Cannabis Iron Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes, and Solution
Iron is an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants, as it plays a vital role in the production of chlorophyll and other enzymes. Chlorophyll is the green pigment that gives plants their color and allows them to perform photosynthesis, the process of converting light into energy. Without enough iron, marijuana plants will suffer from reduced growth, lower yields, and poor-quality buds.
In this blog post, we will explain what the symptoms are, the common causes, and how to fix it quickly and effectively on your marijuana plants.
What Are The Symptoms of Iron Deficiency in Plants?
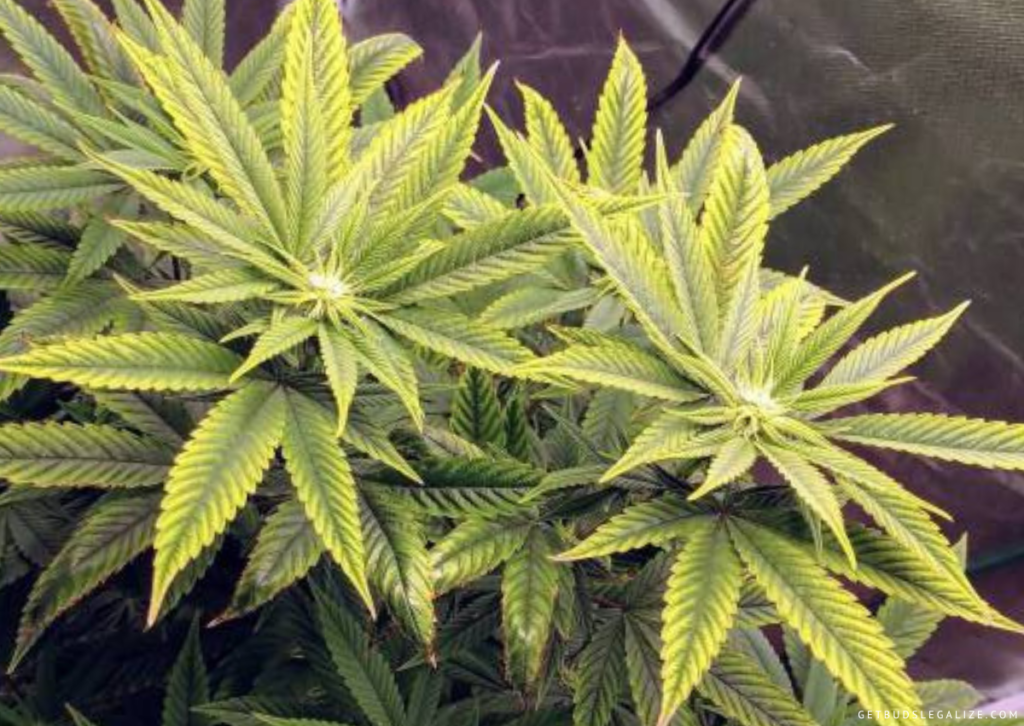
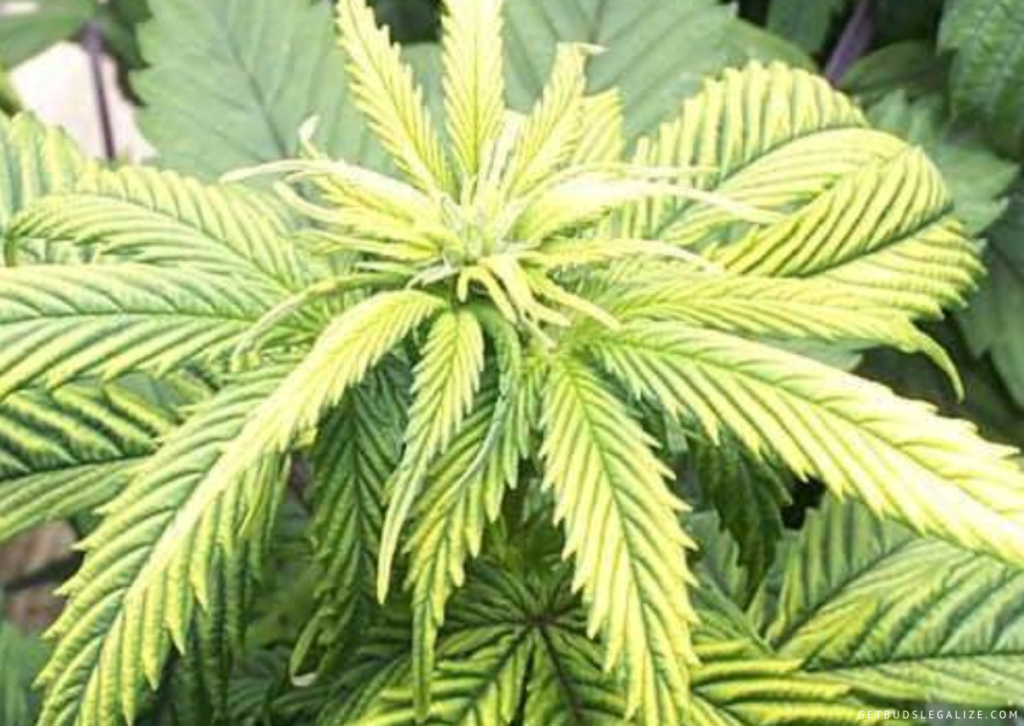


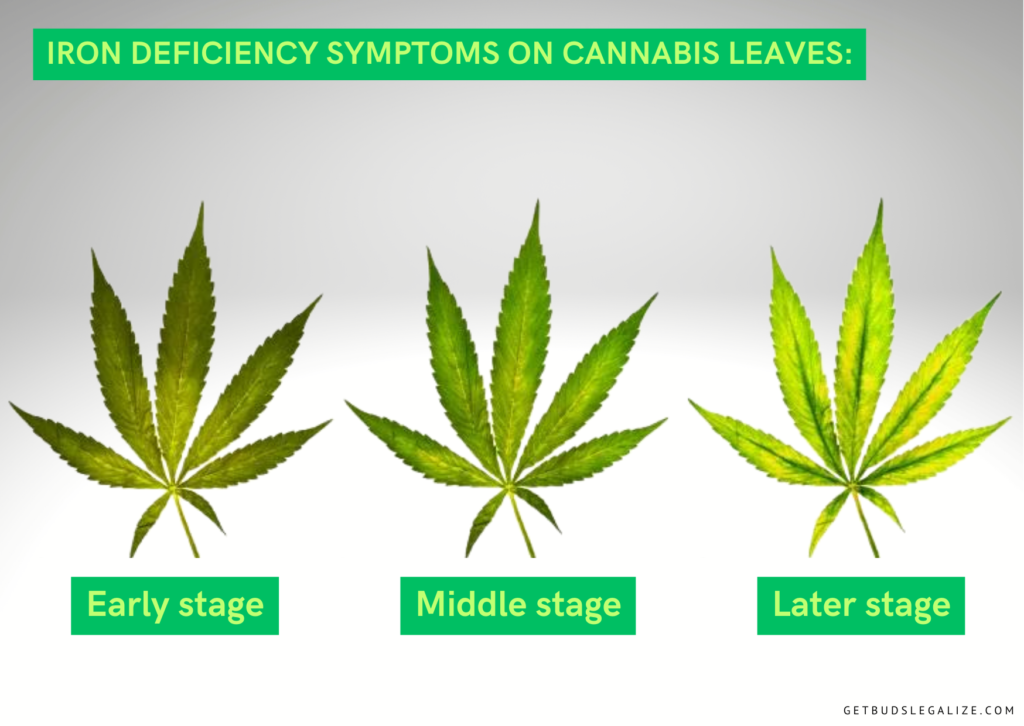
A deficiency of iron usually affects the newest leaves first, as iron is not a mobile nutrient and cannot be easily transported from older to younger leaves. The main symptom of iron deficiency is the yellowing or whitening of the new growth, while the veins remain green. This is called interveinal chlorosis and it can be easily confused with other nutrient deficiencies or pH problems.
The yellowing or whitening of the new leaves may be more pronounced on the tips or edges, or it may affect the whole leaf. Sometimes, the affected leaves may turn green again as they mature, starting from the tips and moving inward. This is a characteristic sign of iron deficiency, as most other nutrient deficiencies cause permanent damage to the leaves.
However, if the iron deficiency is severe or prolonged, the affected leaves may die and fall off, leaving bare stems. The plant may also develop brown spots or necrosis on the leaves or stems. The overall growth and vigor of the plant will be reduced, and the buds will be smaller and less potent.
