A Comprehensive Growing Guide Aeroponics Cannabis
In the field of cannabis cultivation, innovation knows no limits. From traditional soil methods to hydroponics and now aeroponics, enthusiasts are continually searching for the most efficient and effective ways to grow their plants.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of aeroponics, its benefits, setup, and tips for successful cannabis growing.
What Is Aeroponics?
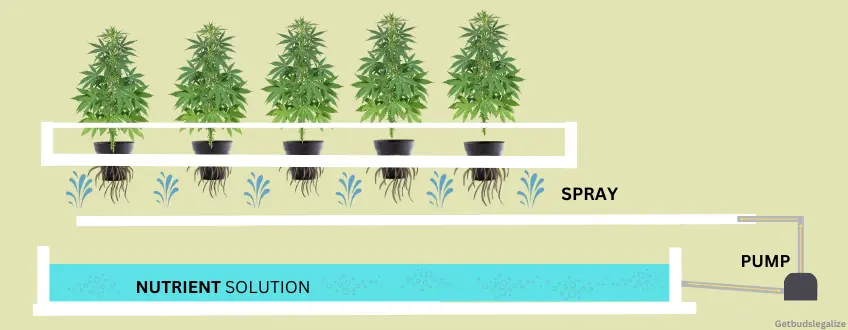
Aeroponics is an innovative soilless growing method that provides optimal oxygenation and nutrient absorption to plants. This cultivation technique involves suspending plant roots in a chamber where they are constantly sprayed with a solution rich in nutrients.
Unlike hydroponics, where the roots are submerged in water, aeroponics delivers nutrients through a fine mist. This ensures that the plants receive a sufficient amount of nutrients while maintaining an ideal level of oxygenation.
How Does Aeroponics Work?
In an aeroponic system, a high-pressure pump propels a nutrient solution through a network of misting nozzles, creating a fine mist that surrounds the plant’s roots. This mist provides ample oxygenation while delivering nutrients directly to the root zone, promoting rapid growth and development. The plant’s roots grow freely in the air and are not restricted by a growing medium, allowing maximum nutrient absorption and uptake.
The aeroponic system is perfect for growing various plants, vegetables, and herbs with high yield and quality, all while conserving water and nutrients.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Aeroponics Cultivation
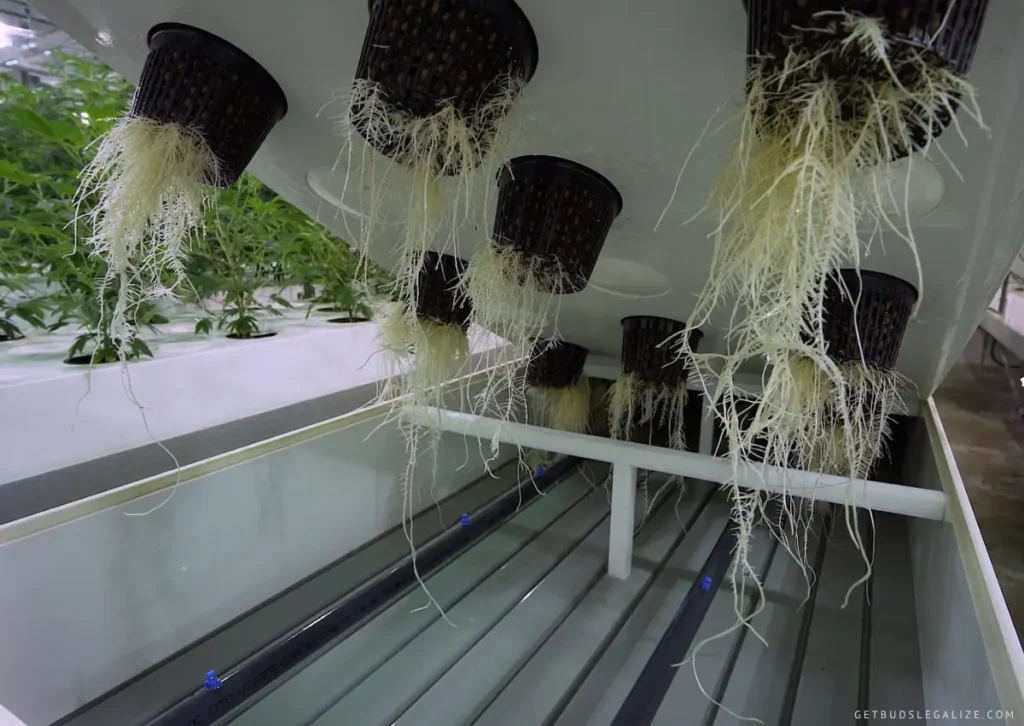

Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s delve into the advantages and disadvantages of using aeroponics to grow cannabis. While aeroponics may not be suitable for all growers, many will find it to be an exceptionally efficient and effective method.
