Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Phosphorus is one of the essential nutrients for cannabis plants, especially during the flowering phase when it helps produce large and potent buds. However, sometimes cannabis may suffer from a phosphorus deficiency, which can affect their health and yield.
By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of how to identify and treat this common problem in your cannabis garden.
What Are the Symptoms of Phosphorus Deficiency in Plants of Cannabis?

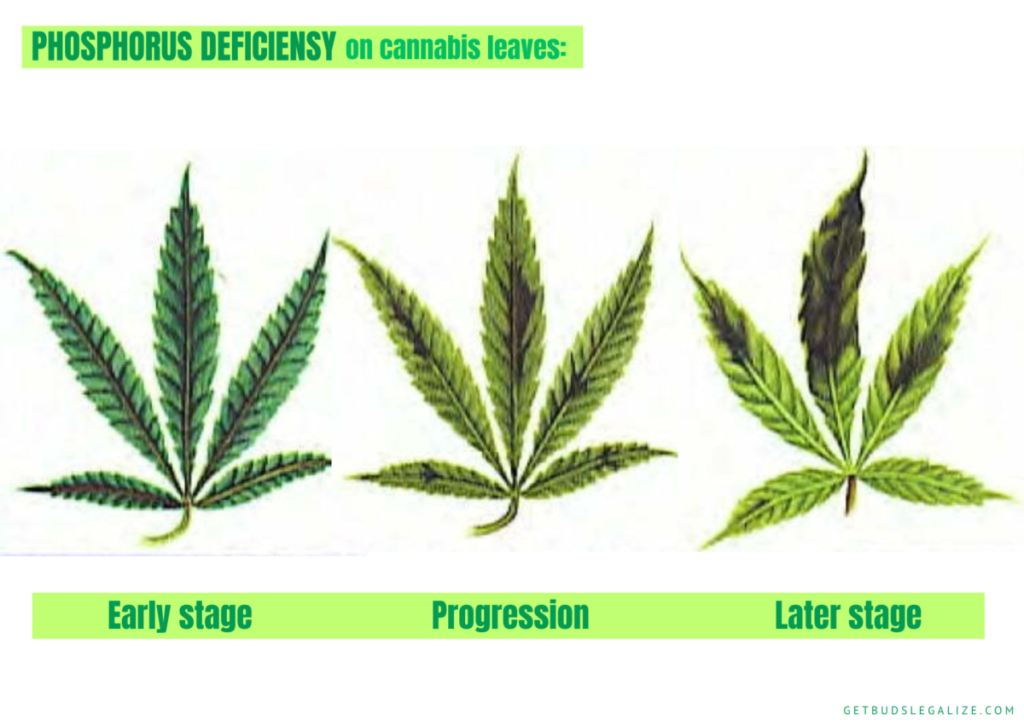
Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants usually affects the lower and older leaves first and then progresses to the upper and newer leaves if left untreated. The phosphorus deficiency symptoms include:
- Discoloration of leaves: The lower and older leaves may turn dark green, yellow, blue, gray, or purple. They may also develop brown, bronze, or purple spots or splotches.
- Dry or stiff leaves: The affected leaves may lose their flexibility and become brittle or crispy. They may also curl downwards or droop.
- Red or purple stems: The stems of the plant may change color from green to red or purple, especially on the underside. This may indicate a lack of phosphorus transport in the plant.
- Stunted growth: The plant may stop growing or grow very slowly. The buds may also be small, airy, or loose.
Phosphorus Deficiency vs Phosphorus Toxicity Symptoms
Phosphorus deficiency should not be confused with phosphorus toxicity, which is a rare condition that occurs when marijuana plants get excess phosphorus. The symptoms of Cannabis phosphorus toxicity are:
- Top leaves turn yellow or pale green, with yellow veins and burnt tips
- Thin blades on new leaves
- Leaves develop brown or black spots or necrosis
- Lower leaves curl
- Growth slows down or stops
What Causes Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis?
