How to Fix Copper Deficiency in Cannabis Plants (Cu): Symptoms and Solution
Copper is an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants. It plays a role in many enzymatic reactions, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and lignin synthesis. Copper also helps the plant to cope with stress and disease resistance.
However, too much or too little copper can cause plant problems. This blog post will explain what causes copper deficiency in cannabis, how to identify it, and how to prevent and treat it.
What Causes Copper Deficiency in Cannabis?
A deficiency of copper in cannabis can be caused by several factors, such as:
- PH imbalance: Copper availability decreases as the pH of the growing medium drops below 6.0. This can happen if you use acidic water or nutrients, or if you over-fertilize your plants with nitrogen or phosphorus.
- High phosphorus: Excessive phosphorus levels can interfere with copper absorption by cannabis plants, especially in hydroponic systems. Phosphorus can also form insoluble compounds with copper in the soil, making it unavailable for plant roots.
- Excessive iron or zinc: Excessive amounts of zinc or iron can interfere with copper uptake by competing for the same transporters in the plant roots. This can happen if you use tap water that contains high levels of these metals, or if you use supplements that are rich in zinc or iron.
- Poor soil quality: Copper deficiency can also occur if your soil is depleted of organic matter, which is a natural source of copper and other micronutrients. This can happen if you reuse the same soil for multiple crops without replenishing it with compost, worm castings, or other organic amendments.
What Are the Copper Deficiency Symptoms?
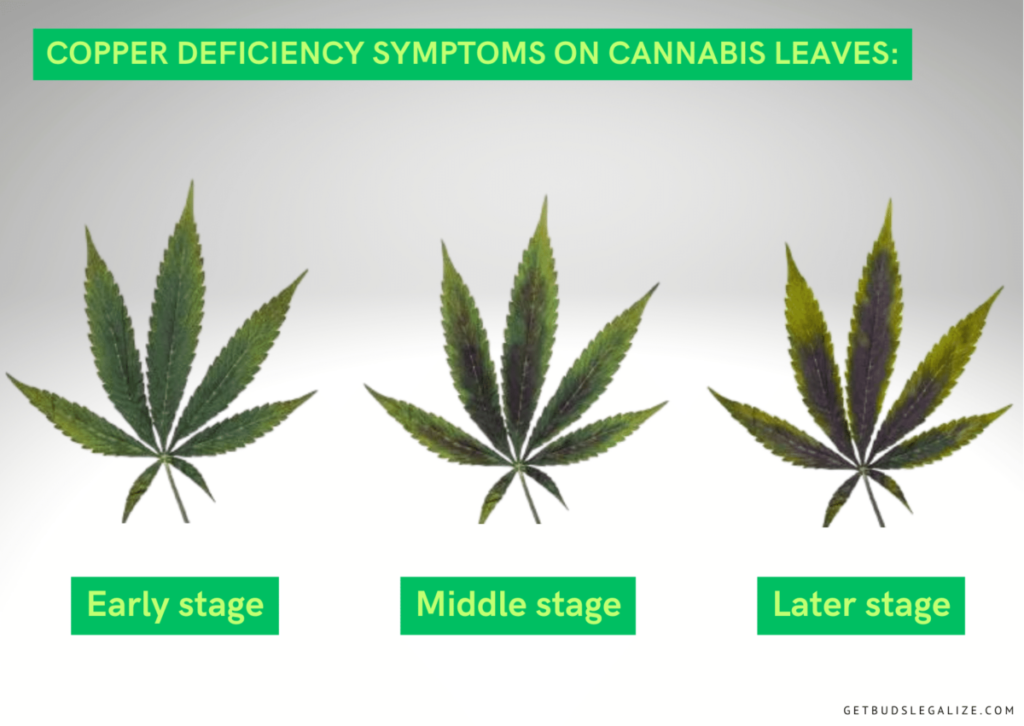
Copper deficiency in weed plants can affect their overall health and productivity. Some of the plant symptoms of copper deficiency are:
- Leaves turn dark with blue or purple undertones
- Tips and edges of leaves turn bright yellow or white
- Shiny or metallic sheen on leaves
- Leaves may feel stiff and start turning under
- Tends to affect leaves directly under the light
- Buds do not ripen, or grow very slowly
Copper deficiency can have a negative impact on the health and yield of cannabis plants, especially during flowering. Therefore, it is important to identify and treat it as soon as possible.
