adjusting the levels of the pH to the optimal range of 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics
- Reducing or eliminating boron-containing fertilizers or supplements and using balanced nutrient solutions
- Improving the environmental conditions by increasing humidity, watering regularly, and ensuring good drainage
How to Prevent It?
To prevent or correct the toxicity of boron, follow these steps:
- Reduce watering: Overwatering can cause boron to accumulate in the soil and roots. Water your plants less frequently and only when the soil feels dry.
- Flush your plants: Flushing your plants with pH-balanced water can help remove excess boron and other nutrients from the soil and roots. Flushing also allows your plants to absorb new nutrients more efficiently.
- Adjust the pH to optimal levels: The optimal pH range for cannabis plants is 5.5 to 6.5 for water and 6.0 to 7.0 for soil. Use a pH meter to check the levels of the pH before watering or feeding your plants. You can also use natural soil amendments, such as lime, dolomite, or coco coir, to balance the levels of the pH.
Bottom Line
Growing marijuana plants may seem easy, but it comes with some challenges, such as dealing with nutrient deficiencies, a problem that can damage your garden but can be prevented with a little care and attention.
Always check the quality of the soil and water your plants receive and make sure they have the right levels of pH. Following our guidelines will ensure you reap a pro crop.
Deficiency and Excess in Cannabis - FAQs
Boron is a micronutrient that plants need in small amounts for healthy growth and development. A deficiency of boron can cause various problems in your plants, such as reduced cell expansion, meristem death, and lower fertility.
A deficiency of boron can occur in soils that are acidic, sandy, or low in organic matter. To prevent or correct a deficiency of boron, plants can be fertilized with a complete micronutrient fertilizer or a boron supplement.
Boron is a micronutrient that is essential for the growth and development of cannabis. It plays a role in cell wall formation, sugar transport, flowering, and resin production.
A deficiency of boron can cause stunted growth, deformed leaves, poor bud formation, and reduced potency. Boron toxicity can cause leaf burn, yellowing, and necrosis. Cannabis growers should monitor the boron levels in their soil or nutrient solution and adjust them accordingly to avoid deficiency or toxicity.
To increase the boron level in your soil, you can apply organic matter such as compost, manure, or green manure crops. You can also use borax or boric acid as a fertilizer, but be careful not to overapply them as they can harm plants and soil organisms. A soil test can help you determine the optimal amount and frequency of boron application for your specific soil and crop needs.
Some boron deficiency symptoms are:
- Reduced growth and yield
- Deformed or twisted leaves and stems
- Brown or black spots on leaves and buds
- Hollow or cracked stems
- Poor root development

