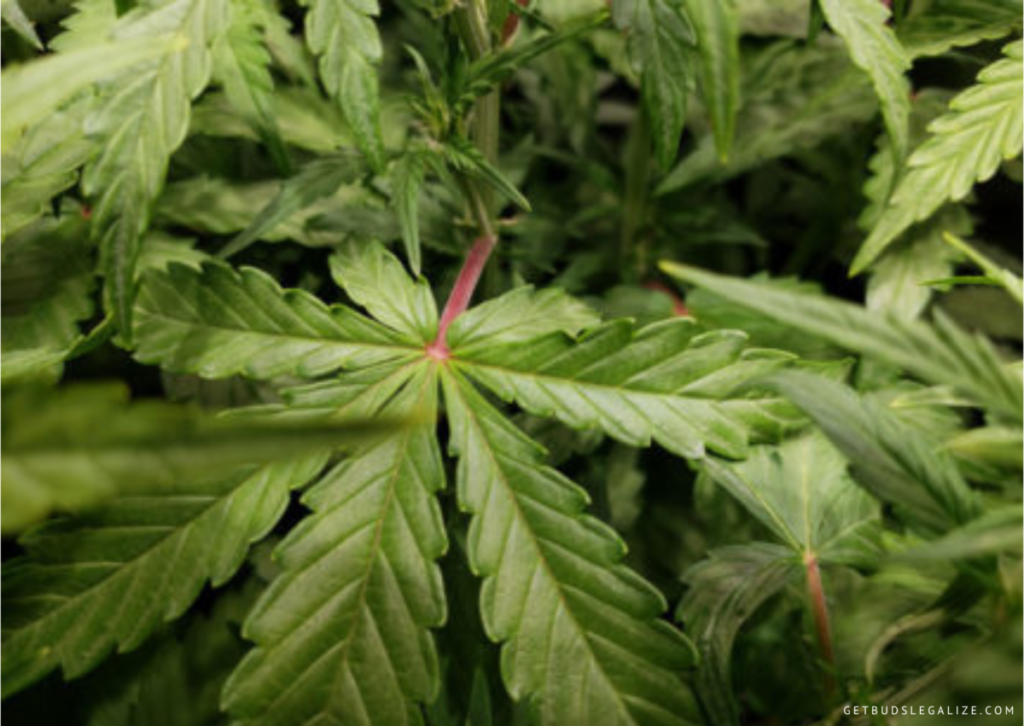
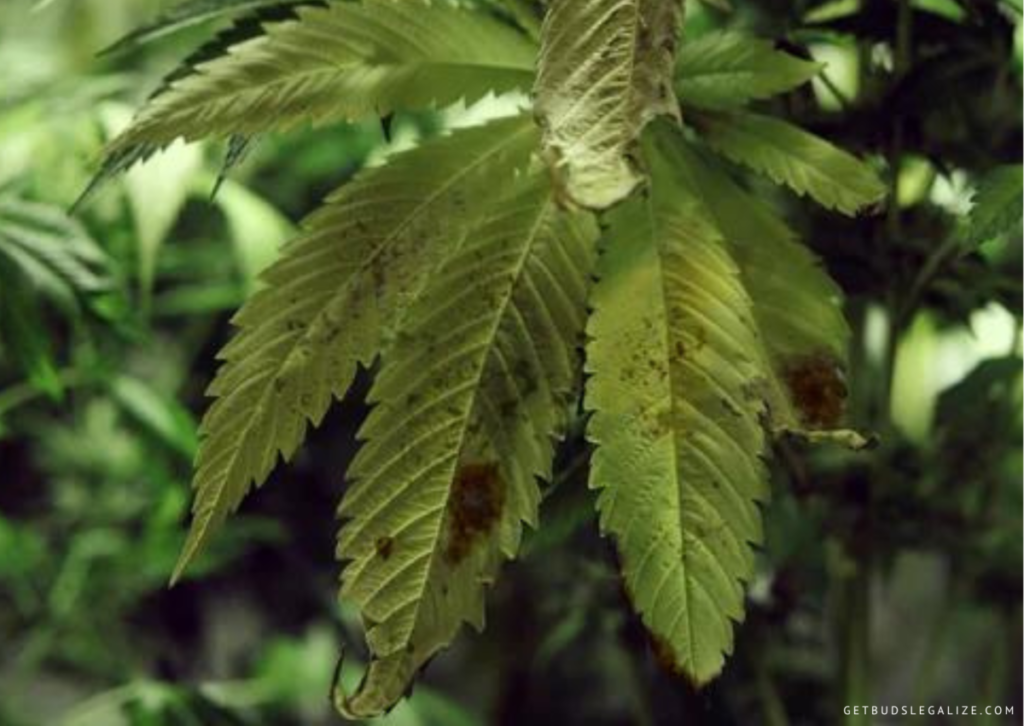


Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis occurs when the roots do not absorb enough of this nutrient from the soil or the nutrient solution. This can happen for several reasons, such as:
pH Imbalance:
The optimal pH range for cannabis plants to absorb phosphorus is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil, and 5.5 and 6.5 for hydroponics. If the pH is too high or too low, it can nutrient lockout from the roots. You can use a pH meter to test the pH of your water and nutrient solution and adjust it with pH up or down products if needed.