How to Prevent and Fix Cannabis Copper Deficiency in Cannabis
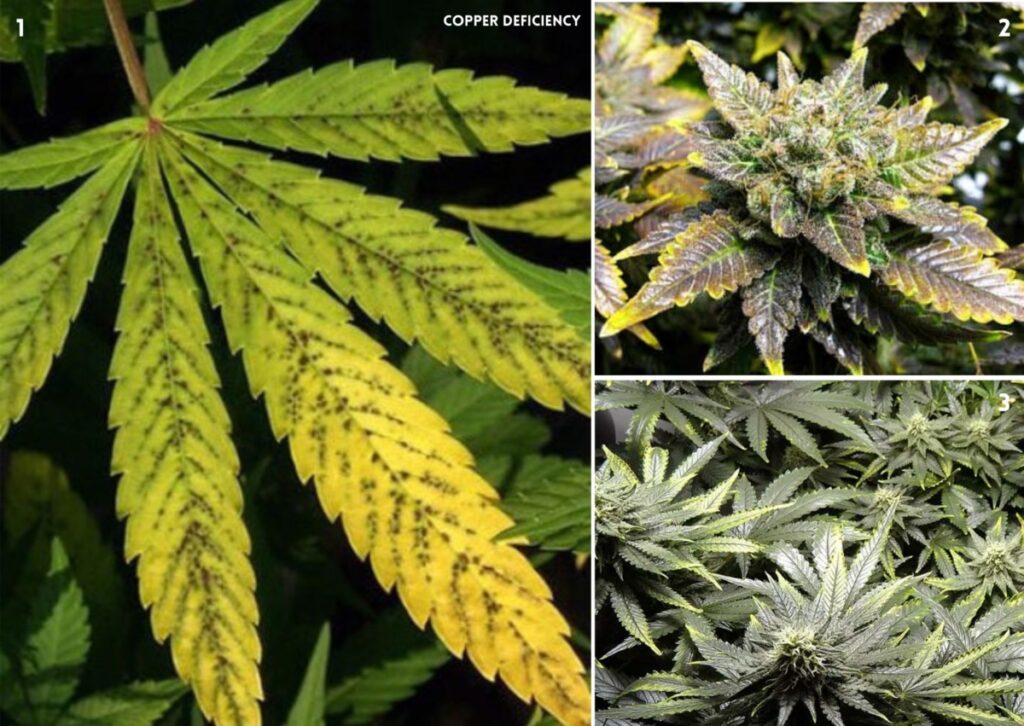

The best way to prevent or fix the copper deficiency in cannabis is:
1. Apply a Foliar Spray of Copper Chelate or Copper Sulfate Solution:
This is a quick and effective way to provide copper directly to the plant leaves. You can use a commercial product or make your own by dissolving 1-2 teaspoons of copper chelate or copper sulfate in a gallon of water.
Spray the solution on the affected leaves once a week until the symptoms disappear. Avoid spraying during the flowering phase or under direct sunlight, as this can damage the buds or cause leaf burn.
2. Adding a Copper Supplement to the Soil or Growing Medium:
This is a long-term solution that can improve the overall health and yield of the plant. You can use a copper-based fertilizer or a compost that contains organic amendments rich in copper, such as manure, seaweed, or alfalfa.
Follow the instructions on the label or apply a small amount every two weeks during the vegetative stage. Do not overdo it, as too much copper can be toxic to the plant and the soil microorganisms.
3. Adjust The PH of The Soil or Growing Medium to The Optimal Range for Cannabis:
This is important because pH affects the availability and absorption of nutrients by the plant roots. The ideal pH range for cannabis plants is 6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics.
You can use a pH meter or test strips to measure the pH and use pH up or down products to adjust it accordingly. You can also use organic amendments such as lime, dolomite, vinegar, or lemon juice to alter the pH naturally.
4. Avoid Overwatering, Overfertilizing, or Exposing the Plant to Extreme Environmental Conditions:
These factors can stress the plant and interfere with its nutrient uptake and metabolism. You should water the plant only when the top inch of the soil feels dry to the touch and drain any excess water from the saucer or tray.
You should also follow a balanced feeding schedule and avoid using too much nitrogen or phosphorus, as they can compete with copper for absorption. You should also protect the plant from extreme temperatures, humidity, wind, pests, and diseases by providing adequate ventilation, lighting, and pest control.
Cannabis Copper Toxicity vs Copper Deficiency: How to Recognize the Differences?