What Are The Common Causes of Iron Deficiency in Cannabis Plants?
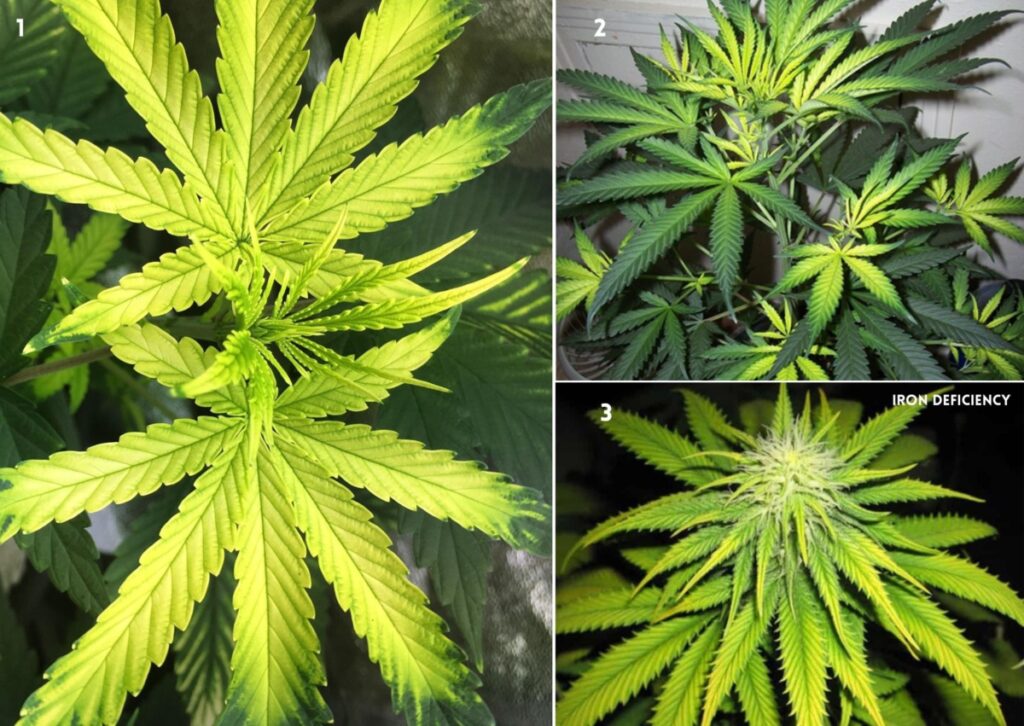

Cannabis iron deficiency can be caused by several factors, such as:
- Bad soil drainage: If the soil is too compacted or waterlogged, it can prevent oxygen from reaching the roots and affect their ability to absorb nutrients, including iron.
- Excess minerals: If the soil or water contains too much calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, or phosphorus, they can compete with iron for uptake by the roots and cause a deficiency.
- Overwatering: If the plants are watered too frequently or too much, it can cause root rot and reduce their ability to absorb nutrients, including iron. Overwatering can also lower the pH of the soil or water, which affects iron availability.
- Using coco coir: Coco coir is a popular growing medium for cannabis plants, but it can naturally bind to iron and make it unavailable for plants. This can be prevented by using a coco-specific nutrient solution or adding iron chelate to the water.
- PH imbalance: The pH level of the soil or water affects the availability of nutrients for the plants. If the pH is too high or too low, it can lock out iron and cause a deficiency. The optimal pH range for cannabis plants in soil is 6.0-7.0, while in coco coir or hydroponics, it is 5.5-6.5.
How To Fix Iron Deficiency In Plants?
The good news is that a deficiency of iron can be easily corrected if detected early and treated properly. Here are some steps you can take to treat iron deficiency:
1. Flush Your Plants:
The first thing you should do is flush your plants with plenty of water to remove any excess salts or minerals that may be interfering with iron uptake. Then, feed your plants with a balanced nutrient solution that contains enough iron for cannabis to grow. You can use a general-purpose fertilizer or a specific one designed for cannabis plants. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how much and how often to feed your plants.
2. Adjust pH To The Correct Range:
Check and adjust the pH of your growing medium or water to the optimal range for marijuana. In soil, iron is best absorbed in the PH range of 6.0 – 7.0 pH, and In hydro and coco coir in the PH range of 5.5 – 6.5 pH. You can use a pH meter or test kit to measure and adjust the pH of your medium or water. You can use pH up or down solutions to raise or lower the pH as needed.