Low Temperature:
Cold temperatures can reduce the activity of the roots and slow down the uptake of phosphorus and other nutrients. The ideal temperature for growing cannabis is between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C). You can use a thermometer to monitor the temperature of your grow area and use heaters, fans, or air conditioners to regulate it if needed.
Overwatering:
Too much water can drown the roots and deprive them of oxygen, which can lead to root rot and nutrient deficiencies. You should water your plants only when the top inch of the soil feels dry, or when the pots feel light when lifted. You should also use well-drained soil or growing medium, and avoid compacting it too much.
Zinc or Iron Excess:
Too much zinc or iron can interfere with the absorption of phosphorus and other nutrients by creating insoluble compounds in the soil or solution. You should avoid using fertilizers that contain high amounts of zinc or iron, or use them sparingly and carefully. You should also flush your plants with plain water every few weeks to remove any excess salts or minerals from the soil or medium.
Low Phosphorus Availability:
Sometimes, your plants may simply not have enough phosphorus in their environment to meet their needs. This can happen if you use low-quality or depleted soil or grow medium, or if you use fertilizers that are low in phosphorus or not suitable for cannabis plants.
You should use high-quality soil or medium that is rich in organic matter and has a good balance of nutrients. You should also use fertilizers that are formulated for cannabis, especially during the flowering stage, when they need more phosphorus. You can look for cannabis nutrients that have a high second number in their N-P-K ratio, such as 10-30-10 or 5-15-5. You can also use organic sources of phosphorus, such as guano, bone meal, rock phosphate, or worm castings.
How to Prevent Phosphorus Deficiency?
The best way to prevent phosphorus deficiency in marijuana plants is to provide them with optimal growing conditions and balanced nutrients. Here are some tips to avoid this problem:
- Monitor your grow room temperature: Keep your grow area temperature within the ideal range for cannabis, between 68 and 75 degrees Fahrenheit. Avoid sudden temperature drops or fluctuations that can stress your plants and affect their nutrient uptake.
- Check your pH levels: Use a pH meter or test strips to measure the pH of your soil or nutrient solution regularly. Adjust it if needed using pH up or down products.
- Use quality nutrients: Choose nutrients that are designed for cannabis and contain adequate amounts of phosphorus. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and do not overfeed your plants. Flush your plants with plain water every few weeks to prevent nutrient buildup and salt accumulation in the soil or medium.
- Amend your soil: If you are growing cannabis in soil, make sure you use rich and well-drained soil that contains organic matter and phosphorus. You can also add compost teas or worm castings to boost your soil’s fertility and microbial activity.