Advantages Of Aeroponics For Cannabis:
1. Enhanced Oxygenation:
Creating a mist environment around plant roots is a great way to ensure easy access to oxygen. Oxygen is essential for root respiration and nutrient absorption. By providing this type of environment, roots can grow more robustly and efficiently, resulting in overall healthier and stronger plants.
2. Precise Control over Nutrients and Environment:
Aeroponic growing systems offer precise control over nutrient concentrations and environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and pH levels. This control allows growers to tailor conditions to the specific needs of their cannabis plants, optimizing growth and maximizing yields.
3. Water Efficiency:
Aeroponic growing systems are known for their efficient use of water compared to traditional soil growing methods or even hydroponics. This makes them a promising solution to water scarcity problems in many regions.
4. Space Optimization:
Aeroponic setups have the advantage of being compact, making them perfect for indoor growing. This feature is especially beneficial for those who have limited space to grow their crops.
5. Direct Nutrient Delivery to Roots:
Direct delivery of nutrients to roots is an effective way to promote rapid absorption and minimize nutrient waste. This method allows for efficient and targeted delivery of essential nutrients to the plants, ensuring their optimal growth and development. By providing nutrients directly to the roots, the plants can absorb them more readily, leading to better overall health and yield.
6. Reduced Risk of Pests:
Aeroponic growing systems are known for their ability to grow plants without the use of soil. One of the benefits of this method is that it significantly lowers the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases. As a result, plants grown in aeroponic systems tend to be healthier and less susceptible to damage from pests. This makes it a valuable technique for those looking to grow plants safely and sustainably.
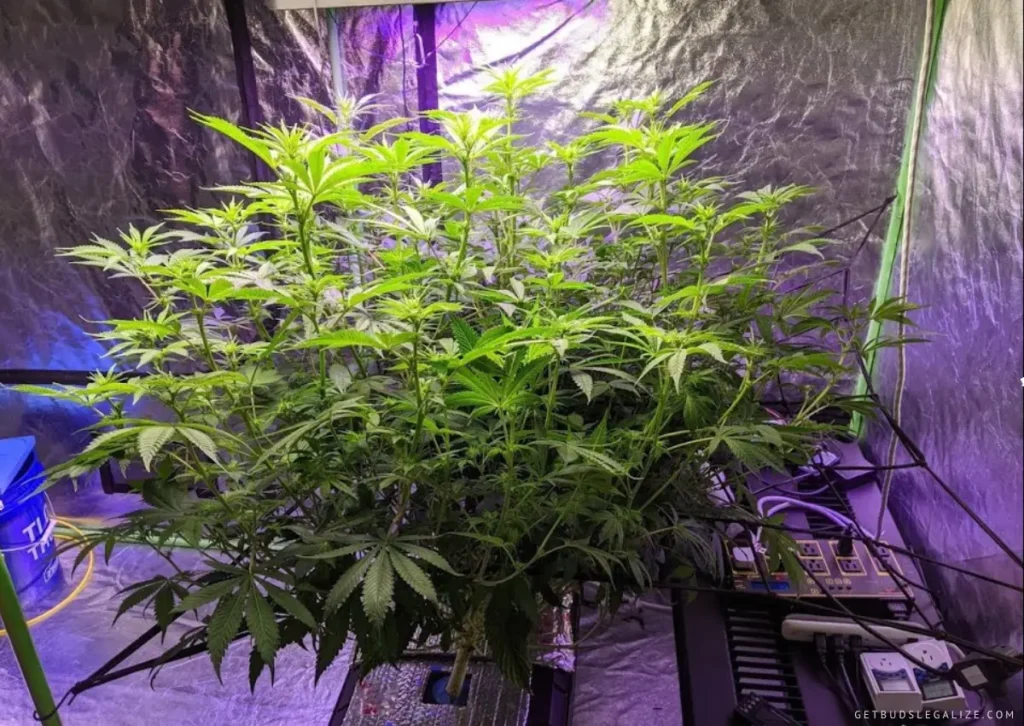

Disadvantages Of Aeroponics For Cannabis:
1. Not suitable for beginners:
Aeroponics requires a high level of precision and management, making it less forgiving to inexperienced growers. Novice growers may find it difficult to navigate the complexities of an aeroponic growing system, which could lead to potential errors and suboptimal results.