3. Add Plant Nutrients:
There are several ways you can add more iron to your plants, such as:
- Spray with iron chelate: Iron chelate is a form of iron that is more readily available and soluble for plant uptake. You can spray your plants with a foliar spray containing iron chelate once or twice a week until you see improvement. Make sure to spray both sides of the leaves and avoid spraying during direct sunlight or high temperatures.
- Use soil additives: You can also use some organic soil fertilizers that can provide iron to your plants, such as blood meal, bone meal, fish meal, compost, worm castings, etc. These additives can also improve the soil structure and microbial activity, which can enhance nutrient availability and absorption. You can mix these additives into your soil before planting or top-dress your plants with them during the vegetative or flowering stage.
- Use iron supplements: You can also use some iron supplements that are specially formulated for cannabis plants, such as Cal-Mag Plus, Ironite, FeED, etc. These supplements can provide iron and other micronutrients that can boost your plant’s health and performance. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how much and how often to use these supplements.
6. Take Good Care of The Roots:
The roots are the main organ that absorbs nutrients and water from the soil or solution, so it is important to take good care of them. You can do this by:
- Avoiding overwatering or underwatering your plants: Overwatering or underwatering your plants can cause stress and damage to the roots, affecting their ability to absorb nutrients and water. You should water your plants when the top inch of the soil feels dry to the touch, or when the pots feel light when lifted. You should also make sure that the water drains well from the bottom of the pots and that there is no standing water in the saucers or trays.
- Providing adequate aeration and drainage: Aeration and drainage are essential for healthy root growth and function. You should use a well-aerated and well-drained medium that allows oxygen and water to reach the roots. You can use perlite, vermiculite, coco coir, clay pebbles, etc. to improve the aeration and drainage of your medium. You should also use pots with holes at the bottom and place them on a rack or stand that allows air circulation under the pots.
- Controlling the temperature and humidity: Temperature and humidity can also affect root health and plant nutrient uptake. You should keep the temperature in the grow room between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F) and the humidity between 40% and 60%. You can use fans, heaters, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, etc. to keep these factors under control and archive perfect conditions.
- Preventing pest or disease infestation: Pest or disease infestation can also harm the roots and reduce their ability to absorb nutrients and water. You should inspect your plants regularly for any signs of pest or disease infestation, such as yellowing, wilting, curling, spots, holes, webs, etc. You should also keep your grow room clean and sanitized, remove any dead or diseased plant material, avoid overwatering or overcrowding your plants, use organic pesticides or fungicides if needed, etc.
7. Watch for Recovery:
After applying any of the above methods, you should monitor your plants closely and look for signs of recovery. The new growth should be green and healthy, while the older leaves may remain yellow or die off. You can prune off any dead or damaged leaves to improve airflow and appearance. It may take a few weeks for your plants to fully recover from iron deficiency and resume their normal growth and flowering.
How To Prevent Cannabis Iron Deficiency?

The best way to prevent cannabis iron toxicity and deficiency is to provide them with optimal growing conditions and a balanced nutrient regimen. Here are some tips to prevent iron deficiency:
1. Use Quality Soil or Grow Medium:
Use a high-quality soil or grow medium that has good drainage, aeration, and water retention properties. Avoid using cheap or low-grade soil that may have pH problems or nutrient imbalances.
2. Use Filtered Water:
Use filtered water or rainwater to water your plants, as tap water may contain chlorine, fluoride, or other minerals that can affect your pH or nutrient availability.
3. Use Organic Fertilizers:
Use organic fertilizers that are rich in micronutrients and beneficial microbes that can improve your soil health and nutrient uptake. Avoid using synthetic fertilizers that may contain salts or heavy metals that can cause nutrient lockout or toxicity.
4. Monitor Your Plants Regularly:
Monitor your plants regularly for any signs of stress or nutrient deficiency. Check the color, shape, and texture of your leaves and the pH and temperature of your water and soil. If you notice any plant problems, act quickly to diagnose and treat them before they get worse.
Bottom Line
Cannabis iron deficiency can be a serious issue if left untreated, but it can also be easily prevented and cured with proper care and attention. By following these steps, you can ensure that your plants have enough iron to grow healthy and produce high-quality buds. Thank you for reading! Happy Growing!