How to Fix a Phosphorus Deficiency in Plants
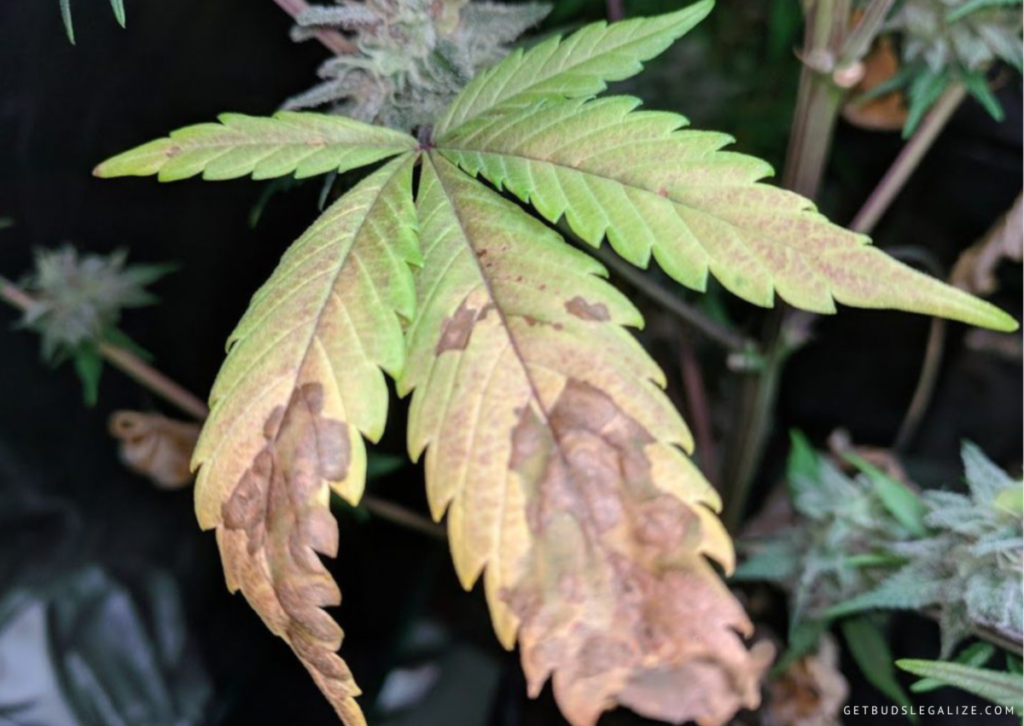

To correct phosphorus deficiency in marijuana, you should follow these steps:
- Flush your plants with clean, pH-balanced water that contains a regular dose of cannabis-friendly fertilizer that includes phosphorus. This will remove any excess salts or minerals that may interfere with phosphorus uptake and restore the nutrient balance in your soil or medium.
- Adjust your pH to the optimal range for cannabis, which is 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics. Use a pH meter to test your water and soil or medium regularly and add lime or vinegar to raise or lower the pH as needed.
- Maintain the right temperature for cannabis in your growing space or tent. Cold temperatures can slow down the metabolism and nutrient absorption of your plants, especially phosphorus. Aim for a temperature of 68 to 75°F (21 to 24°C) during the day and night.
- Use organic amendments to improve the soil structure, drainage, and microbial activity, which can enhance the overall health and vitality of your plants.
- Monitor your plants closely for any signs of improvement or worsening of the phosphorus deficiency. If you follow these steps, you should see your plants recover within a week or two. However, if the problem persists or gets worse, you may need to consult a professional grower or a reputable source of information for more guidance.
Natural Sources of Phosphorus:
Some of the most common sources are:
- Bone meal: Steamed bone meal and fish bone meal are excellent sources of mineral phosphorus that can be mixed with the soil or used as a top dressing. They are fast-acting and can provide up to 15% phosphorus by weight.
- Bat guano: Another excellent source of phosphorus for plants. It can be added to the soil or brewed into tea and applied as a foliar spray. It can provide up to 12% phosphorus by weight and also contains beneficial microbes.
- Manures: Animal manures such as chicken manure or pig manure make good sources of natural phosphorus that can be composted and added to the soil. They can provide up to 3% phosphorus by weight and also improve the soil structure and water retention.
- Rock phosphate: A slow-acting source of phosphorus. It can be crushed and mixed with the soil or used as a mulch. It can provide up to 30% phosphorus by weight and also contains calcium and other trace elements.
- Worm castings: The excrement of earthworms that can be added to the soil or used as tea. They can provide up to 0.3% phosphorus by weight and also contain nitrogen, potassium, humic acids, and beneficial microbes.
- Compost: A well-balanced compost made from organic materials such as kitchen scraps, grass clippings, leaves, and straw can provide a moderate amount of phosphorus as well as other nutrients and humus to the soil. It can provide up to 1% phosphorus by weight.
- Seaweed: A marine plant that contains a variety of minerals and trace elements that can enhance plant growth and resistance to stress. It can be used in fresh, dried, or liquid form as a soil amendment or foliar spray. It can provide up to 0.1% phosphorus by weight.
- Wood ash: The residue of burned wood that can be sprinkled on the soil or mixed with water and applied as a liquid fertilizer. It can provide up to 2% phosphorus by weight and also contains potassium, calcium, magnesium, and other micronutrients.
- Banana peels: This is a home remedy for phosphorus deficiency in plants and can be used by chopping and burying the peels directly into the soil near the roots of the plants. They decompose quickly and release phosphorus and potassium to plants. They also attract earthworms which improve soil quality.