2. High initial cost:
A significant disadvantage of aeroponic farming is the substantial initial investment required for equipment and setup. The initial cost of purchasing aeroponic systems and specialized components can be prohibitive for growers on a limited budget, dissuading them from adopting this growing method.
3. Potential Errors:
The aeroponic growing system leaves little room for error, as any deviation from optimal conditions can quickly damage or even kill plants. Factors such as clogged spray nozzles, nutrient imbalances, or equipment malfunctions can have detrimental effects on plant health and growth. Growers must remain vigilant and proactive in addressing potential issues to safeguard the well-being of their cannabis plants.
4. Equipment management:
Maintaining an aeroponic growing system requires consistent and meticulous equipment management. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, calibration, and troubleshooting, is essential to ensure your system operates efficiently and effectively. Failure to properly manage equipment can lead to reduced performance and compromised plant health.
Hydroponics vs Aeroponics vs Aquaponics
Hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are three innovative soilless cultivation methods, each offering distinct advantages and considerations for growers.
- Hydroponics involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing direct access to essential nutrients for accelerated growth and higher yields.
- Aeroponics takes it a step further by suspending plant roots in a misty environment, ensuring optimal oxygenation and nutrient absorption.
- Aquaponics combines aquaculture and hydroponics, utilizing fish waste to fertilize plants, creating a symbiotic ecosystem.
While hydroponics excels in simplicity and efficiency, aeroponics offers precise nutrient delivery and oxygenation.
Correlated article:
How to Set Up a DIY Aeroponic System for Growing Cannabis: Step-by-Step Guide
Creating your aeroponic system for growing cannabis doesn’t have to break the bank. With a bit of DIY spirit and some basic materials, you can craft a simple yet effective setup to nurture your plants to their fullest potential. Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting up a one-bucket aeroponic growing system suitable for several medium-sized cannabis plants:
Materials and Tools Needed:
- 20-liter bucket with lid
- Threaded poly cut-off riser (30cm length, 1.25cm diameter)
- 360° sprinkler head (1.25cm or ½ inch)
- Hydroponic pump (capable of 1200l/hour, with matching 1.25cm thread)
- Electrical timer (allowing a constant 30mins on, 30mins off cycle)
- Hydroponic net pots with lids (quantity depending on desired plant count)
- Saw (for cutting the riser)
- Electric drill
- Hole saw attachment for drill (slightly smaller diameter than net pots)
- Safety glasses
- Marker
Instructions:
- Prepare the Bucket Lid: Use the hole saw attachment on your drill to create 3–8 holes in the bucket lid. Ensure these holes are slightly smaller than the diameter of your net pots, allowing for a snug fit. The number of holes depends on your desired plant count. Place the net pots into the holes.
- Install the Pump: Screw the threaded poly cut-off riser to the pump and cut it to the desired height using the saw. Attach the 360° sprinkler head on top of the riser.
- Connect the Pump: Run the pump plug through one of the net potholes on the lid. Plug it into the electrical timer. Set the timer to a constant 30-minute on, 30-minute off cycle. This cycle ensures the roots receive a misting for 30 minutes, followed by a resting period, maintaining optimal hydration and nutrient delivery throughout the growth cycle.
- Fill the Bucket: Add approximately 8 liters of water/nutrient solution to the bucket.
- Plant Placement: Insert your cannabis plants into the net pots.
- Completion: Congratulations! Your simple, cost-effective aeroponic setup is now ready to nurture your cannabis plants to their full potential.