FAQs
There are different types of iron supplements available for plants, such as chelated iron, iron sulfate, and iron gluconate. Chelated iron is the most effective form, as it is more readily absorbed by the plant roots and less affected by pH fluctuations. Iron sulfate and iron gluconate are cheaper alternatives, but they are less stable and more prone to precipitation. You can find iron supplements in liquid or granular form, depending on your preference and application method.
- Chelated iron is a form of iron that is bound to an organic molecule, such as EDTA or DTPA. This makes it more soluble and available for the plant roots, even at high pH levels. It is also more resistant to oxidation and precipitation, which can reduce its effectiveness. Chelated iron is usually more expensive than other forms of iron, but it is also more efficient and reliable.
- Iron sulfate is a form of iron that is combined with sulfuric acid. It is a common source of iron for plants, as it is cheap and widely available. However, iron sulfate has some drawbacks, such as its low solubility and stability at high pH levels. Iron sulfate can also react with other nutrients or minerals in the soil or water, forming insoluble compounds that are not available for the plant roots. Iron sulfate can also cause acidification of the soil or water, which can affect the pH balance and nutrient availability.
- Iron gluconate is a form of iron that is derived from glucose. It is a natural and organic source of iron for plants, as it is biodegradable and environmentally friendly. However, iron gluconate has some limitations, such as its low stability and solubility at high pH levels. Iron gluconate can also be easily oxidized or precipitated by light or oxygen, which can reduce its effectiveness. Iron gluconate is usually cheaper than chelated iron, but more expensive than iron sulfate.
The first sign of a deficiency of iron is the yellowing of the young leaves, especially between the veins. This is called interveinal chlorosis, and it occurs because the plant cannot produce enough chlorophyll. The veins remain green, creating a contrast with the pale leaf tissue. The affected leaves may also become thin, brittle, and curled.
If left untreated, a deficiency of iron can spread to the older leaves and affect the whole plant. The yellowing may become more severe, and the leaves may develop brown spots or necrosis. The plant may also show signs of stunted growth, reduced branching, and lower bud production. In extreme cases, the plant may die.
Yes, a plant can recover from a deficiency of iron if it is detected and corrected early. The best way to treat a deficiency of iron is to adjust the pH of the medium, as this affects the availability of iron for the plant. The optimal pH range for cannabis is 6.0 to 7.0 for soil and 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics or coco coir. If the pH is too high or too low, it can lock out iron and other nutrients from the plant. You can use pH meters, pH strips, or pH drops to measure and adjust the pH of your medium. You can also use products such as elemental sulfur, vinegar, or lemon juice to lower the pH, or lime, baking soda, or wood ash to raise the pH.
In addition to adjusting the pH, you can also apply an iron supplement to your cannabis plants, either as a foliar spray or a root drench. Follow the instructions on the product label and avoid overfeeding your plants, as this can cause a nutrient burn or other imbalances. You should see an improvement in your plants within a few days or weeks after applying an iron supplement.
Coco coir is a popular growing-medium for cannabis, as it offers many benefits such as high water retention, good aeration, and natural pest resistance. However, coco coir also has some drawbacks, such as its tendency to lock out iron at high pH levels. To treat it, you need to do the following steps:
- Check and adjust the pH of your water and nutrient solution. The optimal pH range for coco coir is 5.5 to 6.5. If your pH is too high, you can lower it by adding some acid, such as lemon juice or vinegar. If your pH is too low, you can raise it by adding some base, such as baking soda or lime.
- Flush your coco coir with plain water or a mild nutrient solution to remove any excess salts or contaminants that may interfere with iron uptake.
- Apply an iron supplement to your plants according to the manufacturer’s instructions. You can use a foliar spray or a soil drench, depending on your preference and convenience. A foliar spray is faster and more direct, but it may cause leaf burn if applied under strong light or high temperature. A soil drench is slower but more thorough, but it may cause nutrient runoff if applied too much or too often.
- Monitor your plants for signs of improvement or worsening. You should see some improvement within a week or two after applying an iron supplement. If not, you may need to repeat the treatment or adjust the dosage. If you see any signs of worsening, such as leaf burn or nutrient toxicity, you may need to stop the treatment or flush your coco coir again.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.

