Copper toxicity is a condition where the plant has too much copper accumulated in its tissues. This can happen due to over-fertilization, contaminated water or soil, or accidental ingestion of copper-based products, and can interfere with the uptake and metabolism of other nutrients, such as iron, zinc, and manganese.
An excess of copper can also damage the plant cells and tissues, leading to reduced growth, yield, and quality.
What Are The Symptoms of an Excess of Copper in Marijuana Plants?
Copper toxicity can damage the plant’s cells and interfere with its physiological processes. It can cause symptoms such as:
- Young leaves shoots wilt, contort and may die
- Leaf tips and margins turn dark green to copper-gray and die
- Grow is slow and yield decreased
Copper toxicity is more common in older plants, as they have a lower tolerance for copper than younger plants. It can also occur in acidic soils or water, where copper is more soluble and mobile.
What Causes the Toxicity of Copper in Plants?
Copper toxicity can be caused by several factors that increase the availability or uptake of copper by the plant. Some of the common causes are:
- Over-Fertilization: If you are using a fertilizer that contains copper, you may be applying too much or too often. Check the label of your fertilizer and follow the recommended dosage and frequency. You can also switch to a fertilizer that has less or no copper in it.
- Contaminated Water: If you are using tap water or well water to water your plants, it may have high levels of copper or other metals. You can test your water quality with a kit or a meter and see if it meets the optimal EC and pH levels for cannabis. You can also filter your water or use distilled water to reduce the copper content.
- Contaminated Soil: If you are growing in soil, it may have high levels of copper or other metals from previous crops, pollution, or organic soil conditioner. You can test your soil quality with a kit or a meter and see if it meets the optimal pH and EC levels for cannabis. You can also flush your soil with clean water to leach out the excess copper or replace your soil with a fresh batch.
- Contaminated Equipment: If you are using metal pots, pipes, hoses, or tools to grow your plants, they may leach copper or other metals into the water or soil. You can avoid using metal equipment or coat them with a protective layer to prevent corrosion and leaching.
How to Fix an Excess of Copper in Plants?

To fix an excess of copper in plants, you need to do the following steps:
1. Identify and Remove the Source of Excess Copper:
This could be from contaminated water, soil, fertilizer, or equipment. Use a pH meter and a TDS meter to check the water quality and adjust it if needed.
Use organic soil or coco coir as your growing medium and avoid synthetic fertilizers that may contain heavy metals.
Clean your pots, trays, tools, and pipes with distilled water and vinegar to remove any copper residue.
2. Flush Your Plants with Clean Water:
This will help to wash away any excess copper and other salts that may have accumulated in the soil or the roots. Flushing will also prevent a nutrient lockout, which is when the plants cannot absorb the nutrients they need due to an imbalance in the soil pH or EC.
To flush your plants, water them with three times the volume of water as your pot size until the runoff is clear and has a low TDS reading.
3. Apply a Foliar Spray with Chelated Iron and Zinc:
These are two micronutrients that are often affected by excess copper and can cause chlorosis (yellowing) and necrosis (browning) of the leaves. Chelated iron and zinc are more easily absorbed by the plants through their leaves than through their roots.
To make a foliar spray, mix 1 teaspoon of chelated iron and 1 teaspoon of chelated zinc per gallon of water and spray your plants once a week until they recover.
4. Prune Your Plants to Remove Any Damaged or Dead Leaves and Branches:
This will help to improve the airflow and light penetration in your canopy and reduce the risk of mold and pests.
Pruning will also stimulate new growth and help your plants focus their energy on producing buds instead of repairing damaged tissues. Use sharp scissors or pruning shears to cut off any yellow, brown, or wilted leaves and any weak or spindly branches. Be careful not to over-prune your plants as this can stress them out and reduce their yield.
How to Prevent Copper Toxicity in Cannabis?
The best way to prevent copper toxicity is to avoid the sources of excess copper and maintain a balanced pH in the soil or water. Here are some tips:
1. Use clean water sources that have low levels of copper. You can test your water for copper using a water test kit or a digital pH meter.
2. Use fertilizers or supplements that have appropriate amounts of copper. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and do not overfeed your plants.
3. Avoid using copper-based fungicides or pesticides. If you need to use them, follow the label directions and apply them sparingly.
4. Avoid using pots or containers that are made of copper or have copper residues. Use plastic, ceramic, or fabric pots instead.
5. Maintain a pH of 6.0 to 7.0 in the soil or 5.5 to 6.5 in hydroponics. This will ensure optimal nutrient availability and prevent copper from becoming too soluble.