- Phosphate-rich plants: Some plants such as barley, poppy seeds, sunflower seeds, buckwheat, and alfalfa are high in phosphorus and can be grown as cover crops or green manures to enrich the soil. They can also be harvested and fermented to make a liquid fertilizer.
By using these organic and eco-friendly options, you can avoid the environmental and health risks associated with synthetic fertilizers that contain high levels of phosphorus. You can also save money and resources by making your own fertilizers from plants or animals that you grow or gather yourself.
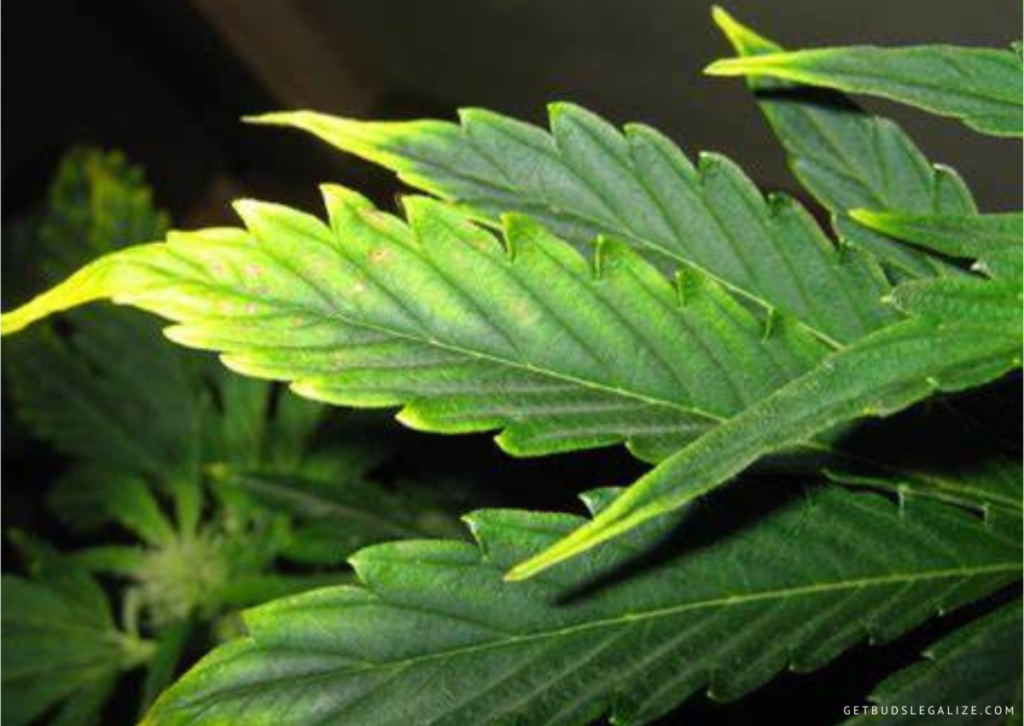
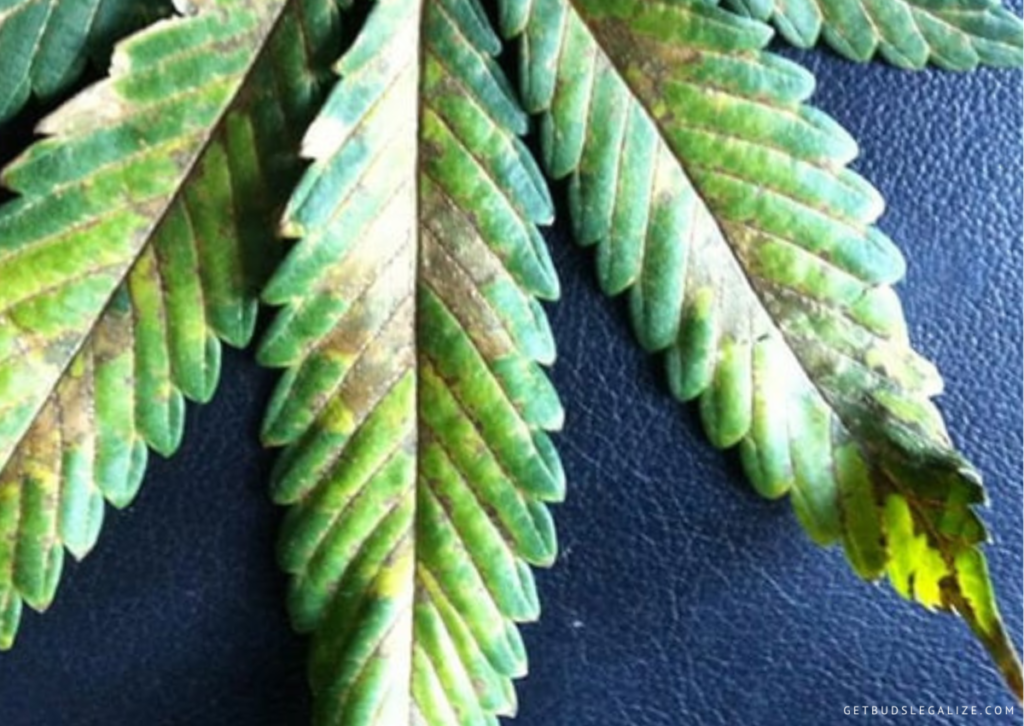


Is a Phosphorus Deficiency Really That Bad?