Low-Pressure vs High-Pressure Aeroponics
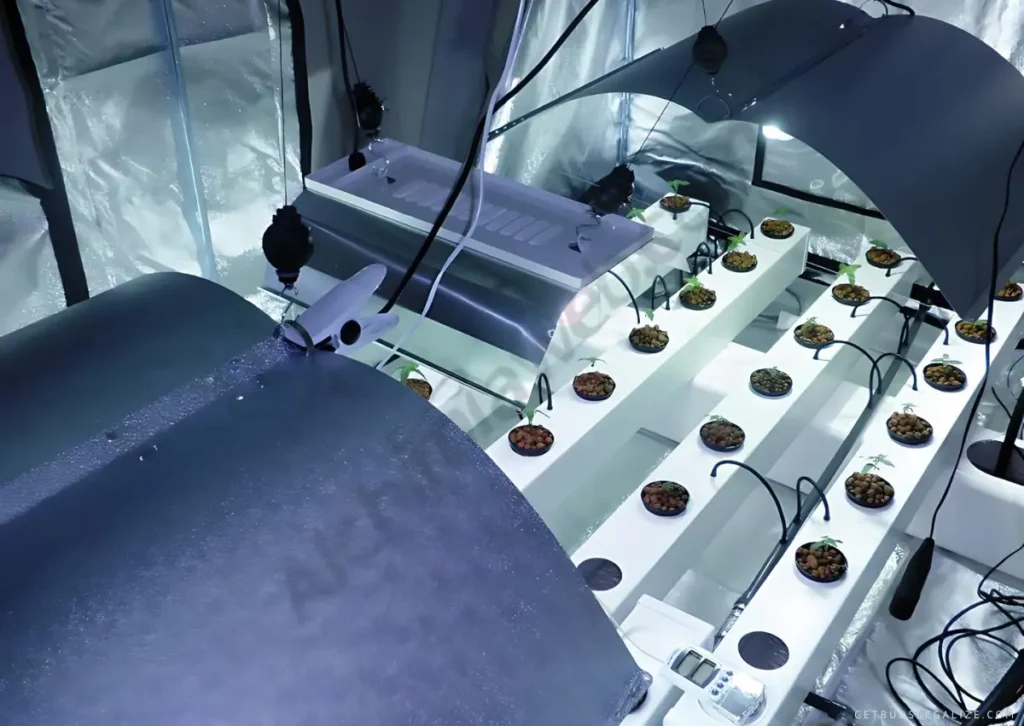

When it comes to aeroponic growing systems, one critical consideration for growers is whether to opt for a low-pressure or high-pressure setup. Each system has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and constraints.
Low-Pressure Aeroponic:
Low pressure aeroponic (LPA) systems typically operate at pressures ranging from 5 to 20 psi (pounds per square inch). These systems use a relatively low-pressure pump to deliver a fine mist of nutrient solution to the plant roots.
Advantages of LPA:
- Simplicity: LPA systems are generally simpler and easier to set up compared to high-pressure systems.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They tend to be more budget-friendly in terms of initial investment and operational costs.
- Reduced Risk of Clogging: Low-pressure misters are less prone to clogging, resulting in fewer maintenance issues.
- Energy Efficiency: LPA systems consume less energy compared to their high-pressure counterparts, making them more environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages of LPA:
- Less Precise Nutrient Delivery: Low-pressure misters may struggle to achieve uniform nutrient distribution, potentially leading to uneven growth.
- Lower Oxygenation Levels: The mist produced by low-pressure systems may not provide as much oxygen to the roots as high-pressure systems, potentially affecting plant health and growth rates.
High-Pressure Aeroponic:
High pressure aeroponic (HPA) systems operate at pressures exceeding 20 psi, often ranging from 80 to 100 psi or higher. These systems use high-pressure pumps to generate a fine mist with exceptional atomization.
Advantages of HPS:
- Enhanced Nutrient Delivery: HPA systems deliver nutrients with greater precision and uniformity, ensuring optimal nutrient absorption by the plant roots.
- Improved Oxygenation: The fine mist produced by high-pressure systems maximizes oxygenation of the roots, promoting vigorous growth and healthier plants.
- Faster Growth Rates: Plants grown in high-pressure aeroponic systems often exhibit faster growth rates and higher yields compared to low-pressure systems.
- Suitability for Advanced Growers: HPA systems are preferred by experienced growers who prioritize precision and efficiency in nutrient delivery.
Disadvantages of HPS:
- Complexity: High-pressure systems tend to be more complex and require meticulous setup and maintenance, which may be challenging for novice growers.
- Higher Costs: They typically involve higher upfront costs for equipment and installation, as well as increased energy consumption.
- Potential for Clogging: The fine mist produced by high-pressure systems may be more prone to clogging, necessitating regular maintenance and cleaning.