Bottom Line
Nutrient deficiencies and excess are serious issues that can affect the health and performance of your plants but can be easily avoided or corrected with proper care and attention.
By maintaining a balanced pH level and providing adequate nutrients, you can ensure your marijuana plants grow healthy and produce high-quality buds. Happy growing!
FAQs
Cannabis needs a balanced and adequate supply of nutrients to grow well and produce high-quality buds. However, sometimes they may suffer from deficiencies or excesses, which can affect their health and yield.
Here are some of the most common, and how to distinguish them:
- Phosphorus deficiency: This is a mobile nutrient that is important for root development, flowering, and resin production. A lack of it causes the lower leaves to turn dark green or purple, and develop brown spots or edges. The plant may also have slow growth and reduced bud formation.
- Potassium deficiency: This is a mobile nutrient that is involved in water regulation, enzyme activation, and sugar transport. A lack of potassium causes the lower leaves to turn yellow with brown tips or edges, and curl up or down. The plant may also have weak stems, poor resistance to pests and diseases, and low-quality buds.
- Magnesium deficiency: This is a mobile nutrient that is part of the chlorophyll molecule and helps with energy production. A lack of magnesium causes the lower leaves to turn yellow with green veins, and develop brown spots or necrosis. The plant may also have reduced photosynthesis, chlorosis, and leaf drop.
- Boron deficiency: This is a mobile nutrient that is essential for cell wall formation, sugar transport, and pollen tube growth. A lack of boron causes the growing tips to die back, and the stems and roots to become brittle and cracked. The plant may also have distorted leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Iron deficiency: This is an immobile nutrient that is required for chlorophyll production and electron transport. A lack of iron causes the young leaves to turn yellow with green veins, a condition known as interveinal chlorosis. The plant may also have poor growth, reduced yield, and susceptibility to diseases.
- See more…
Cannabis deficiency occurs when the plant does not receive enough of a certain nutrient for its optimal growth and development. This can be caused by low-quality or insufficient fertilizers, poor soil quality, incorrect pH, overwatering, or root problems.
A deficiency of nutrients can result in various symptoms depending on the type and severity of the deficiency, such as yellowing, browning, curling, wilting, or dropping of leaves, reduced growth, poor bud formation, or low potency.
Nutrient-burn occurs when the plant receives too much of a certain nutrient for its optimal growth and development. This can be caused by over-fertilizing, using high-strength or incompatible fertilizers, incorrect levels of pH, underwatering, or root problems. Nutrient-burns can result in various symptoms depending on the type and severity of the excess, such as yellowing, browning, curling, wilting, or dropping of leaves, reduced growth, poor bud formation, or low potency.
The main difference between nutrient-deficiency and burn is that symptoms of deficiency appear first on the older or lower leaves (except for immovable nutrients), whereas nutrient-burn causes symptoms to appear first on the newer or upper leaves (except for mobile nutrients).
Another difference is that nutrient-deficiency causes leaves to lose their color gradually from the edges or between the veins towards the center (except for iron), while nutrient-burn causes leaves to lose their color abruptly from the tips or margins toward the center.
Copper is an immobile nutrient that is essential for chlorophyll production, enzyme function, respiration, lignin synthesis, and stress tolerance. A deficiency of copper can occur due to high levels of pH (>7), excessive nitrogen or phosphorus levels, or root damage.
A deficiency of copper causes the new growth to turn pale green or yellow with twisted or curled tips. The plant may also have reduced branching, bud formation, resin production, and aroma. To fix a copper deficiency during flowering you should:
- Flush the growing medium with pH-balanced water to remove any excess nutrients or salts that may be interfering with copper uptake.
- Apply a balanced fertilizer with micronutrients that contain copper at half-strength according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Adjust the pH of the water and soil to 6-7 for soil or 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics to ensure optimal copper availability.
- Avoid overwatering or underwatering the plant as this can affect the root health and nutrient absorption.
- Monitor the plant for signs of improvement or worsening of the deficiency and adjust the fertilizer dosage accordingly.
ILGM Plant Protector

- Protect your cannabis from diseases and harmful pests.
- Contains three 20 ml bottles.
- Enough supplies to protect 20 plants.
- It can be used in soil, hydroponic, and all other growing mediums.
ILGM Fertilizer

- From seedling to harvest, give your plants everything they need.
- Enough for feeding at least 5 plants.
- Discounted Package Deal
- Works well in soil, hydroponics, and other growing mediums.
- The best way to treat your plants



