A phosphorus deficiency can have a significant impact on the health and productivity of your weed plants. Phosphorus is vital for the formation of buds and trichomes, which are the resin glands that contain THC and other cannabinoids. A lack of phosphorus can result in lower potency, flavor, and aroma of your cannabis.
Moreover, a phosphorus deficiency can weaken your plants and make them more vulnerable to other problems, such as pests, diseases, and environmental stress. A weak plant may not be able to recover from a severe deficiency and may die before harvest.
Therefore, it is important to monitor your plants regularly. If you notice any symptoms, act quickly and correct the issue before it gets worse.
How to Spot Phosphorus Deficiency – YouTube
Marijuana Deficiency Faq
Some of the symptoms of phosphorus deficiency are:
- Leaves turn to a blue-green or reddish-purple color, starting from the lower leaves
- Stems may also develop a purple hue
- Growth is stunted and slow
- Leaves may curl, develop brown or blue blotches, or die
- Seed formation and root growth are reduced
Some solutions are:
- Water your plants with a nutrient blend that includes phosphorus
- Don’t overwater or underwater your plants, as this can affect their root health and nutrient absorption
- Keep your plants warm by growing them indoors if possible or using heaters or insulation if necessary
- Correct the pH of your water and grow medium by using pH meters, testers, and adjusters
- Use organic sources of phosphorus such as guano, bone meal, or rock phosphate
Some of the symptoms of phosphorus deficiency are:
- Dark green or purple leaves with yellow or brown spots
- Lower leaves curling or dropping off
- Slow or stunted growth
- Reduced bud formation and quality
One of the challenges of growing marijuana is to identify and correct nutrient deficiencies that can affect the health and yield of the plants. Nutrient disorders can manifest as deficiency or toxicity symptoms, depending on whether the plant is receiving too little or too much of a certain element. To diagnose nutrient disorders in marijuana, it is important to observe the visual signs on the leaves and stems, as well as to measure the pH and nutrient concentrations of the soil or grow medium. Some common nutrient disorders are:
- A Nitrogen deficiency causes the yellowing of older leaves at the base of the plant, followed by curling and wilting. The plant may also become stunted and produce small buds.
- A Phosphorus deficiency causes dark green or purple leaves with brown spots or edges. The plant may also have weak stems and delayed flowering.
- A Potassium deficiency causes the yellowing or browning of leaf margins and tips, especially on younger leaves at the top and outer branches of the plant. The plant may also have reduced growth and bud size.
- A Calcium deficiency causes distorted or curled leaves with brown or yellow spots. The plant may also have poor root growth and bud rot.
- A Magnesium deficiency causes the yellowing or reddening of veins and interveinal areas on older leaves, as well as leaf curling and dropping. The plant may also have reduced resin production and susceptibility to pests.
To correct nutrient disorders, it is necessary to adjust the pH and nutrients of the soil or grow medium according to the specific needs of the plant. It is also advisable to use organic fertilizers and supplements that provide a balanced and complete range of nutrients for optimal growth.
Some of the symptoms are:
- Yellowing of the older and lower leaves, especially near the base of the plant
- Purple or Reddish stems
- Browning and wilting of the leaves
- Drooping and falling off of the leaves
- Pale or lime-colored appearance of the whole plant