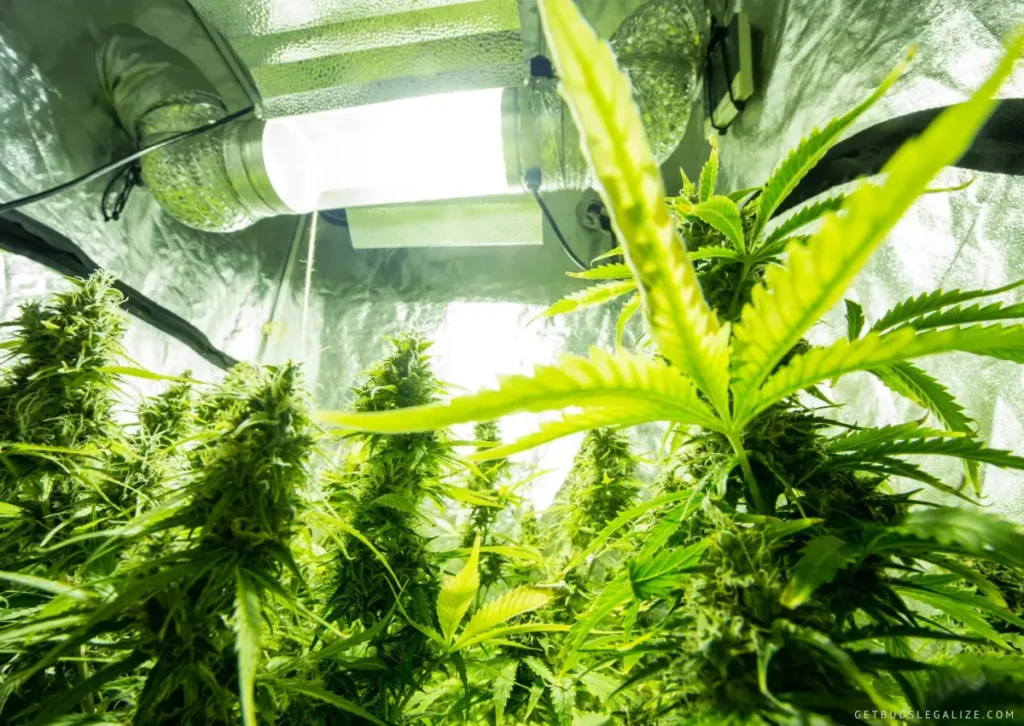

Aeroponics Tips and Tricks
Aeroponics offers a high-tech approach to cannabis cultivation, but mastering this method requires attention to detail and fine-tuning. Here are some essential tips and tricks to optimize your aeroponic cannabis grow:
1. Choose the Correct Grow Lights:
In aeroponic, maintaining optimal water temperature is crucial to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms. High-intensity discharge (HID) lights can elevate reservoir temperatures, increasing the risk of algae formation. Opt for cooler-running grow lights like LEDs or CFLs, which produce less heat. Full-spectrum LED lights are particularly effective for providing adequate light intensity while keeping temperatures within the desired range throughout the plant’s lifecycle.
2. Regulation and Optimization of Nutrient Levels:
Before embarking on your aeroponic grow, research the appropriate nutrient regimen for your cannabis plants. Manufacturers often recommend higher nutrient doses than necessary, so start with conservative doses and gradually increase as needed. Monitor plant response closely and adjust nutrient levels accordingly to avoid overfeeding or deficiencies.
3. Meticulously Monitor Aeroponic Conditions:
Aeroponic growing requires meticulous attention to maintain optimal conditions. Regularly monitor nutrient levels, water pH, and temperature to ensure a healthy environment for your plants. Any deviations from the optimal range can quickly impact plant health and growth. Use an electrical conductivity (EC) or total dissolved solids (TDS) meter to measure nutrient strength and make adjustments as needed. Additionally, maintain water pH between 5.5 and 6.5 and water temperature between 18–24°C for optimal nutrient uptake.
4. Optimize the Environment for Ideal Growing Conditions:
Maintaining a consistent room temperature of around 21°C is essential for maximizing cannabis yields. Extreme temperatures can hinder plant growth and lead to various issues. Invest in good air circulation to prevent hot spots and ensure adequate ventilation. While standing fans may suffice for smaller setups, consider installing a professional exhaust system with a carbon filter for larger operations to maintain optimal airflow and minimize odors.
Conclusion
Aeroponics offers a promising approach to cannabis cultivation, combining efficiency with optimal nutrient delivery. While it may require a higher initial investment and greater attention to detail, the rewards of healthy, high-yielding plants make it a worthwhile endeavor for dedicated growers.
By following the steps outlined in this guide and implementing best practices, you can embark on a successful journey of aeroponic cannabis cultivation.
FAQs about Growing Aeroponics Cannabis
Aeroponics is a soilless cultivation technique where plant roots are suspended in a misty environment and receive nutrients directly through the mist. This method promotes rapid growth and efficient nutrient absorption for cannabis plants.
Yes, aeroponics can be a highly effective method for growing cannabis at home, especially for indoor cultivation where space is limited.
Some advantages include faster growth rates, higher yields, reduced water usage, and fewer pest issues compared to traditional soil cultivation methods.
While aeroponics cultivation offers many benefits, it also requires careful monitoring of nutrient levels, maintenance of equipment, and a learning curve for beginners.
You’ll need a basic setup including a reservoir or bucket, a pump to deliver the nutrient solution, misters or sprayers to deliver the mist, and net pots to hold the plants.
Misting frequency can vary depending on factors like plant growth stage, environmental conditions, and nutrient solution concentration. Generally, plants are misted several times a day for short durations.
In an aeroponic growing system, cannabis plants require a balance of essential nutrients to support healthy growth and development. These nutrients include:
- Nitrogen (N): Vital for vegetative growth, nitrogen plays a key role in chlorophyll production and overall plant vigor.
- Phosphorus (P): Essential for root development, flowering, and fruiting, phosphorus is crucial during the transition from vegetative to flowering stages.
- Potassium (K): Important for overall plant health, potassium regulates water uptake, enhances stress tolerance, and promotes flower formation and resin production.
- Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg): These secondary nutrients are essential for cell structure, enzyme activation, and nutrient uptake, ensuring robust plant growth.
- Sulfur (S): Necessary for protein synthesis and chlorophyll formation, sulfur aids in nutrient absorption and plant metabolism.
- Micronutrients (Boron, Copper, Iron, Manganese, Zinc, etc.): Although required in smaller quantities, micronutrients are critical for enzyme activity, photosynthesis, and overall plant health.
It’s essential to provide cannabis plants with a well-balanced nutrient solution tailored to their specific growth stage. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels, pH, and plant health is crucial to prevent deficiencies or nutrient imbalances. Adjusting nutrient concentrations based on plant responses and growth stage requirements helps ensure optimal nutrient uptake and maximize crop yields.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning the misting nozzles and ensuring proper filtration of the nutrient solution, can help prevent clogs and ensure consistent nutrient delivery to the plants.
Yes, aeroponics can be used throughout the entire growth cycle of cannabis plants, from seedling to flowering stages, with appropriate adjustments to nutrient levels and misting schedules.
Cannabis plants thrive in temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C) with relative humidity levels between 40-60%. Adequate airflow and ventilation are also important to prevent mold and maintain optimal plant health.
Whether aeroponics is better than hydroponics depends on various factors and the specific needs of the grower and plants.
Aeroponics offers advantages such as efficient nutrient absorption, enhanced oxygenation, and reduced water usage. It can result in faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based methods. Additionally, aeroponic growing systems are less prone to certain pests and diseases associated with soil.
On the other hand, hydroponics is a well-established and widely-used cultivation method known for its simplicity, versatility, and proven effectiveness. Hydroponic systems are relatively easy to set up and maintain, making them suitable for beginners and experienced growers alike. They also provide precise control over the delivery of nutrients and the management of environmental factors.
Ultimately, the choice between aeroponics and hydroponics depends on factors such as grower experience, available resources, space constraints, crop type, and specific goals. Some growers may prefer the efficiency and advanced technology of aeroponics, while others may opt for the familiarity and reliability of hydroponics.
When adding nutrients to aeroponic clones, it’s essential to wait until the clones have developed a healthy root system. This typically occurs once the clones have successfully rooted and started to show signs of new growth.
Once roots are established, gradually introduce a diluted nutrient solution into the aeroponic system. Start with a lower concentration of nutrients to avoid overwhelming the young plants, as they may be sensitive to nutrient levels initially.
Regularly monitor the health and growth of the clones, adjusting the nutrient concentration as needed based on their development. Aim to maintain a balanced nutrient solution that meets the specific needs of the clones and supports healthy growth without causing nutrient burn or other issues.
Aeroponics was pioneered in the 20th century, with notable advancements made by NASA in the 1980s for space-bound agriculture. Since then, it has gained traction in commercial and home cultivation settings for various crops, including cannabis.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.






















